Abstract
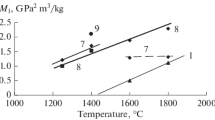
The phase composition of hollow fused corundum microspheres is investigated. The problem of the presence of extraneous phases and their removal is discussed. The effect of heat treatment on the phase composition of the microspheres is studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu. L. Krasulin,Porous Structural Ceramics [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1980).
L. M. Aksel’rod, Z. E. Goryacheva, N. A. Chuprina, et al., “Heat-insulating ceramics based on aluminosilicate microspheres.”Ogeneup. Tekh. Keram., No. 10, 5–9 (1996).
E. I. Apraksina and A. S. Vlasov, “Porous base for corundum microsphere membranes,” in:Proceedings of the All-Russia Conf. “Science and Technology of Silicate Materials under Contemporary Market-Economy Conditions” [in Russian], Moscow (1995), p. 95.
G. D. Semchenko, “Ultralight-weight corundum ceramics using sol-gel composites,”Steklo Keram., No. 11, 15–18 (1997).
Plasma Processes in the Metallurgy and Technology of Inorganic Materials [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1973).
A. N. Krasnov, V. G. Zil’berberg, and S. Yu. Sharivker,Low-Temperature Plasma in Metallurgy [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Steklo i Keramika, No. 4, pp. 22–23, April, 2000.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vlasov, A.S., Postnikov, S.A. Phase composition of microspheres for production of heat-insulating corundum ceramics. Glass Ceram 57, 130–131 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02681527
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02681527