Abstract
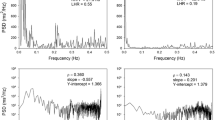
Rationale. Functional reinnervation of the transplanted human heart by the autonomic nervous system has not been demonstrated. A lack of autonomic control of the transplanted allograft is reflected by an increased resting heart rate, a sluggish heart rate response to dynamical exercise and a reduced heart rate variability. Recent evidence suggests that a measure of deterministic chaos in the heartbeat interval series (point correlation dimension, PD2i) is superior to the conventional power spectrum or other stochastic measures in detecting changes in the mechanism underlying heartbeat generation.Methods. The PD2i is based on the presumption that the variability is determined and patterned, whereas the stochastic measures all assume that the variability is around a stationary mean and is noise. The PD2i reconstructs the degrees of freedom (number of independent variables) in the system that generates the time series examined, and does this irrespective of whether the system is stochastic or deterministic and is stationary in time.Results. PD2i was determined for heartbeat intervals (RR, ECG digitized at 1200 Hz; supine posture) of 23 heart transplant recipients (HTR: 9 adults, 14 children; 0.04-7.7 years after transplantation) and 21 healthy control subjects (CTL; 13 adults, 8 children). The PD2i (+/− SD) averaged 5.4 +/− 0.7 for the CTL adults and 5.4 +/− 0.6 for the CTL children. Mean PD2i was reduced after transplantation to 1.1 +/− 0.1 in 6 HTRs recorded within 1 year after surgery; in one HTR recorded 2 weeks after surgery the mean PD2i was 3.7. Between 1 to 2 years PD2i was found increased in 2 of 3 subjects and between 2 to 8 years it was increased in 13 of 13, but not to control levels. In normal hearts the QT subinterval of each heartbeat cycle is associated with inotropy and the RR-QT remainder with chronotropy (i.e., the dyastolic interval during which RR is primarily regulated). To examine more closely the residual and returning heartbeat dynamics of the HTR subjects, these subinterval series were examined during mild exercise (40 to 90 Watts) and its recovery. In recent HTRs, resting QT and RR-QT were moderately reduced and modulated by exercise and recovery, but with an approximate 100 beat latency. In long-term (7-8 years) HTR subjects there was a rapid and larger response to exercise/recovery, but compared to normal the range was smaller and the complexity of the subinterval trajectories in time was simpler.Conclusions. Recurrence of low-dimensional deterministic dynamics after transplantation suggests recovery of neurocardiac control attributable to 1) reorganization of the viable intrinsic cardiac nervous system, 2) reinnervation by the extrinsic autonomic nervous system, or 3) both.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armour J.A. (1994) Peripheral Autonomic Neuronal Interactions in Cardiac Regulation. In:Neurocardiology, J.A. Armour and J.L. Ardell (eds.). New York, Oxford University Press, pp. 219–244.
Arrowood, J.A., Goudreau, E., Minisi, J., Davis, A.B., Mohanty, P.K. (1995). Evidence against reinnervation of cardiac vagal affeents after human orthotopic cardiac transplanation.Circulation 92: 402–408
Babloyantz, A., Desthexhe, A. (1988). Is the heart a periodic oscillator?Biol Cybern 58: 203–211.
Burke, M.N., McGinn, A.L. Homans, D.C., Christensen, B.V., Kubo, S.H., Wilson, R.F. (1995). Evidence for functional sympathetic reinnervation of left ventricle and coronary arteries after orthotopic cardiac transplanation in humans.Circulation 91: 72–78.
Cerretelli, P., Marconi, C., Meyer, M., Ferretti, G., Grassi, B. (1992). Gas exchange kinetics in heart transplant recipients.Chest 101: 199S-205S.
Elbert T., Ray W.J., Kowalik Z.J., Skinner J.E., Graf K.E., Birbaumer N. (1994) Chaos and Physiology.Physiological Reviews 74: 1–47.
Farmer, J.D., Ott, E., Yorke, J.A. (1983). The dimension of chaotic attractors.Physica D7: 53–180.
Glass, L., Malta, C.P. (1990) Chaos in multi-looped negative feedback systems.J. Theor. Biol. 145: 217–223
Goldberger, A.L., West, B. (1987). Chaos in physiology. In:Chaos in Biological Systems. A.V. Holden, H. Degn, L.F. Olsen (eds.). New York: Plenum, pp. 1–5.
Goldberger, A.L., Rigney, D.R., West, B.J. (1990). Chaos and fractals in human physiology.Sci. Am. 262: 42–49.
Grassberger, P., Procaccia, I. (1983). Measuring the strangeness of strange attractors.Physica 9D: 189–208.
Haken H. (1985) Operational approaches to complex systems. In Haken, H. (ed.)Complex Systems: Operational Approaches in Neurobiology, Physics and Computers. New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 1–16.
Hsu, D.T., Garofano, R.P., Douglas, J.M., Michler, Re., Quaegebeur, J.M., Gersony, W.M., Addonizio, L.J. (1993). Exercise performance after pediatric heart transplantation.Circulation 88: 238–242.
Huang M.H., Sylven C., Pelleg A., Smith F.M., Armour J.A. (1993) Modulation of in situ canine intrinsic cardiac neurons by locally applied acetylcholine, ATP or ATP-analogues.Amer J Physiol 265:R914–22.
Huang M.H., Wolf S.G., Armour J.A. (1995) Shortening of the QT interval of the EKG is associated primarily with increased ventricular contractility rather than heart rate.Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 30:1–11.
Izrailtyan I., Kresh J.Y. (1995) Evidence for intrinsic cardiac neural system in isolated heart.Abstr. FASEB 9: A40.
Kaplan D.T., Glass L. (1992) Direct test for determinism in a time series.Physical Review Letters, 68:427–430.
Kaye, D.M., Ester, M., Kingwell, B., McPherson, G., Esmore, D., Jennings, G. (1995). Functional and neurochemical evidence for partial cardiac sympathetic reinnervation after cardiac transplantation in humans.Circulation 88: 1110–1118.
Kitney, R.I, Rompelman, O. (1980).The Study of Heart-Rate Variability. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Kowalik Z.J., Elbert T. (1994). Changes of chaoticness in sontaneous EEG/MEG.Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 29: 270–282.
Liem, L.B., Dibiase, A, Schroeder, J.S. (1990). Arrythmia and clinical electrophysiology of the transplanted human heart.Semn. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2: 271–278.
Lyapounov A.M. (1892) The general problem of the stability of motion. Commun.Soc Math. Kharkov. Translated and reprinted inAnnals Math. Studies 17 (1947), Princeton Univer. Press. DC:NASA.
Mayer-Kress, G., Yates, F.E., Benton, L., Keidel, M. Tirsch, W., Poppl, S.J., Geist, K. (1988). Dimensional analysis of nonlinear oscillations in brain, heart, and muscle.Math. Biosci. 90: 155–182
Meyer, M., Marconi, C., Grassi, B., Rieu, M., Cerretelli, P., Cabrol, C. (1992). Adjustment of cardiac output to step exercise in heart transplant recipients.Applied Cardiopulmonary Pathophysiology 4: 213–223.
Meyer, M., Rahmel, A., Marconi, C., Grassi, B., Cerretelli, P., Cabrol, C. (1994). Adjustment of cardiac output to step exercise in heart transplant recipients.Z. Kardiol. 83 (Supp. 3): 103–109.
Muhlnickel W., Rendtorff N., Kowalik Z.J., Rockstroh B., Miltner W., Elbert T. (1994). Testing the determinism of EEG and MEG.Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 29: 262–269.
Murphy, D.A., O’Blenes S., Hanna B.D., Armour J.A. (1994a) Capacity of intrinsic cardiac neurons to modify autotransplanted myocardium.J Heart and Lung Transplant 13: 847–856.
Murphy, D.A., O’Blenes, S., Hanna, B.D., Armour, J.A. (1994b). Functional capacity of nicotine-sensitive canine intrinsic cardiac neurone to modify the heart.Am. J. Physiol. (Regulatory Integrative Comp. Physiol. 35) 266: R1127-R1135.
Negoescu R., Skinner J.E., Wolf S. (1993) Forebrain regulation of cardiac function: Spectral and dimensional analysis of RR and QT intervals.Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 28: 331–342.
Poincaré J.H.(1892).Les Methodes Nouvelles de la Mechanique Celeste, Vols 1–3. Paris: Gauthier-Villars. English translation (1967) as NASA TTF-450-453, Washington, D.C.
Rapp P.E. (1994). A guide to dynamical analysis.Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 29: 311–327.
Schwaiger, M., Hutchins, G.D., Kolff, V., Rosenspire, K., Haka, M.S., Mallette, S., Deeb, G.M., Abrama, G.D., Wieland, D. (1991). Evidence of regional catecholamine uptake and storage sites in the transplanted human heart by positron emission tomography.J. Clin. Invest. 87: 1681–1690.
Skinner, J.E., Carpeggiani, C., Landisman, C.E., Fulton, K.W. (1991). Correlation dimension of heartbeat intervals is reduced in conscious pigs by myocardial ischemia.Circ. Res. 68: 966–976.
Skinner, J.E., Molnar, M., Vybiral, T., Mitra, M. (1992). Application of chaos theory to biology and medicine.Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 27: 39–53.
Skinner, J.E., Pratt, C.M., Vybiral, T. (1993). A reduction in the correlation dimension of heartbeat intervals procedes imminent ventricular fibrillation in human subjects.Am. Heart J. 125: 731–743.
Skinner, J.E., Molnar, M., Tomberg, C. (1994). The point correlation dimension: Performance with nonstationary surrogate data and noise.Integr. Physiol. Behav. 29: 217–234.
Skinner, J.E.; Kresh, J.Y. (1996) Self-organization in a simple biological system: The intrinsic cardiac nervous system. In:Nonlinear Techniques in Physiological Time Series Analysis, Gottfried Mayer-Kress, Holger Kantz and Jergen Kurthas, (eds.). New York:Springer.
Skinner, J.E.; Zebrowski, J.J.; Kowalik, Z.J. (1996a) New nonlinear algorithms for analysis of heart rate variability: Low-dimensional chaos predicts lethal arrhythmias. In:Nonlinear Techniques in Physiological Time Series Analysis, Gottfried Mayer-Kress, Holger Kantz and Jergen Kurthas, (eds.). New York:Springer.
Skinner, J.E.; Wolf, S.G.; Kresh, J.Y.; Izrailtyn, I. (1996b) Application of chaos theory to a model biological system: The intrinsic cardiac nervous system of the ischemic rabbit heart shows transient increases in dimension followed by persistent reorganizations of the heartbeat subinterval relationship (QT vs RR-QT)Integr. Physiol. Behav. Sci. 31:122–146.
Theiler J., Eubank S., Longtin A., Galdrikian B., Farmer J.D. (1992). Testing for nonlinearity in time series: The method of surrogate data.Physica D 58:77–94.
Wilson, R.F., Christensen, B.V., Olivari, M.T., Simn, A., White, C.W., Laxson, D.D. (1991). Evidence for structural sympathetic reinnervation after orthotopic cardiac transplantation in humans.Circulation 83: 1210–1220.
Wilson, R.F., Laxson, D.D., Christensen, B.V., McGinn, A.L., Kubo, S.H. (1993). Regional differences in sympathetic reinnervation after human orthotopic cardiac transplantation.Circulation 88: 165–171.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meyer, M., Marconi, C., Ferretti, G. et al. Heart rate variability in the human transplanted heart: Nonlinear dynamics and QT vs RR-QT alterations during exercise suggest a return of neurocardiac regulation in long-term recovery. Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 31, 289–305 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02691433
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02691433