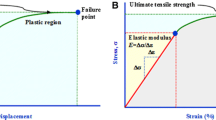
Abstract
Osteoporosis is a major complication in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM), particularly in those with insulin dependency. Recently, many therapeutic effects ofNigella sativa L. (NS) extracts have been exhibited such as anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and antidiabetic with clinical and experimental studies. Mechanical strength in the femur and vertebrae increases with human parathyroid hormone (hPTH) treatment. The aim of the present study was to test the hypothesis that combined treatment with NS and hPTH is more effective than treatment with NS or hPTH alone in improving bone mass, connectivity, and biomechanical behavior using the finite element method (FEM) in insulin-dependent diabetic rats. In the mechanical analysis, five rat bones (control, diabetic diabetic NS treated, diabetic hPTH treated, and diabetic NS + hPTH treated) have been studied for bending analysis using the finite element analysis program ANSYS. Combined treatment of NS and hPTH was more effective on bone histomorphometry and mechanical strength than treatment with NS or hPTH alone for streptozotocin-induced diabetic osteopenia, which notably decreased bone volume.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. W. Baynes, and S. R. Thorpe, The role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications,Curr. Opini. Endocrinol. 3, 277–284 (1996).
J. Auwerx, J. Dequeker, R. Bouillon, P. Geusens, and J. Nijs, Mineral metabolism and bone mass at peripheral and axial skeleton in diabetes mellitus,Diabetes 37, 8–12 (1988).
J. W. Baynes, Role of oxidative stress in development of complications in diabetes,Diabetes 40, 405–412 (1991).
P. Gillery, J. C. Monboisse, F. X. Maquart, and J. P. Borel, Does oxygen free radical increased formation explain long term complications of diabetes mellitus?Med. Hypotheses 29, 47–50 (1989).
A. Seven, S. Guzel, O. Seymen, et al., Nitric oxide synthase inhibition by l-NAME in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats: impacts on oxidative stress,Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 199, 205–210 (2003).
B. L. Riggs, H. W. Wahner, E. Seeman, et al., Changes in bone mineral density of the proximal femur and spine with aging: differences between the postmenopausal and senile osteoporosi syndrome,J. Clin. Invest. 70, 716–723 (1982).
I. R. Reid, Therapy of osteoporosis: calcium, vitamin D and exercise,Am. J. Med. Sci. 312, 278–286 (1996).
P. Morley, J. E Whitfield, and G. E. Willick, Anabolic effects of PTH on bone,Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 8, 225–231 (1997).
J. M. Hock, I. Gera, J. Fonesca, and L. G. Raisz, Human PTH increases rat bone mass in ovariectomized and orchidectomized rats,Endocrinology 122, 2899–2904 (1998).
R. I. Jilka, R. S. Weinstein, T. Bellido, P. Roberson, A. M. Parfitt, and S. C. Manolagas, Increased bone formation by prevention of osteoblast apoptosis with PTH,J. Clin. Invest. 104, 439–446 (1999).
B. D. Baumann and T. J. Wronski, Response of cortical bone to anti-resorptive agents and PTH in aged ovariectomized rats,Bone 16, 247–253 (1995).
P. T. Cheng, C. Chan, and K. Muller, Cyclical treatment of osteopenic ovariectomized adult rats with PTH (1-34) and pamidronate,J. Bone Miner. Res 10, 119–126 (1995).
Y. H. An, Q. Kang, and R. J. Friedman, Mechanical symmetry of rabbit bones studied by bending and indentation testing,Am. J. Vet. Res. 57(12), 1786–1789 (1996).
R. A. Ayers et al., Correlation of flexural structural properties with bone physical properties: a four species survey,Biomed. Sci. Instrum. 32, 251–260 (1996).
P. H. Jorgensen, B. Bak, and T. T. Andreassen, Mechanical properties and biochemical composition of rat cortical femur and tibia after long-term treatment with biosynthetic human growth hormone,Bone 12(5), 353–359 (1991).
E. I. Barengolts et al., Effects of endurance exercise on bone mass and mechanical properties in intact and ovariectomized rats,J. Bone Miner. Res. 8(8), 937–942 (1993).
C. Ejersted et al., Human parathyroid hormone (1-34) and (1-84) increase the mechanical strength and thickness of cortical bone in rats,J. Bone Miner. Res. 8(9), 1097–1101 (1993).
E. S. Kurland, F. Cosman, D. J. McMahon, C. J. Rosen, R. Lindsay, and J. P. Bilezikian, Parathyroid hormone as a therapy for idiopathic osteoporosis in men: effects on bone mineral density and bone markers,J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 3069–3076 (2000).
R. M. Neer, C. D. Arnaud, J. R. Zanchetta, et al., Effect of parathyroid hormone (1-34) on fractures and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis,N. Engl. J. Med. 344, 1434–1441 (2001).
M. F. Altan, M. Kanter, S. Donmez, M. E. Kartal, and S. Buyukbas, Combination therapy ofNigella sativa and human parathyroid hormone on bone mass, biomechanical behavior and structure in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats,Acta Histochem. (2007).
M.A.K. Liebschner, Biomechanical considerations of animal models used in tissue engineering of bone,Biomaterials 25, 1697–1714 (2004).
G. Cheung, P. Zalzal, M. Bhandari, J. K. Spelt, and M. Papini, Finite element analysis of a femoral retrograde intramedullary nail subject to gait loading,Med. Eng. Phys. 26, 93–108 (2004).
M. Viceconti, L. Bellingeri, L. Cristofolini, and A. Toni, A comparative study on different methods of automatic mesh generation of human femurs,Med. Eng. Phys. 20, 1–10 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altan, M.F. Effects ofNigella sativa and human parathyroid hormone on bone mass and strength in diabetic rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 116, 321–328 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698016
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698016