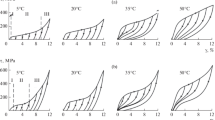
Abstract
The structure of titanium specimens with different grain sizes and initial defect density that were subjected to large high-rate strains is studied, and the critical parameters of the onset of an unstable plastic flow in the specimens are determined. It is established that the formation of a titanium structure and the critical parameters governed by this structure are determined mainly by twinning. Twinning in shock-loaded titanium is the mechanism of plastic deformation that ensures the minimum change in the internal energy. Twinning in titanium under high-rate strain develops at the earlier stages over all admissible twinning systems and results in fragmentation of the structure. The twins are not the structural elements that contribute to the evolution of a uniform plastic strain. Fragmentation of the structure in the formation of twins decreases the critical parameters of the onset of an unstable plastic flow. It is found that as the strain increases, the twins fill the material up to a certain limit level, after which energy relaxation occurs owing to the formation of adiabatic-shear bands and/or cracking. The titanium structure formed in the deformation is highly stable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. P. Bondar’ and V. F. Nesterenko, “Strain correlation at different structural levels for dynamically loaded hollow copper cylinders,”J. Phys.,4, October, 3.163–3.170 (1991).
V. F. Nesterenko and M. P. Bondar’, “Investigation of deformation localization by the ‘thick-walled cylinder’ method,”Dymat J.,1, No. 3, 245–251 (1994).
V. F. Nesterenko and M. P. Bondar’, “Strain localization in the collapse of a thick-walled cylinder,”Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva,30, No. 4, 99–111 (1994).
M. P. Bondar’, O. L. Pervukhina, V. F. Nesterenko, and Ya. L. Luk’yanov, “Development of the titanium structure in the explosive collapse of a thick-walled cylinder,”Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva,34, No. 5, 122–129 (1998).
A. A. Deribas, V. F. Nesterenko, G. A. Sapozhnikov, et al., “Attenuation of shock waves in metals loaded by contact explosion,”Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva,15, No. 2, 126–132 (1979).
N. N. Rybin,Large Plastic Strains and Fracture of Metals [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1986).
T. S. Liu and M. A. Steinberg, “Twinning in single crystals of Ti,”J. Metals, No. 4, 1043–1044 (1952).
V. F. Nesterenko, M. A. Meyers, J. C. LaSalvia, et al., “Shear localization and recrystallization in high-strain, high-strain-rate of tantalum,”Mater. Sci. Eng.,A229, 23–41 (1997).
M. P. Bondar’ and T. S. Teslenko, “Effect of the degree of defectness of an original material on the deformation structure formed in the explosive collapse of hollow thick-walled cylinders,”Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva,33, No. 6, 108–121 (1997).
M. P. Bondar’, “Formation of the structure under high-rate deformation,”Fiz. Mezomekh.,1, No. 1, 37–54 (1998).
M. V. Mal’tsev, T. A. Barsukova, and F. A. Borin,Metallography of Nonferrous Metals and Alloys [in Russian], Moscow (1960).
E. Ferreyra, L. E. Murr, and F. Horz, “A preliminary study of the effect of target microstructure on thick copper plates,” in:Shock-Wave and High-Strain-Rate Phenomena (EXPLOMET’95), Elsevier, Amsterdam (1995), pp. 303–312.
J. E. Burke and D. Turnbull, “Recrystallization and grain growth,” in:Progress in Metal Physics, Vol. 3, Pergamon Press, London (1952), p. 220.
G. N. Epshtein,Structure of Explosion-Deformed Metals, [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1968).
M. P. Bondar’ and V. F. Nesterenko, “Contact strain and criteria for forming a compound under pulse loadings,”Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva,27, No. 3, 103–117 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated fromFizika Goreniya i Vzryva, Vol. 36, No. 2, pp. 110–121, March–April, 2000.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bondar’, M.P., Pervukhina, O.L. Dependence of the titanium structure formed under high-rate loading on its initial state. Combust Explos Shock Waves 36, 261–271 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02699372
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02699372