Abstract
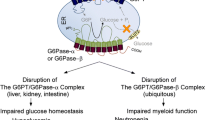
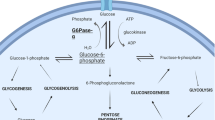
Glycogen storage disease type 1a (GSD-1a), characterized by growth retardation, hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, kidney enlargement, hyperlipidemia, hyperuricemia, and renal dysfunction, is caused by deficiencies in glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase), a key enzyme in glucose homeostasis. Over the last 20 years, dietary therapies have greatly improved the prognosis of GSD-1a patients. However, the underlying pathological process remains uncorrected and the efficacy of dietary treatment is frequently limited by poor compliance. Therefore, long-term complications till develop in adult patients. To develop future therapeutic approaches for GSD-1a, we have generatedG6Pase-deficient (G6Pase-/-) mice that mimic the pathophysiology of human GSD-1a patients. To evaluate the feasibility of gene replacement therapy for this disorder, we have infused recombinant adenovirus containing murineG6Pase gene (Ad-mG6Pase) into G6Pase-/- mice. While only 15% of G6Pase-/- mice under glucose therapy survived weaning, a 100% survival rate was achieved when G6Pase-/- mice were infused with Ad-mG6Pase and 90% of which lived to 3 months of age. Hepatic G6Pase activity in Ad-mG6Pase-infused mice was restored to 19% of that in G6Pase+/+ mice at 7 through 14 post-infusion days. Ad-mG6Pase infusion also greatly improved growth of G6Pase-/- mice and normalized plasma glucose, cholesterol, triglyceride, and uric acid profiles. Further, liver and kidney enlargement were less pronounced with near normal levels of glycogen depositions in both organs.Conclusion: our data demonstrate that a single administration of a recombinant adenovirus vector can alleviate the clinical manifestations of glycogen storage disease type 1a in mice, suggesting that this disorder in humans can potentially be corrected by gene therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ad-mG6Pase :
-
recombinant adenovirus containing murineG6Pase gene
- ER :
-
endoplasmic reticulum
- G6P :
-
glucose-6-phosphate
- G6 Pase :
-
glucose-6-phosphatase
- GSD-1a :
-
glycogen storage disease type 1a
References
Arden SD, Zahn T, Steegers S, Webb S, Bergman B, O'Brien, RM, Hutton JC (1999) Molecular cloning of a pancreatic isletspecific glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit-related protein. Diabetes 48: 531–542
Arion WJ, Lange AJ, Walls HE, Ballas LM (1980) Evidence of the participation of independent translocases for phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate in the microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system. J Biol Chem. 255: 10396–10406
Chen Y-T, Burchell A (1995) Glycogen storage diseases. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds). The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 935–965
Chou JY (2001) Molecular basic of type 1 glycogen storage disease. Curr Mol Med 1: 25–44
Chou JY, Mansfield BC (1999) Molecular genetics of type 1 glycogen storage diseases. Trend Endocrinol Metab 10: 104–113
Hemrika W, Renirie R, Dekker HL, Barnett P, Wever R (1997) From phosphatases to vanadium peroxidases: a similar architecture of the active site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94: 2145–2149
Kirschner BS, Baker AL, Thorp FK (1991) Growth in adulthood after liver transplantation for glycogen storage disease type I. Gastroenterology 101: 238–241.
Kozarsky KF, Wilson JM (1993) Gene therapy; adenovirus vectors. Curr Opin Genet Dev 3: 499–503
Lei K-J, Shelly LL, Pan C-J, Sidbury JB, Chou JY (1993) Mutations in the glucose-6-phosphatase gene that cause glycogen storage disease type 1a. Science 262: 580–583
Lei K-J, Shelly LL, Pan C-J, Liu J-L, Chou JY (1995) Structure-function analysis of human glucose-6-phosphatase, the enzyme deficient in glycogen storage disease type 1a. J Biol Chem 270: 11882–11886.
Lei K-J, Chen H, Pan C-J, Ward JM, Mosinger B, Lee EJ, Westphal H, Manfsfield BC, Chou JY (1996) Glucose-6-phosphatase dependent substrate transport in the glycogen storage disease type 1a mouse. Nat Genet 13: 203–209
Mittereder N, Yei S, Bachurski C, Cuppoletti J, Whttsett JA, Tolstochev P, Trapnell BC (1994) Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of in vitro, adenovirus-mediated transfer of the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator cDNA. Hum Gene Ther 5: 719–731
Nordlie RC, Sukalski KA (1985) Multifunctional, glucose-6-phosphatase: a critical review. In: Martosoni AN (ed) The enzymes of biological membranes, 2nd edn. Plenum, New York, pp 349–398
Pan C-J, Lei K-J, Chou JY (1998) Asparagine-linked oligosaccharides are localized to a luminal hydrophilic loop in human glucose-6-phosphatase. J Biol Chem 273: 21658–21662
Pan C-J, Lei K-J, Annabi B, Hemrika W, Chou JY (1998). Transmembrane topology of glucose-6-phosphatase. J Biol Chem 273: 6144–6148
Pan C-J, Lei K-J, Chen H, Ward JM, Chou JY (1998) Ontogeny of the murine glucose-6-phosphatase system. Arch Biochem Biophys 358: 17–24.
Selby R, Starzl TE, Yunis E, Todo S, Tzakis AG, Brown BI, Kendall RS (1993) Liver transplantation for type I and type IV glycogen storage disease. Eur J Pediatr 152[Suppl 1]: S71-S76
Shelly LL, Lei K-J, Pan C-J, Sakata SF, Ruppert S, Schutz G, Chou JY (1993) Isolation of the gene for murine glucose-6-phosphatase, the enzyme deficient in glycogen storage disease type 1a. J Biol Chem 268: 21482–21485
Stratford-Perricaudet LD, Perricaudet M (1991) Gene therapy: the advent of adenovirus. In: Wolff JA (ed) Gene therapeutics: methods and applications of direct gene transfer. Birkhauser, Boston, pp 345–362
Trapnell BC (1993) Adenoviral vectors for gene transfer. Adv Drug Delivery Rev 12: 185–199
Yang Y, Nunes FA, Berencsi K, Gonzol E, Engelhardt JF, Wilson JM (1994) Inactivation of E2a in recombinant adenoviruses improves the prospect for gene therapy in cystic fibrosis. Nat Genet 7: 362–369.
Zingone A, Hiraiwa H, Pan C-J, Lin B, Ward JM, Chou JY (2000) Correction of glycogen storage disease type 1a in a mouse model by gene therapy. J Biol Chem 275: 828–832
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published online: 19 July 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chou, J.Y., Zingone, A. & Pan, CJ. Adenovirus-mediated gene therapy in a mouse model of glycogen storage disease type 1a. Eur J Pediatr 161, S56–S61 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02679996
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02679996