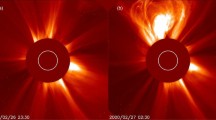
Abstract
This paper describes the space weather effects of a major CME which was accompanied by extremely violent events on the Sun. The signatures of the event in the interplanetary medium (IPM) sensed by Ooty Radio Telescope, the solar observations by LASCO coronagraph onboard SOHO, GOES X-ray measurements, satellite measurements of the interplanetary parameters, GPS based ionospheric measurements, the geomagnetic storm parameter Dst and ground based ionosonde data are used in the study to understand the space weather effects in the different regions of the solar-terrestrial environment. The effects of this event are compared and possible explanations attempted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burlaga, L. F., Skoug, R. M., Smith, C. W., Webb, D. F., Zurbuchen, T. H., Reinard, A. 2001, Fast Ejecta during ascending phase of solar cycle 23: ACE observations, 1998-99;J. Geophys. Res.,106 (A10), 20,957.
Gosling, J. T. 1997, Coronal Mass Ejections: An Overview, Coronal Mass Ejections, Geophysical Monograph 99; (ed.) Nancy Crookeret al.,9.
Jadav, R. M., Iyer, K. N., Joshi, H. P., Hari Om Vats 2005, Coronal mass ejection of 4 April 2000 and associated space weather effects;Planet. Space Sci.,53, 671.
McAllister, A. H., Dryer, M., McIntosh, P., Singer, H., Weiss, L. 1996, A large polar crown coronal mass ejection and a “problem” geomagnetic storm: April 14–23, 1994,J. Geophys. Res.,101, 13,497.
Richardson, I. G., Berdichevsky, D., Desch, M. D., Farrugia, C. J. 2000, Solar-cycle variation of low density solar wind during more than three solar cycles;Geophys. Res. Lett.,27, 23,3761.
St. Cyr. O. C.et al. 2000, Properties of coronal mass ejections: SOHO LASCO observations from January 1996 to June 1998,J. Geophys. Res.,105, 18,169.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iyer, K.N., Jadav, R.M., Jadeja, A.K. et al. Space weather effects of coronal mass ejection. J Astrophys Astron 27, 219–226 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702524
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702524