Abstract
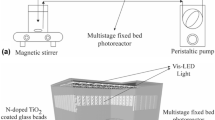
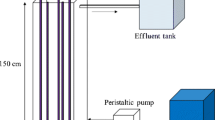
The photocatalytic oxidation of Rhodamine B (RhB) was studied by using a newly developed immobilized photocatalyst (TiO2 immobilized by support consisting of a perlite and silicone sealant) and a fluidized-bed reactor. Three 8W germicidal lamps were used as the light source and the reactor volume was 2.8l. When this photocatalyst was employed in a batch process, a total decolorization of the RhB in reaction times lower than 60 min was observed. The optimum dosage of photocatalyst was 33.8 g/l. The initial RhB decolorization rate of the immobilized TiO2 was higher than that of the suspended TiO2 and this did not agree with pseudo first-order kinetics because of the adsorption onto the surface of the immobilized TiO2. This result indicated that the adsorption capacity of the immobilized photocatalyst is very important in photocatalysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, K.B., Na, S.N. and Park, Y. S., “Ozone Lamp/Photocatalytic Decolorization of Rhodamine B,”Korean Soc., of Environ. Eng.,26(10), 1063 (2004).
Bhatkhande, D. S., Pangarkar, V.G. and Beenackers, A. A. C. M., “Photocatalytic Degradation of Nitro Benzene Using Titanium Dioxide and Concentrated Solar Radiation: Chemical Effects and Scaleup,”Wat. Res.,37, 1223 (2003).
Chai, Y. S., Lee, J. C. and Kim, B.W., “Photocatalytic Disinfection ofE. coli in a Suspended TiO2/UV Reactor,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,17(6), 633 (2000).
Chun, H.D., Kim, J. S., Yoon, S. M. and Kim, C.G., “Physical Properties and Photocatalytic Performance of TiO2 Coated Stainless Steel Plate,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,18(6), 908 (2001).
Fernandez, A., Lassaletta, G., Jimenez, V. M., Justo, A., Gonzalez-Elipe, A. R., Herrmann, J. M., Tahiri, H. and Ait-Ichou, Y., “Preparation and Characterization of TiO2 Photocatalysts Supported on Various Rigid Supports (Glass, Quartz and Stainless Steel). Comparative Studies of Photocatalytic Activity in Water Purification,”Appl. Catal. B: Environ.,7, 49 (1995).
Lim, T.H. and Kim, S.D., “Photocatalytic Degradation of Trichloroethylene over TiO2/SiO2 in an Annulus Fluidized Bed Reactor,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,19(6), 1072 (2002).
Mattews, R.W., “Purification of Water with Near-UV Illuminated Suspensions of Titanium Dioxide,”Wat. Res.,24, 653 (1990).
Mazzarino, I., Oiccinini, P. and Spinelli, L., “Degradation of Organic Pollutants in Water by Photochemical Reactors,”Catalyst Today,48, 315 (1999).
Ministry of Health Singapore,http://www.gov.sg/moh/mohiss/poison/ rhodam.html (2002).
Na, Y. S.,The Treatment of Nonbiodegradable Wastewater by TiO 2 Photocatalytic Reactor, Ph. D. Thesis, Busan National University, (Korea), 54–135 (2002).
Nam, W. S. and Han, G.Y., “A Photocatalytic Performance of TiO2 Photocatalyst Prepared by the Hydrothermal Method,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,20(1), 180 (2003).
Nam, W. S., Kim, J. M. and Han, G.Y., “Photocatalytic Oxidation of Methyl Orange in a Three-phase Fluidized Bed Reactor,”Chemosphere,47, 1019 (2002).
Nazawa, M., Tanigawa, K., Hosomi, M., Chikusa, T. and Kawada, E., “Removal and Decomposition of Malodorants by Using Titanium Dioxie Photocatalyst Supported on Fiber Activated Carbon,”Wat. Sci. Tech.,44, 127 (2001).
Park, Y. S.,Comparison of Color Removal Between Powder and Im- mobilized TiO2. In: Proceedings of the Korean Environmental Sciences Society Conference, The Korean Environmental Sciences Society, May. 16–17, Chungbook Province, pp. 267–270. ISSN 1598-6268 (2003).
Pazzo, R.A., Baltanas, M.A. and Cassano, A. E., “Towards a Precise Assessment of the Performance of Supported Photocatalysts for Water Detoxification Processes,”Catalysis Today,54, 143 (1999).
Pazzo, R.A., Giombi, J. L., Baltanas, M.A. and Cassano, A. E., “The Performance on a Fluidized Bed Reactor of Photocatalysts Immobilized onto Inert Supports,”Catalyst Today,62, 175 (2000).
Rachel, A., Lavedrine, B., Subrahmanyam, M. and Boule, P., “Use of Porous Lavas as Supports of Photocatalysts,”Catalysis Communications,3, 165 (2002).
Schmelling, D. C. and Gray, K.A., “Photocatalytic Transformation and Mineralization of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene in TiO2,”Wat. Res.,29, 2651 (1995).
Shifu, C., “Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pesticide Containing Phosphorus by TiO2 Supported ob Fiber Glass,”Environ. Sci.,17, 33 (1996).
Shourong, Z., Qingguo, H., Jun, Z. and Bingkun, W., “A Study on Dye Photoremoval in TiO2 Suspension Solution,”J. of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry,108, 235 (1997).
Spadary, J. T., Isebelle, L. and Renganathan, V., “Hydroxyl Radical Mediated Degradation of Azo Dyes,”Environ. Sci. Technol.,28, 1389 (1994).
Sunada, F. and Heller, A., “Effects of Water, Salt Water, and Silicone Overcoating of the TiO2 Photocatalyst on the Rates and Products of Photocatalytic Oxidation of Liquid 3-Octanol and 3-Octanone,”Environ. Sci. Technol.,32, 282 (1998).
Takeda, N., Iwata, N., Torimoto, T. and Yoneyama, H., “Influence of Carbon Black as an Adsorbant used in Photocatalyst Films on Photodegradation Behaviors of Propyzamide,”J. Catal.,177, 240 (1998).
Tang, W. Z. and An, H., “UV/TiO2 Photocatalytic Oxidation of Commercial Dyes in Aqueous Solutions,”Chemosphere,31, 4157 (1995).
Turchi, C. S. and Ollis, D. F., “Mixed Reactant Photocatalysis: Intermediates and Mutual Rate Inhibition,”J. Catal.,119, 483 (1989).
You, Y. S., Chung, K.H., Kim, J.H. and Seo, G., “Photocatalytic Oxidation of Toluene over TiO2 Catalysts Supported on Glass Fiber,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,18(6), 924 (2001).
Zhu, C., Wang, L., Kong, L., Yang, Z., Wang., L., Zheng, S., Chen, F., MaiZhi, F. and Zong, H., “Photocatalytic Degradation of Azo Dyes by Supported TiO2+UV in Aqueous Solution,”Chemosphere,41, 303 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Na, Y., Song, S. & Park, Y. Photocatalytic decolorization of rhodamine B by immobilized TiO2/UV in a fluidized-bed reactor. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 22, 196–200 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02701484
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02701484