Abstract
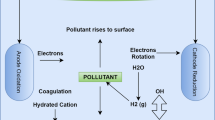
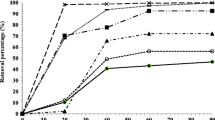
Electrocoagulation is applied to sewage sludge as a pretreatment process of an electrodewatering system to reduce the water content of sludge generated in wastewater treatment. The electrodewatering system, by incorporating an electric field as an additional driving force to the conventional pressure dewatering, has been evaluated as a function of an electrode material, applied voltage and filtration time. Experiments were carried out using sewage sludge with a pressure up to 392.4 kPa and applied electrical field ranging up to 120 V/cm. Mass median diameter of the sewage sludge by the effect of electrocoagulation increases from 34.7 µm to the 41.3 µm. The final water content of sewage sludge in the combination of both electrocoagulation and electrodewatering system can be reduced to 55 wt%, as compared to 78 wt% achieved with pressure dewatering alone. The combination of electrocoagulation and electrodewatering system shows a potential to be an effective method for reducing the water content in sludge.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA,Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 17 th Edition (1989).
Barton, W. A., Miller, S. A. and Veal, C. J., “The electrodewatering of sewage sludge,”Drying Technology,17(3), 497 (1999).
Biwyk, A.,Electrocoagulation of biologically treated sewage, Proc. 35th Purdue Ind. Waste Conf., Lafayette, IN. (1980).
Chen, L. L. and Sheng, H. L., “Treatment of chemical mechanical polishing wastewater by electrocoagulation: system performances and sludge settling characteristics,”Chemosphere,54, 235 (2004).
Chen, X., Chen, G. and Yue, P. L., “Separation of pollutants from restaurant wastewater by electrocoagulation,”Sep. & Purifi. Tech.,19, 65 (2000).
Gazber, S., Abadie, J. M. and Colin, F., “Combined action of electroosmotic drainage and mechanical compression on sludge dewatering,”Wat. Sci. Tech.,30(8), 169 (1994).
Ibanez, J. G., Takimoto, M. M. and Ruben, C. V., “Laboratory experiments on the electrochemical remediation of the environment: electrocoagulation of oily wastewater,”Journal of Chemical Education,72(11), 1050(1995).
Kobya, M., Can, O. T. and Bayramoglu, M., “Treatment of textile wastewaters by electrocoagulation using iron and aluminum electrodes,”Journal Hazardous Materials B,100, 163 (2003).
Kondoh, S. and Hiraoka, M., “Commercialization of pressurized electroosmotic dehydrator,”Wat. Sci. Tech.,22, 259 (1990).
Koren, J. P. F. and Syversen, U., “State-of-the-art electroflocculation,”Filtration and Separation, February,32(2), 146 (1995).
Lee, J. K., Shin, H. S., Park, C. J., Lee, C. G., Lee, J. E. and Kim, Y. W., “Performance evaluation of electrodewatering system for sewage sludge,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,19, 41 (2002).
Lockhart, N. C., “Electroosmotic dewatering of clays. II. Influence of salt, acid, and flocculants,”Colloids and Surfaces,6, 239 (1983).
Pouet, M. F. and Grasmick, A., “Urban wastewater treatment by electrocoagulation and flotation,”Wat. Sci. Tech.,31(3-4), 275 (1995).
Rubach, S. and Saur, I. F., “Onshore testing of produced water by electroflocculation,”Filtration and Separation,34(8), 877 (1997).
Shin, H. S., Yeo, C. S., Byun, S. H. and Lee, J. K.,Development of the electroosmotic belt press for sewage sludge, The 4th Korean Conference on Aerosol and Particle Technology, Yong-Pyong, Korea, 63 (2003).
Shin, S. H., Kim, Y H., Jung, S. K., Suh, K. H., Kang, S. G., Jeong, S. K. and Kim, H. G., “Combined performance of electrocoagulation and magnetic separation processes for treatment of dye wastewater,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,21, 806 (2004).
Sung, D. J. and Park, B. K., “Statical evaluation of hyperbaric filtration for fine coal dewatering,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,13, 304 (1996).
Tsouris, C., DePaoli, D. W., Shor, J. T., Hu, M. Z. C. and Ying, T. Y., “Electrocoagulation for magnetic seeding of colloidal particles,”Colloids and Surfaces,177, 223 (2001).
Vijh, A. K. and Novak, J. P., “A new theoretical approach to electroosmotic dewatering (EOD) based on non-equilibrium thermodynamics,”Drying Technology,15(2), 699 (1997).
Vik, E. A., Carlson, D. A., Eikum, A. S. and Gjessing, E. T., “Electrocoagulation of portable water,”Water Res.,18(11), 1355 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, HS., Lee, JK. Performance evaluation of electrocoagulation and electrodewatering system for reduction of water content in sewage sludge. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 23, 188–193 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705714
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705714