Abstract
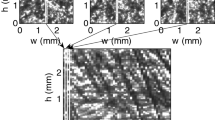
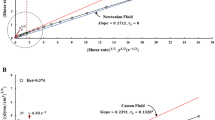
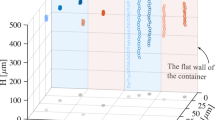
The shear-induced particle diffusivity in the red blood cell suspensions was evaluated based on the flow model and experimental results in a rectangular flow chamber. The effective diffusivity (De) of solute in the particle suspensions is equal to the stationary diffusivity (Ds) of the solute plus the shear-induced particle diffusivity (Dp). The effective diffusivity (De) of bovine serum albumin (BSA) in the red blood cell (RBC) ghost suspensions was determined under diffusion-limited conditions using a total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) method as a function of suspended RBC ghost volume fractions (0.05-0.7) and shear rates (200-1,000 s,-1). The stationary diffusivity (Ds) of BSA in RBC ghost suspensions was calculated by Meredith and Tobias model. Therefore the shear-induced particle diffusivity undergoing laminar shear flow can be evaluated. The shear-induced RBC ghost diffusivity was ranged from 0.35xl0-7 to 21.2xl0-7 cm2/s and it increased with increasing shear rate. Also the shear-induced RBC ghost diffusivity increased as a particle volume fraction increased as well, up to a particle volume fraction of 0.45. However, for RBC ghost volume fractions above 0.45, the shear-induced particle diffusivity decreased with increasing particle volume fraction. The shear-induced particle diffusivity in RBC ghost suspensions is a function of a particle Peclet number (or shear rate) and particle volume fractions. The dimensionless particle diffusivity (Dρ/a2γ) was investigated as a function of particle volume fraction and these results are in good agreement with the literature values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bird, R. B., Stewart, W. E. and Lightfoot, E. N., “Transport Phenomena”, John Wiley & Sons Inc. (1960).
Cha, W., Ph.D. Dissertation, “Red Blood Cell-Augmented Mass Transport of Albumin in Sheared Suspensions to Surfaces,” Illinois Institute of Technology (1993).
Cha, W. and Beissinger, R. L., “Macromolecular Mass Transport to a Surface: Effects of Shear Rate, pH and Ionic Strength,”J. Colloid Interface Sci.,177, 666 (1996a).
Cha, W. and Beissinger, R L., “Augmented Mass Transport of Macromolecules in Sheared Suspensions to Surfaces; B. Bovine Serum Albumin”,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,178, 1 (1996b).
Chin, B. D. and Park, O. O., “Electrorheological Responses of Particulate Suspensions and Emulsions in a Small-Strain Dynamic Shear Flow: Viscoelasticity and Yielding Phenomena,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,18,54(2001).
Eckstein, E. C, Bailey, D. G. and Shapiro, A. H., “Self-Diffusion of Particles in Shear Flow of a Suspensions,”J. Fluid Mech.,79, 191 (1977).
Gauthier, F. J., Goldsmith, H. L. and Mason, S. G., “Flow of Suspensions Through Tubes, X. Liquid Drops as Models of Erythrocytes,”Biorheology,9, 205 (1972).
Goldsmith, H. L., “Red Cell Motions and Wall Interactions in Tube Flow”,Fed. Proc.,30,1578 (1971).
Goldsmith, H. L. and Marlow, J. C., “Flow Behavior of Erythrocytes, II. Particle Motions in Concentrated Suspension of Ghost Cells,”J. Colloid Interface Sci.,71, 383 (1979).
Jefferey, G. B., “The Motion of Ellipsoidal Particle Immersed in a Viscous Fluid”,Proc. Roy. Soc,A102,161 (1922).
Kim, D., Ph.D. Dissertation, “Augmentation of Macromolecular Mass Transport in Sheared Suspensions: The Effective Diffusivity of Gamma Globulin in Red Blood Cell Ghosts Suspensions”, Illinois Institute of Technology (1990).
Kim, D. and Beissinger, R L., “Mass Transport of Macromolecules in Solution to Surfaces”,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,159, 9 (1993).
Leal, L. G., “Macroscopic Transport Properties of a Sheared Suspension”,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,58, 296 (1977).
Leighton, D. and Acrivos, A., “The Shear-Induced Migration of Particles in Concentrated Suspensions”,J. Fluid Mech.,181,415 (1987).
Meredith, R E. and Tobias, C. W., “Conductives in Emulsions”,J. Electrochemical Soc,108,286 (1968).
Yim, S. S., “A Theoretical and Experimental Study on Cake Filtration with Sedimentation”,Korea J. Chem. Eng.,16,308 (1999).
Zydney, A. L. and Colton, C. K., “Augmented Solute Transport in the Shear Flow of a Concentrated Suspension,”Physicochemical Hydrodynamics,10, 77 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cha, W., Beissinger, R.L. Evaluation of shear-induced particle diffusivity in red cell ghosts suspensions. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 18, 479–485 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698294
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698294