Abstract
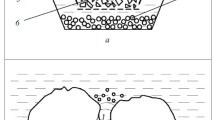
A description is presented of a manufacturing process for large-diameter (180–300 mm) disks of sintered titanium, corrosion-resistant steel, and bronze. The properties of the initial powders and sintered disks are presented, and the dimensions of the bubbles which are formed are examined in relation to the parameters of the pore structure. Photographs of the microstructure of a disk are shown along with a scan of the disk surface. A description is given of porous disperser PA-2, which is designed for dispersing ozone and air in water. Its porous disk is made from titanium powder, while its housing and nozzle are made of corrosion-resistant steel. It is shown that replacing 1000 ceramic tube dispersers made by the German firm “Schumacher” by 2000 PA-2 dispersers in the city of Minsk's treatment system for drinking water, which has a daily capacity of 200000 m 3, made it possible to reduce the amount of ozone and gas that has to be injected for the treatment while keeping the purification level constant. None of the PA-2 dispersers had to be replaced over a 10-year period of operation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. C. Singer, “Assessing ozonation research needs in water treatment,”Amer. Water Works Assoc. J.,82, No. 10, 78–88 (1990).
J. Hoigne and H. Bader, “Ozonation of water: selectivity and rate of oxidation of solutes,”Ozone Sci. and Eng.,1, No. 1, 73–82 (1979).
I. L. Rakevich, “Aerators and aeration systems,”Voda, No. 7, 4–7 (1977).
Prospectus of the Company “Didier fir Tertechnick” (Germany) (1991).
S. A. Bedenko, A. E. Galkin, L. P. Pilinevich, V. V. Savich, et al., “Author's Certificate No. 1632951 USSR. Unit for the Ozonation of Drinking Water,”Otkrytiya. Izobret., No. 9 (1991).
R. G. Rice and A. E. Netzer (eds.),Handbook of Ozone Technology and Applications, Vols. 1 and 2, Ann Arbor Sci. Publ., Michigan (1982).
W. H. Glaze, “Evaluation of ozonation by-product from two California surface waters,”Amer. Water Works Assoc. J. 81, No. 6, 66–73 (1989).
R. P. Todorov and V. P. Georgiev, “Comparative studies of porous permeable materials for aerating partitions,”Tr. Inst. Metallokeramiki (Sofia), No. 3, 115–127 (1986).
G. S. Popkovich and B. N. Repin, “Engineering modeling of the bubble dissolution of oxygen in a liquid,”Zhurn. Prikl. Khim.,56, No. 8, 1803–1808 (1983).
P. A. Vityaz', V. M. Kaptsevich, and V. K. Sheleg,Porous Powder Materials and Products Made of Them [in Russian], Vysheish. Shk., Minsk (1987).
S. S. Saltykov,Stoichiometric Metallography [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1976).
A. K. Zhernoklev, L. P. Pilinevich, and V. V. Savich, “Experience with the use of fine-bubble aerators in a drinking-water ozonation system,”Vodosnabzh. Sanit. Tekh., No. 8, 14–16 (1994).
V. M. Kaptsevich, V. K. Sheleg, L. P. Pilinevich, et al., “Method of monitoring the local permeability of porous powder materials with the use of a hot-wire anemometer,”Poroshk. Metall., No. 7, 60–63 (1987).
L. P. Pilinevich, M. P. Anashchenko, S. A. Bedenko, et al., “Study of the hydrodynamic properties of porous aerators for the ozonation of drinking water and optimization of their pore structure,”Materialy, Tekhnologi, Instrument, No. 3, 32–33 (1996).
Additional information
Scientific Research Institute of Powder Metallurgy (with pilot plant), Minsk (Republic of Belarus'). Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Nos. 5–6(407), pp. 117–125, May–June, 1999.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anashchenko, M.P., Bedenko, S.A., Pilinevich, L.P. et al. Porous powder dispersers for dispersing ozone and air in water. Powder Metall Met Ceram 38, 314–321 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02675783
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02675783