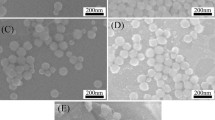
Abstract
Silica slurry in aqueous medium for wafer polishing was prepared by sol-gel reaction of silicon alkoxide utilizing commercial silica particles as seeds that were grown stepwise through intermittent additions of tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) as a silica precursor. Before the growth reaction, the commercial silica particles were pre-treated in the vibratory mill partially filled with zirconia ball and the sonicator to ensure good dispersion. The alcohol left after growth reaction was removed by vacuum distillation and repeated washings with distilled water followed by centrifugations. Then, the alcohol-free silica particles were redispersed in water. The dispersion stability of the silica slurries was examined by measuring surface charge of silica particles and rheological properties. Finally, wafer-polishing performance of the prepared silica slurries was considered by measuring the polishing (or removal) rate, and RMS (root mean square) roughness of the polished wafer surface. For the polishing, MEA (monoethanolamine) and TMAH (tetramethylammonium hydroxide) were used as polishing accelerators. The polishing result showed that the removal rate was nearly independent of the concentrations of MEA and TMAH in the range of 0.3-0.5 wt% and 100-500 ppm, respectively. One of the most interesting features is that hydrothermal treatment of the prepared silica slurries in autoclave increased the removal rate as high as ten times. Although the removal rate was increased by the increased size of the abrasive particle, surface roughness of the polished wafer surface was deteriorated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogush, G. H., Tracy, M. A. and Zukoski IV C. E, “Preparation of Monodisperse Silica Particles: Control of Size and Mass Fraction”,J. Non-Crystalline Solid,104, 95 (1988).
Brinker, C. J. and Scherer, G. W., “Sol-Gel Science,” Academic Press Inc., New York, USA (1990).
Buining, P. A., Liz-Marzan, L. M. and Philipse, A. P., “A Simple Preparation of Small, Smooth Silica Spheres in a Seed Alcohol for Stober Synthesis”,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,179, 318 (1996).
Chang, C. Y. and Sze, S. M., “ULSI Technology”, McGraw-Hill Companies Inc., New York, USA (1996).
Coenen, S. and de Kruif, C. G, “Synthesis and Growth of Colloidal Silica Particles”,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,124, 104 (1988).
Cook, L. M., “Chemical Processes in Glass Polishing”,J. Non-Crystalline Solid,120,152 (1990).
Deal, P. W. and Werho, D. B., “Non-Contaminating Wafer Polishing Slurry; US Patent, 5,139571 (1992).
Eisenlauer, J. and Killmann, E., “Stability of Colloidal Silica (AERO-SIL) Hydrosols, 1. Preparation and Characterization of Silica (AE-ROSIL)Hydrosols”,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,74,108 (1980).
Han, Y.-S., Lee, K.-M., Kim, S.-G., Jang, H.-D. and Park, K.Y., “Modeling of the Monomer Role and the Coalescence Limitation in Primary Particle Growth”,Korean J. Chem. Eng.,16,104 (1999).
Hunter, R J., “Foundations of Colloid Science”, Oxford Univ. Press, New York, USA (1989).
Her, R K., “The Chemistry of Silica”, Wiley, New York, USA (1979).
Konno, M., Inomata, H., Matsunaga, T. and Saito, S., “Growth Rate of Silica Particles from Ammonia-Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Tetraethylorthosilicate”,J. Chem. Eng. Japan,27,134 (1994).
Oh, M.-H., So, J.-H., Lee, J.-D. and Yang, S.-M., “Preparation of Silica Dispersion and its Phase Stability in the Presence of Salts”,Korean J. Chem. Eng.,16, 532 (1999).
Pierre, A. C., “Introduction to Sol-Gel Processing”, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, USA (1998).
Romberger, J. A. and Payne, C. C., “Low Sodium, Low Metal Silica Polishing Slurries”, European Patent, 0,520109, A1 (1991).
Sasaki, S. and Maeda, H., “Electrostatic Effects on the Hydration Layer of Colloidal Silica Particles”,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,167, 146 (1994).
Satoh, T, Akitaya, M., Konno, M. and Saito, S., “Tarticle Size Distributions Produced by Hydrolysis and Condensation of Tetraethylorthosiliicate”,J. Chem. Eng. Japan,30, 759 (1997).
Seo, K. W. and Kong, H. G, “Hydrothermal Preparation of BaTiO3 Thin Film”,Korean J. Chem. Eng.,17, 373 (2000).
So, J.-H., Oh, M.-H., Lee, J.-D. and Yang, S.-M., “Effects of Polyvinyl Alcohol on the Rheological Behavior and Phase Stability of Aqueous Silica Suspensions”,J. Chem. Eng. Japan,34(2), 262 (2001a).
So, J.-H., Yang, S.-M. and Hyun, J. C., “Microstructure Evolution and Rheological Responses of Hard Sphere Suspensions”,Chem. Eng. Sci.,56(9), 2967 (2001b).
So, J.-H., Yang, S.-M., Kim, C. Y. and Hyun, J. C., “Microstructure and Rheological Behaviour of Electrosterically Stabilized Silica Particle Suspensions”,Colloids & Surfaces -A- Physiochemical and Engineering Aspects,190, 89 (2001c).
Stober, W., Fink, A. and Bohn, E., “Controlled Growth of Monodisperse Silica Spheres in the Micron Size Range”,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,26, 62 (1968).
Sze, S. M., “VLSI Technology”, McGraw-Hill Companies Inc., New York, USA (1988).
Tadros, Th. F., “Adsorption of Polyvinyl Alcohol on at Various pH Values and its Effect on the Flocculation of the Dispersion”,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,64, 36 (1978).
Tan, C. G., Bowen, B. D. and Epstein, N., “Production of Monodisperse Colloidal Silica Spheres: Effect of Temperature,”J. Colloid Interface Sci.,118, 290 (1987).
Yasseen, A. A., Mourlas, N. J. and Mehregany, M., “Chemical-Mechanical Polishing for Polysilicon Surface Micromachining,”J. Electrochem. Soc.,144, 237 (1997).
van Blaaderen, A. and Kentgens, A. P. M., “Tarticle Morphology and Chemical Microstructure of Colloidal Silica Spheres from Alkoxysilanes”,J. Non-Crystalline Solids,149,161 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
So, JH., Bae, S.H., Yang, SM. et al. Preparations of silica slurry for wafer polishing via controlled growth of commercial silica seeds. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 18, 547–554 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698304
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698304