Abstract
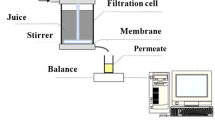
The glass-ball-inserted membrane module has been designed to enhance the filtration of a flat-sheet membrane. Three different modes of filtration experiments were conducted and compared to demonstrate the flux enhancement due to the presence of glass balls: normal dead-end filtration, vortex flow filtration, and enhanced vortex flow filtration using glass balls. In the case of enhanced vortex flow filtration, the permeate flux was found to be three times as large as that of dead-end filtration and two times larger than vortex flow filtration. In addition, the flux decline was observed to be relatively low. The effect of the amount of glass balls on the permeate flux was also investigated by changing the glass ball volume fraction from 0.059 to 0.356. It has been observed that the permeate flux shows a maximum value of the volume fraction of 0.119. For the glass-ball-inserted membrane module, the permeate flux tends to increase with the feed flow rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aim, R. B. and Peuchot, M. M., “Membranes for Water and Wastewater Treatment,”Water Supply,9(1), 185 (1991).
Bird, R. B., Stewart, W. E. and Lightfoot, E.N., “Transport Phenomena,” John Wiley and Sons, New York (1960).
Choi, J. S., Song, I. K. and Lee, W.Y., “A Composite Catalytic Polymer Membrane Reactor Using Heteropolyacid Polymer Membrane,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,17, 280 (2000).
Chung, K.Y., Brewster, M. E. and Belfort, G., “Dean Vortices with Wall Flux in a Curved Channel Membrane System: 2. The Velocity Field,”AIChE J.,42, 347 (1996).
Chung, K.Y., “Instabilities of Viscous Fluid Flow in a Curved Channel: A New Approach to Membrane Module Design,” Ph.D. Thesis, R.P.I. (1992).
Cui, Z. F. and Wright, K. I. T., “Flux Enhancements with Gas Sparging in Downwards Crossflow Ultrafiltration: Performance and Mechanism,”J. Membr. Sci.,117, 109 (1996).
Ghosh, R., Li, Q. and Cui, Z., “Fractionation of BSA and Lysozyme Using Ultrafiltration: Effect of Gas Sparging,”AIChE J.,44, 61 (1998).
Hall, K. R., “Another Hard Sphere Equation of State,”J. Chem. Phys.,57, 2252 (1972)
Howell, J. A., Sanchez, V. and Field, R.W., “Membranes in Bioprocessing-Theory and Applications-,” Chapman & Hall, London (1993).
Kim, H.-J. and Hong, S.-I., “The Transport Properties of CO2 and CH4 for Brominated Polysulfone Membrane,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,16, 343 (1999).
Kim, Y.-S., Kusakabe, K., Morooka, S. and Yang, S.-M., “Preparation of Microporous Silica Membrane for Gas Separation,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,18, 106 (2001).
Kobayashi, T., Nagai, T., Ono, M. and Fujii, N., “Charged Membranes for Ultrafiltration Treatment of Synthetic Waste Water Containing Peptone,”J. Chem. Tech. Biotechnol.,65, 49 (1996).
Kunii, D. and Levenspiel, O., “Fluidization Engineering,” John Wiley and Sons, New York (1969).
Lowe, E. and Durkee, E. L., “Dynamic Turbulence Promotion in Reverse Osmosis Processing of Liquid Foods,”J. Food Sci.,36, 31 (1971).
Maartens, A., Swart, P. and Jacobs, E. P., “Membrane Pretreatment: A Method for Reducing Fouling by Natural Organic Matter,”J. Colloid Interface Sci.,221, 137 (2000).
Matsumoto, K., Katsuyama, S. and Ohya, H., “Separation of Yeast by Cross-Flow Filtration with Backwashing,”J. Ferment. Technol.,65, 77 (1987).
Millward, H. R., Bellhouse, B. J. and Walker, G., “Screw-Thread Flow Promoters: An Experimental Study of Ultrafiltration and Microfiltration Performance,”J. Membr. Sci.,106, 269 (1995).
Mueller, J. and Davis, R.H., “Protein Fouling of Surface-Modified Polymeric Microfiltration Membranes,”J. Membr. Sci.,116, 47 (1996).
Musale, D. A. and Kulkarni, S. S., “Effect of Membrane-Solute Interations on Ultrafiltration Performance,”Rev. Macromol. Chem. Phys.,C38, 615 (1998).
Russel, W. B., Saville, D. A. and Schowalter, W. R., “Colloidal Dispersions,” Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge (1989).
Shiraha, H., Koide, N., Hada, H., Ujike, K., Nakamura, M., Shinji, T., Gotoh, S. and Tsuji, T., “Improvement of Serum Amino Acid Profile in Hepatic Failure with the Bioartificial Liver Using Multicellular Hepatocyte Spheroids,”Biotechn. & Bioeng.,50, 416 (1996).
Takadono, S., Iwahori, H., Yabushita, T. and Imamura, Y., “Treatment of Highly Fouling Waste Waters with Tubular Membrane Systems,”Desalination,49, 347 (1984).
Van Vlack, L. H., “Elements of Materials Science and Engineering,” 5th ed., Addison-Wesley Pub., Massachusetts (1985).
Vigo, F., Uliana, C. and Lupino, P., “The Performance of a Rotating Module in Oily Emulsions Ultrafiltration,”Sep. Sci. Technol.,21, 213 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JP., Kim, JJ. Flux enhancement with glass ball inserted membrane module for the ultrafiltration of dextran solution. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 20, 99–103 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02697192
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02697192