Abstract
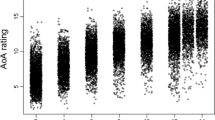
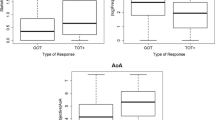
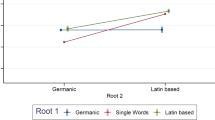
This paper reviews research concerned with word age-of-acquisition (AOA) effects in adult word recognition and production. Methodological issues, including the use of multiple regression techniques, are considered first. The pattern of substantive results is presented and is interpreted as indicating that AOA effects are most marked in word production as against word recognition. Possible theoretical interpretations are discussed and future research possibilities are outlined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battig, W.F. & Montague, W.E. (1969). Category norms for verbal items in 56 categories: a replication and extension of the Connecticut category norms. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 80, 3.
Butler, B. & Hains, S. (1979). Individual differences in word recognition latency. Memory and Cognition, 7, 68–76.
Butterfield, G.B. & Butterfield, E.C. (1977). Lexical codability and age. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 16, 113–118.
Carroll, J.B. & White, M.N. (1973a). Word frequency and age of acquisition as determiners of picture-naming latency. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 25, 85–95.
Carroll, J.B. & White, M.N. (1973b). Age-of-acquisition norms for 220 picturable nouns. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 12, 563–576.
Clark, H.H. (1973). The language-as-fixed-effect fallacy: a critique of language statistics in psychological research. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 12, 335–359.
Cohen, J. & Cohen, P. (1975). Applied Multiple Regression Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Coltheart, M. (1978). Lexical access in simple reading tasks. In G. Underwood (ed.), Strategies of Information Processing, pp.151–216. London: Academic Press.
Cronbach, L.J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika, 16, 297–334.
Dale, E. (1948). Dale list of 3000 familiar words. Educational Research Bulletin, 27, 45–54.
Darlington, R.B. (1968). Multiple regression in psychological research and practice. Psychological Bulletin, 69, 161–182.
Duncan, C.P. (1966). Effect of word frequency on thinking of a word. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 5, 434–440.
Ebel, R.L. (1951). Estimation of the reliability of ratings. Psychometrika, 16, 407–424.
Ellis, H.D. & Young, A.W. (1977). Age-of-acquisition and recognition of nouns presented in the left and right visual fields: a failed hypothesis. Neuropsychologia, 15, 825–828.
Freedman, J.L. & Loftus, E.F. (1971). Retrieval of words from long term memory. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 10, 107–115.
Gilhooly, K.J. (1978). Bigram statistics for 205 five-letter words having single solution anagrams. Behavior Research Methods and Instrumentation, 10, 389–392.
Gilhooly, K.J. & Gilhooly, M.L. (1979). Age-of-acquisition effects in lexical and episodic memory tasks. Memory and Cognition, 7, 214–223.
Gilhooly, K.J. & Gilhooly, M.L.M. (1980). The validity of age-of-acquisition ratings. British Journal of Psychology, 71, 105–110.
Gilhooly, K.J. & Hay, D. (1977). Imagery, concreteness, age-of-acquisition, familiarity and meaningfulness values for 205 five-letter words having single solution anagrams. Behavior Research Methods and Instrumentation, 9, 12–17.
Gilhooly, K.J. & Johnson, C.E. (1978). Effects of solution word attributes on anagram difficulty: a regression analysis. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 30, 57–70.
Gilhooly, K.J. & Logie, R.H. (1980a). Age-of-acquisition, imagery, concreteness, familiarity and ambiguity measures for 1944 words. Behavior Research Methods and Instrumentation, 12, 395–427.
Gilhooly, K.J. & Logie, R.H. (1980b). Meaning-dependent ratings of imagery, age-of-acquisition, familiarity and concreteness for 387 ambiguous words. Behavior Research Methods and Instrumentation, 12, 428–450.
Gilhooly, K.J. & Logie, R.H. (1981a). Word age-of-acquisition and visual recognition thresholds. Current Psychological Research, 1, 215–226.
Gilhooly, K.J. & Logie, R.H. (1981b). Word age-of-acquisition, reading latencies and auditory recognition. Current Psychological Research, 1, 251–262.
Gilhooly, K.J. & Logie, R.H. (1982). Word age-of-acquisition and lexical decision making. Acta Psychologica, 50, in press.
Kucera, H. & Francis, W. (1967). Computational Analysis of Present Day American English. Providence, RI: Brown University Press.
Lachman, R. (1973). Uncertainty effects on time to access the internal lexicon. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 99, 199–208.
Lachman, R. & Lachman, J.L. (1980). Picture naming: retrieval and activation of long term memory. In L. W. Poon, J. L. Fozard, L. S. Cermak, D. Arenberg & L. W. Thompson (eds.), New Directions in Memory and Ageing: Proceedings of the George Talland Memorial Conference. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Lachman, R., Shaffer, J.P. & Hennrikus, D. (1974). Language and cognition: effects of stimulus codability, name-word frequency, and age-of-acquisition on lexical reaction time. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 13, 613–625.
Lachman, R., Lachman, J.L., Thronesberg, C. & Sala, L. (1980). Object salience and code separation in picture naming. Bulletin of the Psychonomic Society, 16, 187–190.
Landauer, T.K. (1975). Memory without organization: properties of a model with random storage and undirected retrieval. Cognitive Psychology, 7, 495–531.
Lewis-Beck, M.S. (1980). Applied Regression: an Introduction. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage Publications.
Loftus, E.F. & Suppes, P. (1972). Structural variables that determine the speed of retrieving words from long-term memory. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 11, 770–777.
Loftus, E.F., Freedman, J.L. & Loftus, G.R. (1970). Retrieval of words from subordinate and superordinate categories in semantic hierarchies. Psychonomic Science, 21, 235–236.
Lyons, A.W., Teer, P. & Rubenstein, H. (1978). Age-at-acquisition and word recognition. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 7, 179–187.
Mendelsohn, G.A. (1976). An hypothesis approach to the solution of anagrams. Memory and Cognition, 4, 637–642.
Morris, P.E. (1981). Age-of-acquisition, imagery, recall and the limitations of multiple regression analysis. Memory and Cognition, 9, 277–282.
Morton, J. (1969). Interaction of information in word recognition. Psychological Review, 76, 165–178.
Morton, J. & Patterson, K. (1980). A new attempt at an interpretation, or, an attempt at a new interpretation. In M. Coltheart, K. Patterson and J.C. Marshall (eds.), Deep Dyslexia, pp. 91–118. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
Murray, D.J. (1975). Graphemically cued retrieval of words from long-term memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Learning and Memory, 104, 65–70.
Noble, C.E. (1952). An analysis of meaning. Psychological Review, 59, 421–430.
Oldfield, R.C. (1966). Things, words and the brain. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 18, 340–353.
Oldfield, R.C. & Wingfield, A. (1964). The time it takes to name an object. Nature, 202, 1031–1032.
Oldfield, R.C. & Wingfield, A. (1965). Response latencies in naming objects. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 17, 273–281.
Paivio, A. (1971). Imagery and Verbal Processes. New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Paivio, A. (1976). Imagery in recall and recognition. In J. Brown (ed.), Recall and Recognition. London: J. Wiley.
Penfield, W. (1955). The permanent record of the stream of conciousness. Proceedings of the 14th International Congress of Psychology, June, 1954, pp. 47–69. Amsterdam: North Holland.
Raven, J.C. (1954). Guide to Using the Mill Hill Vocabulary Scale with Progressive Matrices (1938). London: H. K. Lewis.
Raven, J.C. (1961). Guide to Using the Crichton Vocabulary Scale with Progressive Matrices (1947) Sets A, Ab, B. London: H. K. Lewis.
Rinsland, H.D. (1945). A Basic Vocabulary of Elementary School Children. New York: Macmillan.
Rochford, G. & Williams, M. (1962). Studies in the development and breakdown of the use of names. Parts I and II. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 25, 222–233.
Rubin, D.C. (1980). 51 properties of 125 words: a unit analysis of verbal behavior. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 19, 736–755.
Seymour, P.H.K. (1979). Human Visual Cognition. London: Collier Macmillan.
Stratton, R.P., Jacobus, A.J. & Brinley, B. (1975). Age-of-acquisition, imagery, familiarity and meaningfulness norms for 543 words. Behavior Research Methods and Instrumentation, 7, 1–6.
Thorndike, E.L. & Lorge, I. (1944). The Teacher’s Word Book of 30,000 Words. New York: Teacher’s College Press.
Tryk, H.E. (1968). Subjective scaling of word frequency. American Journal of Psychology, 81, 170–177.
Underwood, B.J. & Schulz, R.W. (1960). Meaningfulness and Verbal Learning. Chicago: Lippincott.
Whaley, C.P. (1978). Word-nonword classification time. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 17, 143–154.
Wingfield, A. (1968). Effects of frequency on identification and naming of objects. American Journal of Psychology, 81, 226–234.
Winnick, W.A. & Daniel, S.A. (1970). Two kinds of response priming in tachistoscopic recognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 84, 74–81.
Young, A.W. & Bion, P.J. (1980). Hemifield differences for naming bilaterally presented nouns varying on age-of-acquisition. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 50, 366.
Young, A.W. & Ellis, H.D. (1980). Ear asymmetry for the perception of monaurally presented words accompanied by binaural white noise. Neuropsychologia, 18, 107–110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilhooly, K.J., Watson, F.L. Word age-of-acquisition effects: a review. Current Psychological Reviews 1, 269–286 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02684489
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02684489