Abstract
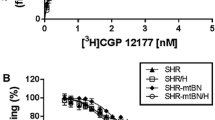
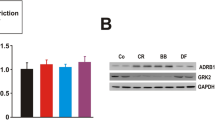
With the aim to study if selenium (Se) deficiency affects the basal frequency and cardiac response to isoproterenol (ISO), mice were fed a Se-deficient diet (Se-) or the same diet supplemented with 0.2 ppm Se as sodium selenite (Se+) for 4 wk. Atria frequency, cyclic AMP (cAMP) accumulation, nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity, and β-adrenoceptor-binding assay were then examined. Results showed that Se-mice have both a reduction in atria frequency as well as in cAMP content but higher NOS activity levels either at basal or after ISO stimulation. These differences were suppressed by feeding Se-mice with a Se-supplemented diet for 1 wk or by inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Alterations observed after ISO stimulation in atria of Se-mice were not related to a β-adrenoceptor expression modification because specific radioligand-binding parameters in cardiac membranes from Se-mice and Se+ mice were similar. The reduced response on rate and cAMP in atria from Se-mice to direct adenylate cyclase (AC) stimulation by forskolin and the shifted upward levels present in 2-amino-4-methylpyridine-treated Se-mice is in agreement with a negative crosstalk between iNOS activity and AC activity in Se-mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. F. J. Combs and S. B. Combs, Selenium deficiency diseases of animals, inThe Role of Selenium in Nutrition, G. F. J. Combs and S. B. Combs, eds., Academic, New York, pp. 266–326 (1986).
P. Chariot and O. Bignani, Skeletal muscle disorders associated with selenium deficiency in humans,Muscle Nerve 27, 662–668 (2003).
J. T. Salonen, R. Salonen, I. Pentila, et al., Serum fatty acids, apolipoproteins, selenium and vitamin antioxidants and the risk of death from coronary artery disease,Am. J. Cardiol. 56, 226–231 (1985).
J. T. Salonen, R. Salonen, K. Seppanen, et al., Relationship of serum selenium and antioxidants to plasma lipoproteins, platelet aggregability and prevalent ischaemic heart disease in Eastern Finnish men,Atherosclerosis 70, 155–160 (1988).
E. Altekin, C. Coker, A. R. Sisman, B. Onvural, F. Kuralay, and O. Kirimli, The relationship between trace elements and cardiac markers in acute coronary syndromes,J. Trace Elements Med. Biol. 18, 235–242 (2005).
G. S. Li, F. Wang, D. Kang, and C. Li, Keshan disease: an endemic cardiomyopathy in China,Hum. Pathol. 16, 602–609 (1985).
M. A. Beck, J. Handy, and O. A. Levander, Host nutritional status: the neglected virulence factor,Trends Microbiol. 12, 417–423 (2004).
S. W. Yusuf, Q. Rehman, and W. Casscells, Cardiomyopathy in association with selenium deficiency: a case report,J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 26, 63–66 (2002).
M. P. Burke and K. Opeskin, Fulminant heart failure due to selenium deficiency cardiomyopathy (Keshan disease),Med. Sci. Law 42, 10–13 (2002).
R. A. Sunde, Intracellular glutathione peroxidases: structure, regulation, and function, inSelenium in Biology and Human Health, R. F. Burk, ed., Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 45–78 (1994).
M. de Lorgeril, P. Salen, M. Accominotti, et al., Dietary and blood antioxidants in patients with chronic heart failure. Insights into the potential importance of selenium in heart failure,Eur. J. Heart Fail. 3, 661–669 (2001).
R. F. Burk, Protection against free radical injury by selenoenzymes,Pharmacol. Ther. 45, 383–385 (1990).
R. M. Gómez, O. A. Levander, and L. Sterin-Borda, Reduced inotropic heart response in selenium-deficient mice relates with inducible nitric oxide synthase,Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 284, H442-H448 (2003).
E. K. Joe, A. E. Schussheim, D. Longrois, et al., Regulation of cardiac myocyte contractile function by inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS): mechanisms of contractile depression by nitric oxide,J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 30, 303–315 (1998).
D. J. Pinsky, B. Cai, X. Yang, C. Rodriguez, R. R. Sciacca, and P. J. Cannon, The lethal effects of cytokine-induced nitric oxide on cardiac myocytes are blocked by nitric oxide synthase antagonism or transforming growth factor beta,J. Clin. Invest. 95, 677–685 (1995).
R. M. Gómez, M. I. Berria, and O. A. Levander, Host selenium status selectively influences susceptibility to experimental viral myocarditis,Biol. Trace Element Res. 80, 23–31 (2001).
L. Sterin-Borda, A. Vila-Echague, C. Perez-Leiros, A. Genaro, and E. Borda, Endogenous nitric oxide signalling system and the cardiac muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-inotropic response,Br. J. Pharmacol. 115, 1525–1531 (1995).
E. S. Borda, J. Pascual, P. R. Cossio, M. De La Vega, R. P. Arana, and L. Sterin-Borda, A circulating IgG in Chagas’ disease which binds to β adrenoreceptors of myocardium and modulates their activity,Clin. Exp. Immunol. 57, 679–686 (1984).
L. Sterin-Borda, A. Genaro, C. Perez-Leiros, G. Cremaschi, A. Vila-Echague, and E. Borda, Role of nitric oxide cardiac β adrenoceptor-inotropic response,Cell Signal. 10, 253–257 (1998).
L. Sterin-Borda, G. Bernabeo, S. Ganzinelli, L. Joensen, and E. Borda, Role of nitric oxide/cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP in beta(3) adrenoceptor-chronotropic response,J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 40, 580–588 (2006).
L. Sterin-Borda, C. F. Del Zar, and E. Borda, Differential CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptor-inotropic response of rat isolated atria: endogenous signal trasduction pathways,Biochem. Pharmacol. 69, 1705–1713 (2005).
L. Joensen, E. Borda, T. Kohout, S. Perry, G. Garcia, and L. Sterin-Borda, Trypanosoma cruzi antigen that interacts with the beta1-adrenergic receptor and modifies myocardial contractile activity,Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 127, 169–177 (2003).
K. O. Godwin, Abnormal electrocardiograms in rats fed a low selenium diet,Q. J. Exp. Physiol. Cogn. Med. Sci. 50, 282–288 (1965).
I. L. Grupp, I. S. Jamall, R. W. Millard, and G. Grupp, Effects of dietary selenium deficiency and selenium and calcium supplementation on myocardial contractile force and ouabain sensitivity of the rat heart,IRCS Med. Sci. 11, 22–23 (1983).
J. Ringstad, P. M. Tande, G. Norheim, and H. Refsum, Selenium deficiency and cardiac electrophysiological and mechanical function in the rat,Pharmacol. Toxicol. 63, 189–192 (1988).
K. Ytrehus, J. Ringstad, R. Myklebust, G. Norheim, and O. D. Mjos, The selenium-deficient rat heart with special reference to tolerance against enzymatically generated oxygen radicals,Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 48, 289–295 (1988).
B. Turan, O. Hotomaroglu, M. Kilic, and E. Demirel-Yilmaz, Cardiac dysfunction induced by low and high diet antioxidant levels comparing selenium and vitamin E in rats,Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 29, 142–150 (1999).
K. Sayar, M. Ugur, H. Gurdal, O. Onaran, O. Hotomaroglu, and B. Turan, Dietary selenium and vitamin E intakes alter beta-adrenergic response of L-type Ca-current and beta-adrenoceptor-adenylate cyclase coupling in rat heart,J. Nutr. 130, 733–740 (2000).
A. B. Gustafsson and L. L. Brunton, Attenuation of cAMP accumulation in adult rat cardiac fibroblasts by IL-1beta and NO: role of cGMP-stimulated PDE2,Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 283, C463-C471 (2002).
M. K. Chung, T. S. Gulick, R. E. Rotondo, G. F. Schreiner, and L. G. Lange, Mechanism of cytokine inhibition of beta-adrenergic agonist stimulation of cyclic AMP in rat cardiac myocytes. Impairment of signal transduction,Circ. Res. 67, 753–763 (1990).
N. Defer, M. Best-Belpomme, and J. Hanoune, Tissue specificity and physiological relevance of various isoforms of adenylyl cyclaseAm. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 279, F400-F416 (2000).
J. Hill, A. Howlett, and C. Klein, Nitric oxide selectively inhibits adenylyl cyclase isoforms 5 and 6,Cell Signal. 12, 233–237 (2000).
M. McVey, J. Hill, A. Howlett, and C. Klein, Adenylyl cyclase, a coincidence detector for nitric oxide,J. Biol. Chem. 274, 18,887–18,892 (1999).
B. Tavernier, J. M. Li, M. M. El-Omar, et al., Cardiac contractile impairment associated with increased phosphorylation of troponin I in endotoxemic rats,FASEB J. 15, 294–296 (2001).
J. W. Denninger and M. A. Marletta, Guanylate cyclase and the NO/cGMP signaling pathway,Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1411, 334–350 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gómez, R.M., Pacienza, N., Schattner, M. et al. Decreased β-adrenoceptor chronotropic response in selenium-deficient mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 117, 127–138 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698089
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698089