Abstract
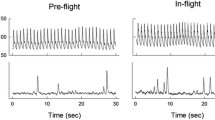
We investigated the effects of exposure to microgravity on the baseline autonomic balance in cardiovascular regulation using spectral analysis of cardiovascular variables measured during supine rest. Heart rate, arterial pressure, radial flow, thoracic fluid impedance and central venous pressure were recorded from nine volunteers before and after simulated microgravity, produced by 20 hours of 6° head down bedrest plus furosemide. Spectral powers increased after simulated microgravity in the low frequency region (centered at about 0.03 Hz) in arterial pressure, heart rate and radial flow, and decreased in the respiratory frequency region (centered at about 0.25 Hz) in heart rate. Reduced heart rate power in the respiratory frequency region indicates reduced parasympathetic influence on the heart. A concurrent increase in the low frequency power in arterial pressure, heart rate, and radial flow indicates increased sympathetic influence. These results suggest that the baseline autonomic balance in cardiovascular regulation is shifted towards increased sympathetic and decreased parasympathetic influence after exposure to short-term simulated microgravity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akselrod, S., Gordon, D., Madwed, J.B., Snidman, N.C., Shannon, D.C., & Cohen, R.J. (1985). Hemodynamic regulation: Investigation by spectral analysis.American Journal of Physiology, 249 (Heart Circulatory Physiology 18): H867-H875.
Baisch F., Beck, L., Karemaker, J.M., Arbeilles, Ph., Gaffney, A., & Blomqvist, C.G. (1992). Head-down tilt bedrest HDT’88—an international collaborative effort in integrated systems physiology.Acta Physiologica Scandenavia, 144 (S604): 1–12.
Baselli, G., Cerutti, S., Civardi, S., Lombardi, F., Malliani, A., Merri, M., Pagani, M., & Rizzo, G. (1987). Heart rate variability signal processing: A quantitative approach as an aid to diagnosis in cardiovascular pathologies.International Journal of Bio-Medical Computing, 20: 51–70.
Blomqvist, C.G. & Stone, H.L. (1983). Cardiovascular adjustments to gravitational stress. InHandbook of Physiology: The Cardiovascular System, Peripheral Circulation and Organ Blood Flow, 3: 1027–1063. Bethesda, MD: American Physiological Society.
Bungo, M.W., Charles, J.B., and Johnson, P.C. (1985). Cardiovascular deconditioning during space flight and the use of saline as a countermeasure to orthostatic intolerance.Aviation Space and Environmental Medicine, 56: 985–990.
Charles, J.B., & Bungo, M.W. (1986). Post-space flight changes in resting cardiovascular parameters are associated with preflight left ventricular volume. Abstract, 57th Annual Scientific Meeting, Aerospace Medical Association, Nashville, TN.
Convertino, V.A., Doerr, D.F., Eckberg, D.L., Fritsch, J.M., & Vernikos-Danellis, J. (1990). Head-down bedrest impairs vagal baroreflex responses and provokes orthostatic hypotension.Journal of Applied Physiology, 68: 1458–1464.
DeBoer, R.W., Karemaker, J.M., & Strackee, J. (1984). Comparing spectra of a series of point events particularly for heart rate variability data.IEEE Transactions on Bio-Medical Engineering, BME-31: 384–387.
DeBoer, R.W., Karemaker, J.M. & Strackee, J. (1987). Hemodynamic fluctuations and baroreflex sensitivity in humans: a beat to beat model.American Journal of Physiology 253 (Heart Circulatory Physiology 22): H680-H689.
Eckberg, D.L., & Fritsch, J.M. (1992). Influence of ten-day head-down bedrest on human carotid baroreceptor-cardiac reflex function.Acta Physiologica Scandenavia, 144 (S604): 69–76.
Fritsch, J.M., Charles, J.B., Bennett, B.S., Jones, M.M., & Eckberg, D.L. (1992). Short-duration spaceflight impairs human carotid baroreceptor-cardiac reflex responses.Journal of Applied Physiology, 73: 664–671.
Gaffney, F.A., Nixon, J.V., Karlsson, E.S., Campbell, W., Dowdey, A.B.C., & Blomquist, G. (1985). Cardiovascular deconditioning produced by 20 hours of bedrest with head down tilt (-5 degrees) in middle-aged healthy men.American Journal of Cardiology, 56: 634–638.
Goldberger, A.L., Goldwater, D., & Bhargava, V. (1986). Atropine unmasks bed-rest effect: A spectral analysis of cardiac interbeat intervals.Journal of Applied Physiology, 61: 1843–1848.
Goodman, L.S., and Gilman, A.G. (1985).The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 7th ed., p. 1722. New York: McMillan Press.
Hayano, J., Sakakibara, Y., Yamada, A., Yamada, M., Mukai, S., Fujinami, T., Yokoyama, K., Watanabe, Y. & Takata, K. (1991). Accuracy of assessment of cardiac vagal tone by heart rate variability in normal subjects.American Journal of Cardiology, 67: 199–204.
Hirsch, J.A. & Bishop, B. (1981). Respiratory sinus arrhythmia in humans: How breathing pattern modulates heart rate.American Journal of Physiology 241 (Heart Circulatory Physiology 10): H620-H629.
Hughson, R.L., Maillet, A., Gharib, C., Fortrat, J. O., Yamamoto, Y., Pavy-Letraon, A., Riviere, D. & Guell, A. (1994). Reduced spontaneous baroreflex response slope during lower body negative pressure after 28 days of head-down bed rest.Journal of Applied Physiology, 77: 69–77.
Inoue, K., Miyake, S., Kumashiro, M., Ogata, H. & Yoshimura, O. (1991). Power spectral analysis of heart rate variability in traumatic quadriplegic humans.American Journal of Physiology 258 (Heart Circulatory Physiology 27): H1722-H1726.
Jenkins, G.M. & Watts, D.G. (1968).Spectral Analysis and its Applications. Oakland, CA: Holden-Day.
Johnson, S.J. & Anderson, N. (1978). On power estimation in maximum entropy spectral analysis.Geophysics, 43: 681–690.
Katona P.G., & Jih, F. (1975). Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: Noninvasive measure of parasympathetic cardiac control.Journal of Applied Physiology, 39: 801–805.
Kay, S.M. & Marple, S.L. (1981). Spectrum analysis—A modern perspective.Proc. of IEEE, 69: 1380–1419.
Levenhagen D.K., Evans, J.M., Wang, M., & Knapp, C.F. (1994). Cardiovascular regulation in humans in response to oscillatory lower body negative pressure.American Journal of Physiology, (Heart Circulatory Physiology 36): H593–H604.
Madwed J.B. & Cohen, R.J. (1991). Heart rate response to hemorrhage-induced 0.05-Hz oscillations in arterial pressure in conscious dogs.American Journal of Physiology 29 (Heart and Circulatory Physiology 4): H1248-H1253.
Malliani A., Pagani, M., Lombardi, F., & Cerutti, S. (1991). Cardiovascular neural regulation explored in the frequency domain.Circulation, 84: 482–492.
Nicogossian, A., Pool, S.L. & Rambaut, P.C. (1983). Cardiovascular responses to space flight.The Physiologist, 26: 5–78.
Pagani M., Lombardi, F., Guzzeti, S., Rimoldi, O., Furlan, R., Pizzinelli, P., Sandrone, G., Malfatto, G., Dell’Orto, S., Piccaluga, E., Turiel, M., Baselli, G., Cerutti, S. & Malliani, A. (1986). Power spectral analysis of heart rate and arterial pressure variabilities as a marker of sympatho-vagal interaction in man and conscious dog.Circulation Research, 59: 178–193.
Parati G., Castiglioni, P., Di Rienzo, M., Omboni, S., Pedotti, A., & Maneia, G. (1990). Sequential spectral analysis of 24 hour blood pressure and pulse interval in humans.Hypertension, 16: 414–421.
Pomeranz, B., Macaulay, R.J.B., Caudill, M.A., Kutz, I., Adam, D., Gordon, D., Kilborn, K.M., Berger, A.C., Shannon, D.C., Cohen, R.J., & Benson, H. (1985). Assessment of autonomic function in humans by heart rate spectral analysis.American Journal of Physiology, 248: H 151-H153.
Randall, D. C., Brown, D. R., Raisch, R. M., Yingling, J. D. & Randall, W. C. (1991). SA nodal parasympathectomy delineates autonomic control of heart rate power spectrum.American Journal of Physiology 260 (Heart Circulatory Physiology 29): H985-H988.
Rimoldi, O., Pierini, S., Ferrari, S., Cerutti, S., Pagani, M. & Malliani, A. (1990). Analysis of short-term oscillations of R-R and arterial pressure in conscious dogs.American Journal of Physiology 258 (Heart Circulatory Physiology 27): H967-H976.
Saul, J.P., Rea, R.F., Eckberg, D.L., Berger, R.D., & Cohen, R.J. (1990). Heart rate and muscle sympathetic nerve variability during reflex changes of autonomic activity.American Journal of Physiology 258 (Heart Circulatory Physiology 27): H713-H721.
Saul, J.P., Albrecht, P., Berger, R.D., & Cohen, R.J. (1988). Analysis of long-term heart rate variability: Methods, l/f scaling and implications.Computers in Cardiology, 14: 419–422.
Tapp, W.N., Knox, F.S. III, & Natelson, B.H. (1990). The heart rate spectrum in simulated flight: Reproducibility and effects of atropine.Aviation Space and Environmental Medicine, 61: 887–892.
Ten Harkel, A.D.J., Baiseh, F. & Karemaker, J.M. (1992). Increased orthostatic blood pressure variability after prolonged head-down tilt.Acta Physiologica Scandenavia, 144 (S604): 89–99.
Yamamoto, Y., & Hughson, R. L. (1991). Coarse-graining spectral analysis: New method for studying heart rate variability.Journal of Applied Physiology, 71: 1143–1150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by National Aeronautics and Space Administration grant NAG 9-298, and by the Clinical Research Center (NIH M01-2602), University of Kentucky.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patwardhan, A.R., Evans, J.M., Berk, M. et al. Spectral indices of cardiovascular adaptations to short-term simulated microgravity exposure. Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 30, 201–214 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698574
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698574