Abstract
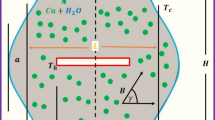
Finite-difference simulations of electrical excitation of conductive contaminant plumes indicated that the approximate dimensions of a plume and the approximate location of its center of mass can be derived, under specified circumstances, from the resulting electrical potential fields. Direct electrical excitation of a contaminant plume by a point current source was simulated for homogenous and isotropic conditions as well as in the presence of conductive clay layers and lenses. When a very shallow water table was assumed, changes in the electrical potential field between baseline (preplume) conditions and conditions that included a developing plume graphically formed a difference dipole. Simulations suggested that electrical flow is channeled preferentially through the negative difference pole at the approximate location of the center of mass in a dispersive contaminant plume. Electrical flow was channeled directly through the negative difference pole at the terminal end of a conductive clay lens. Simulations showed that even in the presence of conductive clays, the approximate location of the center of mass of an evolving contaminant plume could be delineated. This illustrates the potential future value of this approach, assuming continued technological advances in the field. *** DIRECT SUPPORT *** A03BX002 00003
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archie, G.E. 1942. The Electrical Resistivity Log as an Aid in Determining Some Reservoir Characteristics. Am. Inst. Min. Metallurg. Pet. Eng. Tech. Paper 1422, pp.146–154.
Beasley C.W. and S.H. Ward, 1986. Three-dimensional Mise-a-la-masse Modeling Applied to Mapping Fracture Zones. Geophysics, v. 51, no. 1, pp. 98–113.
Bevc, D. and H.F. Morrison, 1989. Borehole-to-surface Electrical Resistivity Monitoring of a Salt Water Injection Experiment. Proceedings of the Society of Exploration Geophysists 59th Annual International Exposition & Meeting, pp. 216–218.
Bevc, D. and H.F. Morrison, 1991. Borehole-to-surface Electrical Resistivity Monitoring of a Salt Water Injection Experiment. GEOPHYSICS, v. 56, no. 6, pp. 769–777.
Bowker, A. 1987. Size Determination of Slab-like Ore Bodies—an Interpretation Scheme for Single Hole Mise-a-la-masse Anomalies. Geoexploration, v. 24, pp. 207–218.
Dey, A. and H.F. Morrison, 1979. Resistivity Modeling for Arbitrarily Shaped Three-dimensional Structures. Geophysics, v. 44, no. 4, pp. 753–780.
Domenico, P.A. and G.A. Robbins, 1985. A New Method of Contaminant Plume Analysis. Ground Water, v. 23, no. 4, pp. 486–485.
Eloranta, E. H. 1985. A Comparison Between Mise-a-la-masse Anomalies Obtained by Pole-pole Electrode Configurations. Geoexploration, v. 23, pp. 471–481.
Eloranta, E.H. 1986. The Behavior of Mise-a-la-masse Anomalies Near a Vertical Contact. Geoexploration, v. 24, pp. 1–14.
Freeze, R.A., and J.A. Cherry, 1979. Groundwater. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 604pp.
Jansen, J.R. and R.W. Tayor. 1995. Using MODFLOW to Model Several Geophysical Methods. Proceedings of the Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems SAGEEP’95, Orlando, FL; EEGS, Englewood CO, pp. 197–222.
Keller, G.V. 1987. Rock and Mineral Properties. Electromagnetic Methods in Applied Geophysics—Theory, Volume 1, Society of exploration Geophysicists, pp. 13–51.
Ketola, M. 1972. Some Points of View Concerning Mise-a-la-masse Measurements. Geoexploration, v. 10, pp. 1–21.
Mansinha, L. and C.J. Mwenifumbo, 1983. A Mise-a-la-masse Study of the Cavendish Geophysical Test Site, Geophysics, v. 48, no. 9, pp. 1252–1257.
McClymont, G.L. and F.W. Schwartz, 1987. Development and Application of an Expert System in Contaminant Hydrogeology—The Expert ROKEY Computer System. Final Report and Users’ Manual, Simco Groundwater Research Ltd., Alberta, Canada, 206 pp.
McDonald, M.G., and A.W. Harbaugh, 1988. A Modular Three-dimensional Finite-difference Ground-water flow Model, Chapter A1, Book 6 Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations of the U.S. Geol. Survey.
Newkirk, D.J. 1982. Downhole Electrode Resistivity Interpretation with Three-dimensional Models: Dept. of Geology and Geophysics, University of Utah Technical Report DOE/ID/12079-47 for the U.S. Dept. of Energy.
Osiensky, J.L. 1995. Time Series Electrical Potential Field Measurements for Early Detection of Ground Water Contamination. J. Environ. Sci. Health, A30(7): 1601–1626.
Osiensky, J.L. and P.R. Donaldson, 1994. A Modified Mise-a-la-masse Method for Contaminant Plume Delineation. Ground Water, v. 32, no. 3, pp.448–457.
Osiensky, J.L. and P.R. Donaldson, 1995. Electrical Flow Through an Aquifer for Contaminant Source Leak Detection and Delineation of Plume Evolution. Journal of Hydrology, v. 169/1–4, pp. 243–263.
Osiensky, J.L. and R.E. Williams, 1996. A Two-dimensional MODFLOW Numerical Approximation of Mise-a-la-masse Electrical Flow Through Porous Media. Ground Water, v. 34, no. 4, pp.727–733.
Osiensky, J.L. 1997. Ground Water Modeling of Mise-a-la-masse Delineation of Contaminated Ground Water Plumes. Journal of Hydrology, 197(1997), pp.146–165.
Parasnis, D.S. 1967. Three-dimensional Electric Mise-a-la-masse Survey of an Irregular Leadzinc-copper Deposit in Central Sweden. Geophys. Prosp., v. 15, no. 3, pp. 407–437.
Parasnis, D.S. 1997. Principles of Applied Geophysics. Chapman & Hall, London, 429 pp.
Parkhomenko, E.I. 1967. Electrical Properties of Rocks, Monographs in Geoscience, Plenum Press, New York, 314 pp.
Schlumberger, C. 1920. Etude Sur la Prospection Electrique du Sous-sol. Gauthier-Villars, Paris, 94 pp.
Wilt, M.J. and C.F. Tsang, 1985. Monitoring of Subsurface Contaminants with Borehole/surface Resistivity Measurements. Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Report LBL-19106, pp 167–177.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osiensky, J.L., Williams, R.E., Ralston, D.R. et al. Simulation of electrical potential differences near a contaminant plume excited by a point source of current. Mine Water and the Environment 18, 29–44 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02687248
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02687248