Abstract
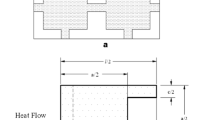
A theoretical model has been developed for real two-phase system assuming linear flow of heat flux lines having ellipsoidal particles arranged in a three-dimensional cubic array. The arrangement has been divided into unit cells, each of which contains an ellipsoid. The resistor model has been applied to determine the effective thermal conductivity (ETC) of the unit cell. To take account of random packing of the phases, non-uniform shape of the particles and non-linear flow of heat flux lines in real systems, incorporating an empirical correction factor in place of physical porosity modifies an expression for ETC. An effort is made to correlate it in terms of the ratio of thermal conductivities of the constituents and the physical porosity. Theoretical expression so obtained has been tested on a large number of samples cited in the literature and found that the values predicted are quite close to the experimental results. Comparison of our model with different models cited in the literature has also been made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antohe B V, Lage J L, Price D C and Weber R M 1996Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 17 594
Babanov A A 1957Sov. Phys. Tech. Phys. 2 476
Baxley A L and Couper J R 1966 Thermal conductivity of two-phase systems Part IV (Thermal conductivity of suspensions): Research report series No. 8, University of Arkansas
Bhattacharya A, Calmidi V V and Mahajan R L 2002Int. J. Heat & Mass Transfer 45 1017
Boomsma K and Poulikakos D 2001Int. J. Heat & Mass Transfer 44 827
Brailsford A D and Major K G 1964Br. J. Appl. Phys. 15 313
Calmidi V V and Mahajan R L 1999ASME J. Heat Transfer 121 466
Cheng S C and Vachon R I 1969Int. J. Heat & Mass Transfer 12 249
Hadley G R 1986Int. J. Heat & Mass Transfer 20 909
Hsu C T, Cheng P and Wong K W 1994Int. J. Heat & Mass Transfer 37 2751
Hunt M L and Tien C L 1988Int. J. Heat & Mass Transfer 31 301
Kampf H and Karsten G 1970Nucl. Appl. Technol. 9 208
Kaviany M 1995Principles of heat transfer in porous media (New York: Springer) p. 119
Knudsen J G and Wand R H 1958Ind. Eng. Chem. 50 1667 27
Koh J C Y and Fortini G 1973Int. J. Heat & Mass Transfer 16 2013
Lee H J and Taylor R E 1976J. Appl. Phys. 47 148
Misra K, Shrotriya A K, Singh R and Chaudhary DR 1994J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 27 732
Nahas N C and Couper J R 1966 Thermal conductivity of two-phase systems Part II, Research Report series, University of Arkansas
Oshima N and Watari N 1989Jap. Soc. Mech. Eng. Int. J. 32 225
Pande R N, Kumar V and Chaudhary DR 1984Pramana-J. Phys. 22 63
Peddicord K L 1976Trans. Am. Nucl. Soc. 24 1976
Poulikakos D P and Renken K J 1987Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 109 880
Ratcliffe E H 1962Trans. Inst. Rubber Ind. 38 181
Singh K J, Singh Ramvir and Chaudhary D R 1998J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 31 1681
Singh Ramvir, Singh K J and Chaudhary D R 1995J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 28 1573
Sugawara A and Hamada A 197010th Thermal conductivity conference (Massachusetts, USA)III p. 7
Tareev B 1975Physics of dielectric materials (Moscow: Mir) p. 128
Tien C L and Vafai K 1979Prog. Astronaut. 65 135
Verma L S, Shrotriya A K, Singh R and Chaudhary DR 1991J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 24 1729
Zehner P and Schlünder E U 1970Chem. Ing. Tech. 42 933
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jagjiwanram, Singh, R. Effective thermal conductivity of real two-phase systems using resistor model with ellipsoidal inclusions. Bull Mater Sci 27, 373–381 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704775
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704775