Abstract
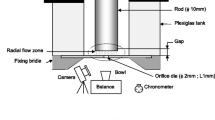
Experimental investigations were performed to see how the die exit geometry and the extrusion velocity influence on extrudate swell and melt fracture for several polymer melts [low-density polyethylene, styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and SBR/HAF (carbon black) compound]. Four different types of die exit geometry were considered; 0° (symmetric. usual capillary die), and 30°, 45° and 60° (asymmetric dies) were chosen for the die exit angle. Extrudate diameters were measured without draw-down under isothermal condition. Polymer melts were extruded into an oil that has the same density and temperature as those of the extrudate. Extrudate swells from dies with different diameters were correlated with volumetric flow rates. It was observed that the extrudate swell increases with increasing volumetric flow rate and exhibits through a minimum value at about 45° die exit angle. As to the fracture phenomena, it was observed that the critical shear for the onset of melt fracture increases with the increasing die exit angle up to 45°. However, for 60° die exit angle, the onset of melt fracture is again similar to that of 0° exit angle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spencer, R. S. and Dillon, R. E.:J. Colloid. Sci.,3, 163 (1948).
Mooney, M.: “Rheology”, Vol. 2, Chap. 5, edited by Eirich, F. R., Academic Press, New York (1967).
Nakajima, N. and Shida, M.:Trans. Soc. Rheol.,10, 299(1966).
Han, C. D.: “Rheology in Polymer Processing”, Academic Press, New York (1976).
Huang, D. C. and White, J. L.:Polym. Eng. Sci.,19, 609 (1979).
Huang, D. C. and White, J. L.:Polym. Eng. Sci. 20, 182 (1980).
Rogers, M. G.:J. Appl. Polym. Sci,14, 1679 (1970).
Vlachopoulos, J., Horie, M. and Lindorikis, S.:Trans. Soc. Rheol.,16, 669(1972).
Arai, T. and Aoyama, H.:Trans. Soc. Rheol.,7, 333 (1963).
Mendelson, R. A., Finger, F. L. and Bagley, E. B.:J. Polym. Sci. c35, 177(1971).
Cogswell, F. N.:Plastics and Polymers, 391 (1970).
Petraglia, G. and Coen, A.:Polym. Eng. Sci.,10, 79 (1970).
Han, C. D. and Charles, M.:Trans. Soc. Rheol.,14, 213 (1970).
Han, C. D. and Yu, T. C.:AIChE J.,17, 1512 (1971).
Utracki, L. A., Bakerdjian, Z. and Kamal, M. R.:J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 19, 48(1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.S., Park, O.O. The effct of asymmetries of die exit geometry on extrudate swell and melt fracture. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 11, 1–7 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02697508
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02697508