Abstract
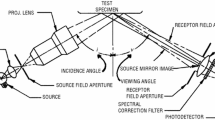
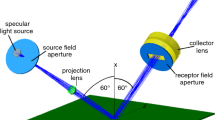
The measurement of specular gloss consists of comparing the luminous reflectance from a test specimen to that from a gloss standard, under the same geometric conditions. The reference goniophotometer described here was designed and characterized to comply with the geometric and spectral conditions specified in the international documentary standards for specular gloss measurements at the standard geometries of 20, 60, and 85°. In addition, this instrument measures the bi-directional luminous reflectance and transmittance for incident angles from 0 to 85°. The goniophotometer and the measurement procedures used to determine the specular gloss of nonmetallic samples are described in this paper, as well as the characterization of the instrument and uncertainty analysis. The minimum relative expanded uncertainty (k=2) for the reference goniophotometer is 0.3%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Commission International de l’Eclairage,International Lighting Vocabulary, Colorimetry, 2nd ed., Publ. No. 15.2, 1986.
“Standard Test Method for Specular Gloss, ASTM D 523,” American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, PA (1995).
International Standard ISO 2813, “Paint and Varnishes-Measurements of Specular Gloss of Nonmetallic Paint Films at 20, 60, and 85°,” International Organization for Standardization (1978).
“Standard Practice for Goniophotometry of Objects and Materials, ASTM E 167,” American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, PA (1995).
Hunter, R.S., “Gloss Investigations Using Reflected Images of a Target Patters,”J. Res., 16, 359 (1936).
Hunter, R.S., “Methods of Determining Gloss,” NBS Research Paper RP 958,J. Res., 18, No. 77, 281 (1937).
Nimeroff, I. “Analysis of Goniophotometric Reflective Curves,”J. Res, 48, No. 5, 441 (1952).
Hsia, J.J.,The NBS 20-, 60-, and 85- Degree Specular Gloss Scales, NIST Technical Note 594-10, 1975.
Nicodemus, F.E., Richmond, J.C., Hsia, J.J., Ginsburg, I.W., and Limperis, T.,Geometrical Considerations and Nomenclature for Reflectance, U.S. NBS Monograph 160, 1977.
Budde, W., “The Calibration of Gloss Reference Standards,”Metrologia, 16, 89–93 (1980).
Nadal, M.E. and Thompson, E.A., “New Primary Standard for Specular Gloss Measurements,”Journal of Coatings Technology, 72, No. 911, 61 (2000).
Ohno, Y.,Photometric Calibrations, NIST SP 250-37, 1997.
Barnes, P.Y. and Hsia, J.J.,45°/0° Reflectance Factor of Pressed Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Powder, NIST Technical Note 1413, 1995.
Larson, T.C., Bruce, S.S., and Parr, A.C.,Spectroradiometric Detector Measurements, NIST SP 250-41, 1998.
Doiron, T. and Stoup, J., “Uncertainty and Dimensional Calibrations,”J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol., 102, 647 (1997).
Saunders, R.D. and Shumaker, J.B., “Automated Radiometric Linearity Tester,”Appl. Opt., 23, 3504 (1984).
Taylor, B.N. and Kuyatt, C.E.,Guidelines for Evaluating and Expressing the Uncertainty of NIST Measurements Results, NIST Technical Note 1297, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Optical Technology Div., Gaithersburg, MD 20899-8441.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadal, M.E., Thompson, E.A. NIST reference goniophotometer for specular gloss measurements. Journal of Coatings Technology 73, 73–80 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698400
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698400