Abstract
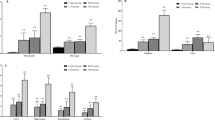
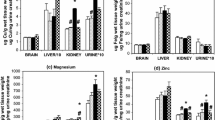
Lanthanides, because of their diversified physical and chemical effects, have been widely used in a number of fields. As a result, more and more lanthanides are entering the environment and eventually accumulating in the human body. Previous studies indicate that the impact of lanthanides on brain function cannot be neglected. Although neurological studies of trace elements are of paramount importance, up to now, little data are provided regarding the status of micronutritional elements in rats after prenatal and long-term exposure to lanthanide. The aim of this study is to determine the ytterbium (Yb) and trace elements distribution in brain and organic tissues of offspring rats after prenatal and long-term exposure to Yb. Wistar rats were exposed to Yb through oral administration at 0,0.1, 2, and 40 mg Yb/kg concentrations from gestation day 0 through 5 mo of age. Concentrations of Yb and other elements (Mg, Ca, Fe, Cu, Mn, and Zn) in the serum, liver, femur, and brain regions (cerebral cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum, and the rest) of offspring rats at the age of 0 d, 25 d, and 5 mo were analyzed by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. The accumulation of Yb in the brain, liver, and femur is observed; moreover, the levels of Fe, Cu, Mn, Zn, Ca, and Mg in the brain and organic tissues of offspring rats are also altered after Yb exposure. This disturbance of the homeostasis of trace elements might induce adverse effects on normal physiological functions of the brain and other organs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Wang,Trace Elements in Life Science, China Metrology Publishing House, Beijing, pp. 16–18 (1991) (in Chinese).
B. S. Guo, W. M. Zhu, B. K. Xiong, Y. J. Ji, Z. Liu, and Z. M. Wu,Rare Earths in Agriculture, China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing, p. 11 (1990) (in Chinese).
N. A. Danilov, Y. S. Krylov, G. V. Korpusov, and G. V. Kostikova, Scintillators based on ytterbium chloride adducts with neutral organophosphorus extractants for detecting solar neutrino for low-energy neutrino spectroscopy experiment,Radiochemistry 45, 128–133 (2003).
S. K. Sarkar, R. E. Rycyna, R. E. Lenkinski, H. A. Solleveld, and L. B. Kinter, Yb-DTPA, a novel contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging: application to rat kidney,Magn. Reson. Med. 17, 328–335 (1991).
W. E Zhu, S. Q. Xu, P. P. Shao, et al., Investigation on intake allowance of rare earth: a study on bio-effect of rare earth in South Jiangxi,China Environ. Sci. 17(1), 63–66 (1997) (in Chinese).
J. H. Feng, X. J. Li, E K. Pei, X. Chen, S. L. Li, and Y. X. Nie,1H NMR analysis for metabolites in serum and urine from rats administrated chronically with La(NO3)3,Anal. Biochem. 301, 1–7 (2002).
H. F. Wu, X. Y. Zhang, X. J. Li, Z. F. Li, Y. J. Wu, and F. K. Pei, Studies on the acute biochemical effects of La(NO3)3 using1H NMR spectroscopy of urine combined with pattern recognition,J. Inorg. Biochem. 99, 644–650 (2005).
W. F. Zhu, S. Q. Xu, H. Zhang, et al., Investigation of children intelligence quotient in REE mining area-I. Bio-effect study of REE mining area in South Jiangxi,Chin. Sci. Bull. 41(10), 914–916 (1996) (in Chinese).
Z. Y. Zhang, Y. Q. Wang, F. L. Li, H. Q. Xiao, and C. F. Chai. Distribution characteristics of rare earth elements in plants from a rare earth ore area,J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 252, 461–465 (2002).
W. F. Zhu, S. Q. Xu, P. P. Shao, et al., Bioelectrical activity of the central nervous system among populations in a rare earth element area,Biol. Trace Element Res. 57(1), 71–77 (1997).
A. Basu, K. Chakrabarty, and G.. C. Chatterjee, The effects of lanthanum chloride administration in newborn chicks on glutamate uptake and release by brain synaptosomes,Toxicol. Lett. 20, 303–308 (1984).
L. X. Feng, H. Q. Xiao, X. He, et al., Long-term effects of lanthanum intake on the neurobehavioral development of the rat,Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 28, 119–124 (2006).
W. Y. Feng, M. Wang, B. Li, et al., Mercury and trace element distribution in organic tissues andregional brain of fetal rat after in utero and weaning exposureto low dose of inorganic mercury,Toxicol. Lett. 152, 223–234 (2004).
M. C. Paul, C. H. Parsons, M. B. Calford, and E. I. von Nagy-Felsobuki, Multi-elemental analysis of brain tissues using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: healthy Wistar rats,Spectrochim. Acta B 59, 1485–1490 (2004).
Z. Y. Dong, D. Chen, Y. Liu, A. J. Chen, J. M. Liu, and Y. X. Nie, Effect of mixed rare earth changle on calcium content and its deposition in the liver of pregnant and fetal rats,J. Jilin Univ. (Med.). 29, 13–15 (2003) (in Chinese).
Z. M. Lei, X. T. Wei, and B. Xue, The effect of nitrate lanthanides exposure on the immune function of infant mice,Chin. J. Public Health 16, 91–94 (2000) (in Chinese).
L. Zhou, H. Chen. K. X. Huang, S. L. Li, and Y. X. Nie, Barrier efect of placenta membrane of pregnancy rat on mixed rare earth Changle,J. Chin. Rare Earth Soc. 22, 295–298 (2004) (in Chinese).
C. H. Evans,Biochemistry of the Lanthanides, Plenum, New York, pp. 25–31 (1990).
S. Hirano and K. T. Suzuki, Exposure, metabolism and toxicity of rare earths and related compounds,Environ. Health Perspect. 104, 85–95 (1996).
G. M. Kanapilly,In vitro precipitation behavior of trivalent lanthanides,Health Phys. 39, 343–346 (1980).
S. Hirano, N. Kodama, K. Shibata, and K. T. Suzuki, Metabolism and toxicity of intravenously injected yttrium chloride in rats,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 121, 224–232 (1993).
Y. Nakamura, Y. Tsumura, Y. Tonogai, T. Shibata, and Y. Ito, Differences in behavior among the chlorides of seven rare earth elements administered intravenously to rats,Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 37, 106–116 (1997).
C. R. Richmond and J. E. London, Long-termin vivo retention of cerium-144 by beagles,Nature 211, 1179 (1966).
P. B. Dean, P. Niemi, L. Kivisaari, and M. Kormano, Comparative pharmacokinetics of gadolinium DTPA and gadolinium chloride,Invest. Radiol. 1, S258-S260 (1988).
H. Q. Xiao, F. L. Li, Z. Y. Zhang, et al., Distribution of ytterbium-169 in rat brain after intravenous injection,Toxicol. Lett. 155, 247–252 (2005).
J. Cumings,Trace Elements in the Brain in Health and in Neurological Disease, The Athlone Press, University of London, London (1965).
M. Kozma and A. Ferke, Trace element localization and changes in zinc and copper concentrations during post-natal development of the rat central nervous system,Acta Histochem. 65, 219–227 (1970).
F. Rath, R. Grahl, and D. Felicetti, Histochemical behaviour of zinc activated tartrate resistant phosphatase in early stages of experimental tumours in the rat trigeminal nerve,Exp. Pathol. 18, 25–30 (1980).
T. Usdin, I. Creese, and S. Snyder, Regulation by cations of tritium labeled spiroperidol binding associated with dopamine receptors of rat brain,J. Neurochem. 34, 669–676 (1980).
D. Atwood and B. Yearwood, The future of aluminium chemistry,J. Organomet. Chem. 600, 186–197 (2000).
D. A. Przywara, S. V. Bhave, A. Bhave, et al., Activation of K+ channels by lanthanum contributes to the block of transmitter release in chick and rat sympathetic neurons,J. Membr. Biol. 125, 155–162 (1992).
P. D. Saltman and L. G.. Strause, The role of trace minerals in osteoporosis,J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 12(4), 384–389 (1993).
B. Ytrehus, H. Skagemo, G., Stuve, T. Sivertsen, K. Handeland, and T. Vikoren, Osteoporosis, bone mineralization, and status of selected trace elements in two populations of moose calves in Norway,J. Wildl. Dis. 35(2), 204–211 (1999).
S. Takahashi, I. Takahashi, H. Sato, Y. Kubota, S. Yoshida, and Y. Muramatsu, Age-related changes in the concentrations of major and trace elements in the brain of rats and mice,Biol. Trace Element Res. 80, 145–158 (2001).
A. F. Castoldi, T. Coccini, S. Ceccatelli, and L. Manzo, Neurotoxicity and molecular effects of methylmercury,Brain Res. Bull. 55, 197–203 (2001).
S. C. Segerstrom and G. E. Miller, Psychological stress and the human immune system: a meta-analytic study of 30 years of inquiry,Psychol. Bull. 130, 601–630 (2004).
Y. L. Huang, J. Y. Sheu, and T. H. Lin, Association between oxidative stress and changes of trace elements in patients with breast cancer,Clin Biochem. 32, 131–136 (1999).
V. N. Izgut-uysal, N. Derin, and A. Agac, Effect of cold-restraint stress on the distribution of trace elements in rat tissues,Biol. Trace Element Res. 78, 149–155 (2000).
J. T. Parsons, A. S. David, J. D. Robert, and B. C. Severn, Neuronal-specific endoplasmic reticulum Mg2+/Ca2+-ATPase Ca{2+} sequestration in mixed primary hippocampal culture homogenates,Anal. Biochem. 330, 130–139 (2004).
C. J. Frederickson and G.. Danscher,Nutritional Modification of Brain Function, Academic, New York, pp. 289–306 (1988).
L. B. John, Iron-deficiency anemia: examining the nature and magnitude of the public health problem,J. Nutr. 131, 568s-580s (2001).
L. X. Feng, H. Q. Xiao, X. He, et al., Neurotoxicological consequence of long-term exposure to lanthanum,Toxicol. Lett. 165, 112–120 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, L., He, X., Xiao, H. et al. Ytterbium and trace element distribution in brain and organic tissues of offspring rats after prenatal and postnatal exposure to ytterbium. Biol Trace Elem Res 117, 89–104 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698086
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698086