Abstract
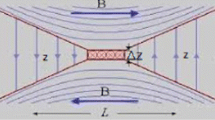
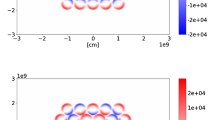
Coronal heating by nanoflares is presented by using observational, analytical, numerical simulation and statistical results. Numerical simulations show the formation of numerous current sheets if the magnetic field is sheared and bipoles have unequal pole strengths. This fact supports the generation of nanoflares and heating by them. The occurrence frequency of transients such as flares, nano/microflares, on the Sun exhibits a power-law distribution with exponent α varying between 1.4 and 3.3. For nanoflares heating α must be greater than 2. It is likely that the nanoflare heating can be reproduced by dissipating Alfven waves. Only observations from future space missions such as Solar-B, to be launched in 2006, can shed further light on whether Alfven waves or nanoflares, heat the solar corona.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antiochos, S. K., Karpen, J. T., De Vore, C. R. 2002,ApJ,575, 570.
Aschwanden, M. 2004, Physics of the Solar Corona, An Introduction, Springer, Praxis Publication.
Aschwanden, M. J., Nightingale, R. W., Tarbell, T. D., Wolfson, C. J. 2000,ApJ,535, 1027.
Aschwanden, M. J., Charbonneau, P. 2002a,ApJ,566, L59.
Aschwanden, M. J., Parnell, C. E. 2002b,ApJ,572, 1048.
Cargill, P. J., Klimchuk, J. A. 2004,ApJ,605, 911.
Dmitruk, P., Gomez, D. O. 1997,ApJ,484, L83.
Dmitruk, P., Gomez, D. O. 1999,ApJ,527, L63.
Dwivedi, B. N. 2002,BASI,30, 549.
Dwivedi, B. N. 2003, In:Lectures on Solar Physics (ed.) H. M. Antiaet al. Springer, Berlin, p. 281.
Galtier, S. 1999,ApJ,521, 483.
Georgoulis, M. K., Vlahos, L. 1996,ApJ,469, L135.
Georogoulis, M. K., Vilmer, N., Crossby, N. B. 2001,A&A,367, 326.
Harra, L. K., Gallagher, P. T., Phillips, K. J. H. 2000,A&A,362, 371.
Karpen, J. T., Antiochos, S. K., De Vore, C. R. 1996,ApJ,460, L73.
Krucker, S., Benz, A. O. 1998,ApJ,501, L213.
McIntosh, S. W., Charbonneau, P. 2001,ApJ,563, L165.
Mercier, C., Trottet, G. 1997,ApJ,474, L65.
Moriyasu, S., Kudoh, T., Yokoyama, T., Shibata, K. 2004,ApJ,601, L107.
Narain, U., Ulmscheider, P. 1996,Space Sci. Rev.,75, 453.
Pandey, K., Narain, U. 2001,BASI,29, 231.
Parker, E. N. 1988,ApJ,330, 474.
Parker, E. N. 1991, In: Mechanisms of Chromospheric & Coronal Heating (eds) P. Ulmschneider, E. R. Priest, R. Rosner, Springer, Berlin, p. 615.
Shimojo, M., Shibata, K. 1999,ApJ,516, 934.
Spitzer, L. 1962, Physics of Fully Ionized Gases, John Wiley, New York.
Tandberg-Hanssen, E., Emslie, A. G. 1988, The Physics of Solar Flares, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge.
Walsh, R. W., Ireland, J. 2003,A&A Rev.,12, 1.
Winebarger, A. R., Emslie, A. G., Mariska, J. T., Warren, H. P. 2002,ApJ,565, 1298.
Winebarger, A. R., Warren, H. P., Mariska, J. T. 2003,ApJ,587, 439.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narain, U., Pandey, K. Nanoflares and heating of the solar corona. J Astrophys Astron 27, 93–100 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702511
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702511