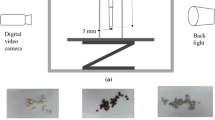
Abstract
The hydrodynamic and gas mixing characteristics have been determined in a FCC regenerator (0.48 m I.D.x3.4 m high) with FCC particles. Solids holdup in the dense bed decreases with increasing gas velocity, but it increases in the freeboard region. The bubble/void fraction increases with an increase along the bed height at a given gas velocity and increases with increasing gas velocity at a constant bed height. Backmixed tracer gas at the wall region is higher than that at the center region of the bed. The gas backmixing coefficient decreases with increasing gas velocity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendat, J. S. and Piersol, A. G., “Random Data, Analysis and Measurement Procedures,” John Wiley & Sons, New York, 361 (1986).
Cankurt, N. T. and Yerushalmi, J., “Gas Backmixing in High Velocity Fluidized Beds,” Fluidization, Davidson, J. F. and Kearins, D. L., eds., Cambridge Univ. Press, London, 387 (1978).
Choi, Y. T. and Kim, S. D., “Bubble Characteristics in an Internally Circulating Fluidized Bed,”J. Chem. Eng. Japan,24, 195 (1991).
Clift, R. and Grace, J. R., “Fluidization,” Davidson, J. F., Harrison, D. and Clift, R., eds., Academic Press Inc., London, 73 (1985).
Farag, H. I., Ege, P. E., Grislingas, A. and de Lasa, H. I., “Flow Patterns in a Pilot Plant-Scale Turbulent Fluidized Bed Reactor: Concurrent Application of Tracers and Fiber Optic Sensors,”Can. J. Chem. Eng.,75, 851 (1997).
Kim, S.W., Namkung, W. and Kim, S.D., “Bubble/void Properties in a FCC Regenerator,” Proc. 6th Asian Conf. on Fluidized-bed and Three-phase Reactors, eds. by H. S. Chun and S. D. Kim, Cheju, Korea, 43 (1998).
Kim, S.W., Namkung, W. and Kim, S. D., “Solids Behavior in Freeboard of FCC Regenerator,”J. Chem. Eng. Japan,33, 78 (2000).
Lee, G. S. and Kim, S.D., “Gas Mixing in Slugging and Turbulent Fluidized Beds,”Chem. Eng. Commun.,86, 91 (1989).
Lee, G. S. and Kim, S.D., “Void Characteristics in Turbulent Fluidized Beds,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,8, 6 (1991).
Namkung, W. and Kim, S. D., “Gas Backmixing in a Circulating Fluidized Bed,”Powder Technology,99, 70 (1998a).
Namkung, W. and Kim, S.D., “Gas Mixing Characteristics in a Fast Fluidized Bed,”HWAHAK KONGHAK,36, 797 (1998b).
Namkung, W. and Kim, S. D., “Gas Backmixing in the Dense Region of a Circulating Fluidized Bed,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,16, 456 (1999).
Namkung, W., Kim, S.W. and Kim, S. D., “Transition Velocity to Turbulent Fluidized Bed and Flow Regime,”HWAHAK KONGHAK,38, 523 (2000).
Senior, R. C. and Avidan, A. A., “Comparison of the Performance of Circulating and Turbulent Bed FCC Regenerators,” Proc. of 5th Int. Conf. on Circulating Fluidized Bed, Beijing, China (1996).
Wilson, J.W., “Fluid Catalytic Cracking-Technology and Operation,” Penn Well Publishing Company, Oklahoma, USA (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Namkung, W., Kim, S.W. & Kim, S.D. Hydrodynamic characteristics of a FCC regenerator. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 20, 110–115 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02697194
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02697194