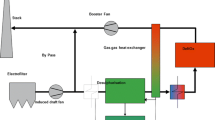
Abstract
The temperature and corrosive action of the effluent gases on the chamotte lining of the stack of an oil-refining enterprise is considered. It is established that fracture of the lining is caused mainly by the interaction between the SO2 present in the effluent gases and mullite. During service of the stack, aluminum sulfates form, and in cooling new formations arise (tschermigite) that disrupt the chamotte lining.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chemist’s Handbook, Vol. II [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow-Leningrad (1964).
D. Taylor and H. Bassett, “The system Al2(SO4)3-H2SO4-H2O,”J. Chem. Soc, 4431–4442 (1952).
I. Va. Guzman and B. I. Polyak, “Computational and graphical interpretations of reaction sintering and their practical use,”Ogneupory, No. 4, 42–48 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Ogneupory i Tekhnicheskaya Keramika, No. 4, pp. 48–52, April, 2000.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goberis, S., Yarushyavichyus, K. & Shpokauskas, A. Causes of fracture in the chamotte lining of a stack. Refract Ind Ceram 41, 148–152 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02693775
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02693775