Abstract
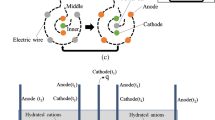
A gravitational settling rate of highly concentrated slurry in which thickening proceeds due to consolidation mechanism is greatly enhanced by applying a D. C. electric field. Consolidation starts from the bottom of sediment and propagates upwards, but an abnormally strong consolidation also takes place in an upper portion of the sediment. The basic differential equation for such electroforced sedimentation is derived by use of Kobayashi’s equation which describes a flow in a porous material under an electric field. The relation among local hydraulic excess pressure, solid compressive pressure and gravitational force on solid particles is also obtained. Based on the theory, the larger the porosity of sediment, the greater the flow rate of electroosmosis; the electroosmotic flow at the settling surface is accordingly the largest among those at any layers in the sediment. An abnormal compaction of the layer near the settling surface is consequently due to the difference between flow rates at the surface and any layer under the surface. The theoretical change of porosity distribution and sediment height with time of Mitsukuri-Gairome clay compares favorably with experimental observations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iwata, M., Igami, H., Murase, T. and Yoshida, H., “Analysis of Electroosmotic Dewatering”,J. Chem. Eng. Japan,24, 45(1991).
Kobayashi, K., Hakoda, M., Hosoda, Y., Iwata, M. and Yukawa, H., “Electroosmotic Flow through Particle Beds and Electroosmotic Pressure Distribution”,J. Chem. Eng. Japan,12, 492 (1979).
Kozicki, W., Chow, C. H. and Tiu, C., “Non-Newtonian Flow in Ducts of Arbitrary Cross-sectional Shape”,Chem. Eng. Sci.,21, 665 (1966).
Kozicki, W., Hsu, C. J. and Tiu, C., “Non-Newtonian Flow through Packed Beds and Porous Media”,Chem. Eng. Sci.,22, 487 (1967).
Shirato, M., Murase, T., Kato, H. and Fukaya, S., “Studies on Expression of Slurries under Constant Pressure”,Kagaku Kogaku,31, 1125(1967).
Shirato, M., Kato, H., Kobayashi, K. and Sakazaki, H., “Analysis of Settling of Thick Slurries Due to Consolidation”,J. Chem. Eng. Japan,3, 98 (1970).
Shirato, M., Aragaki, T., Manabe, A. and Takeuchi, N., “Electroforced Sedimentation of Thick Clay Suspensions in Consolidation Region”,AIChE J.,25, 855 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, W.D., Iwata, M. Analysis of an electroforced sedimentation of highly concentrated clay slurry in consolidation region. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 12, 576–581 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705863
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705863