Abstract
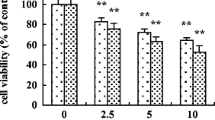
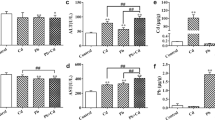
It is well known that cadmium (Cd) has toxic and carcinogenic effects in rodents and humans, but the effects of Cd on apoptosis are still not clear. Although some studies have shown that Cd has apoptotic potential, other studies have shown that Cd can be antiapoptotic. Parameters such as sensitivity of the exposed organism or cells and the exposure conditions should be important in delineating the effect of Cd on apoptosis. In the present study, we aimed to determine the apoptotic index (AI) of Sprague-Dawley rat tissues that are loaded at a lower Cd concentration than the critical concentration (50 μg/g) for its toxic effects. Metallothionein (MT) levels of tissues were also determined and the experiments repeated with copper (Cu)-exposed rats. We detected decreases in the apoptotic index in liver and lung tissues of Cd-exposed groups accompanied with an increase in MT levels. Also, decreases of AI were detected in the liver tissues of Cu-exposed groups. These findings indicate that Cd can suppress apoptosis in vivo. The possible role of MT expression on the suppression of apoptosis and the importance of free-Cd ion concentration on switching antiapoptotic effects to proapoptotic effects are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. L. Goering, M. P. Waalkes, and C. D. Klassen, Toxicology of cadmium, in Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology Toxicology of Metals, Biochemical Effects, R. A. Goyer and M. G. Cherian, eds., Springer-Verlag, New York, vol. 115, pp. 189–214 (1994).
H. M. Perry, G. S. Thind, and E. F. Perry, The biology of cadmium, Med. Clin. North Am. 60(4), 759–769 (1976).
R. A. Goyer and M. G. Cherian, Renal effects of metals, in Metal Toxicology, R. A. Goyer, C. D. Klaassen, and M. P. Waalkes, eds., Academic, San Diego, pp. 389–412 (1995).
International Agency for Research on Cancer, Beryllium, Cadmium, Mercury and Exposures in the Glass Industry, IARC, Lyon, 119–238 (1993).
National Toxicology Program, Tenth Report on Carcinogens, Department of Health and Human Services, Research, Triangle Park, NC, pp. III42-III44 (2000).
B. Pesch, J. Haerting, U. Ranft, A. Klimpel, B. Oelschlagel, and W. Schill, MURC Study Group. Occupational risk factors for renal cell carcinoma: agent-specific results from a case-control study in Germany, Int. J. Epidemiol. 29, 1014–1024 (2000).
M. P. Waalkes and R. R. Misra, Cadmium carcinogenicity and genotoxicity, in Toxicology of Metals, L. Chang, ed., CRC, Boca. Raton, FL, pp. 231–244 (1996).
M. P. Waalkes, Cadmium carcinogenesis, Mutat. Res. 533, 107–120 (2003).
G. G. Schwartz and I. M. Reis, Is cadmium a cause of human pancreatic cancer, Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 9, 139–145 (2000).
World Health Organization, Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 2nd ed. Addendum to Vol. 2, Health Criteria and Other Supporting Information. WHO, Geneva, pp. 31–46 (1998).
K. Schumann, H. G. Classen, H. H. Dieter, et al., Hohenheim consensus workshop: copper, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 56(6), 469–483 (2002).
M. C. Linder and M. Hazegh-Azam, Copper biochemistry and molecular biology, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 63(5), 797S-811S (1996).
B. Desoize, Metals and metal compounds in carcinogenesis, In Vivo 17(6), 529–539 (2003).
T. Theophanides and J. Anastassopoulou, Copper and carcinogenesis, Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 42(1), 57–64 (2002).
D. H. Hamer, Metallothionein, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 55, 913–951 (1986).
D. Curtis, J. L. Klaassen, and C. Supratim, Metallothionein: an intracellular protein to protect against cadmium toxicity, Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 39, 267–294 (1999).
K. Kiningham and E. Kasarskis, Antioxidant function of metallothionein, J. Trace Elements Exp. Med. 11, 219–226 (1998).
L. Cai, M. Satoh, C. Tohyama, and M. G. Cherian, Metallothionein in radiation exposure: its induction and protective role, Toxicology 132(2–3), 85–98 (1999).
R. Shimoda, W. E. Achanzar, W. Qu, et al., Metallothionein is a potential negative regulator of apoptosis, Toxicol. Sci. 73, 294–300 (2003).
W. E. Achanzar, K. B. Achanzar, J. G. Lewis, M. M. Webber, and M. P. Waalkes, Cadmium induces c-myc, p53, and c-jun expression in normal human prostate epithelial cells as a prelude to apoptosis, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 16, 291–300 (2000).
S. S. Habeebu, J. Liu, and C. D. Klaassen, Cadmium-induced apoptosis in mouse liver, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 149(2), 203–209 (1998).
B. A. Hart, C. H. Lee, G. S. Shukla, et al., Characterization of cadmium-induced apoptosis in rat lung epithelial cells: evidence for the participation of oxidant stress, Toxicology 133, 43–58 (1999).
H. Shimada, Y. H. Shiao, M. Shibata, and M. P. Waalkes, Cadmium suppresses apoptosis induced by chromium, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 54, 159–168 (1998).
T. von Zglinicki, C. Edwall, E. Ostlund et al., Very low cadmium concentrations stimulate DNA synthesis and cell growth, J. Cell Sci. 103, 1073–1081 (1992).
C. Yuan, M. Kadiiska, W. E. Achanzar, R. P. Mason, and M. P. Waalkes, Possible role of caspase-3 inhibition in cadmium-induced blockage of apoptosis, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 164(3), 321–329 (2000).
D. Ozcelik, Y. Eralp, G. Oztekin, S. Dursun, and H. Uzunismail, The impact of penicillamine and zinc in hepatic and brain tissues of copper-overloaded rats, Trace Elements Electrolytes 18(1), 34–38 (2001).
D. Ozcelik, R. Ozaras, Z. Gurel, H. Uzun, and S. Aydin, Copper-mediated oxidative stress in rat liver, Biol. Trace Element Res. 96, 209–215 (2003).
L. Cai, S. Iskander, M. G. Cherian, and R. R. Hammond, Zinc- or cadmium-pre-induced metallothionein protects human central nervous system cells and astrocytes from radiation-induced apoptosis, Toxicol. Lett. 146(3), 217–226 (2004).
K. Y. Kwon, J. H. Jang, S. Y. Kwon, C. H. Cho, H. K. Oh, and S. P. Kim, Cadmium induced acute lung injury and TUNEL expression of apoptosis in respiratory cells, J. Korean Med. Sci. 18(5), 655–662 (2003).
R. Shimoda, T. Nagamine, H. Takagi, M. Mori, and M. P. Waalkes, Induction of apoptosis in cells by cadmium: quantitative negative correlation between basal or induced metallothionein concentration and apoptotic rate, Toxicol. Sci. 64(2), 208–215 (2001).
D. X. Deng, S. Chakrabarti, M. P. Waalkes, and M. G. Cherian, Metallothionein and apoptosis in primary human hepatocellular carcinoma and metastatic adenocarcinoma, Histopathology 32, 340–347 (1998).
Y. Kondo, J. M. Rusnak, D. G. Hoyt, C. E. Settineri, B. R. Pitt, and J. S. Lazo, Enhanced apoptosis in metallothionein null cells, Mol. Pharmacol. 52, 195–201 (1997).
A. T. Miles, G. M. Hawksworth, J. H. Beattie, and V. Rodilla, Induction, regulation, degradation, and biological significance of mammalian metallothioneins, Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 35(1), 35–70 (2000).
M. Hamatake, K. Iguchi, K. Hirano, and R. Ishida, Zinc induces mixed types of cell death, necrosis, and apoptosis in molt-4 cells, J. Biochem. 128, 933–939 (2000).
M. Ishido, S. Homma-Takeda, C. Tohyama, and T. Suzuki, Apoptosis in rat renal proximal tubular cells induced by cadmium, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 55, 1–12 (1998).
M. Ishido, C. Tohyama, and T. Suzuki, Cadmium-bound metallothionein induces apoptosis in rat kidneys, but not in cultured kidney LLC-PK1 cells, Life Sci. 64, 797–804 (1999).
C. Erfurt, E. Roussa, and F. Thevenod, Apoptosis by Cd2+ or CdMT in proximal tubule cells: different uptake routes and permissive role of endo/lysosomal CdMT uptake, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 285(6), C1367-C1376 (2003).
J. Liu, S. S. Habeebu, Y. Liu, and C. D. Klaassen, Acute CdMT injection is not a good model to study chronic Cd nephropathy: comparison of chronic CdCl2 and CdMT exposure with acute CdMT injection in rats, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 153, 48–58 (1998).
T. Kjellström, C. G. Elinder, and L. Friberg, Conceptual problems in establishing the critical concentration of cadmium in human kidney cortex, Environ. Res. 33, 284–295 (1984).
World Health Organization, Cadmium, in Safety Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants, 55th Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), WHO Food Additives Series No. 46, WHO, Geneva, pp. 247–305 (2001).
A. Tanimoto, T. Hamada, and O. Koide, Cell death and regeneration of renal proximal tubular cells in rats with subchronic cadmium intoxication, Toxicol. Pathol. 21(4), 341–352 (1993).
A. Tanimoto, T. Hamada, K. Higashi, and Y. Sasagur, Distribution of cadmium and metallothionein in CdCl2-exposed rat kidney: relationship with apoptosis and regeneration, Pathol. Int. 49, 125–132 (1999).
M. P. Waalkes, Cadmium carcinogenesis in review, J. Inorg. Biochem. 79, 241–244 (2000).
C. Davis and S. Newman, Inadequate dietary copper increases the spontaneous tumorigenesis in the Min mouse, Cancer Lett. 159, 57–62 (2001).
P. Senesse, S. Meance, V. Cottet, J. Faivre, and M. C. Boutron-Ruault, High dietary iron and copper and risk of colorectal cancer: a case-control study in burgundy, Nutr. Cancer 49(1), 66–71 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gurel, Z., Ozcelik, D. & Dursun, S. Apoptotic rate and metallothionein levels in the tissues of cadmium-and copper-exposed rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 116, 203–217 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02685931
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02685931