Abstract
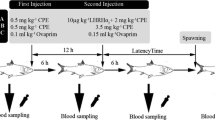
The role of calcitonin (CT) in plasma calcium regulation was studied by the administration of exogenous CT and anti-salmon(s) CT antibody using goldfish,Carasius auratus, loaded or otherwise with calcium. CT elicited a decrease in plasma calcium concentrations at a dose of 10 ng/g body weight 1 h after administration. However, no effects were observed following doses of 30 ng and 50 ng/g 1 h, nor for the three doses 3 h after administration. In calcium-loaded fish, the effect of CT was different depending on the dosage of CT. Ten ng and 50 ng/g induced a decrease and an increase in plasma calcium concentrations, respectively, 3 h after administration. Anti-sCT antibody (0.02 μg or 0.1 μg/g) did not affect plasma calcium concentrations. In calcium-loaded fish, neither dose of anti-sCT antibody changed plasma calcium concentrations 1 h after administration. However, following a dose of 0.1 μg/g, plasma calcium concentrations decreased after 3 h. A positive correlation between plasma calcium concentrations and the gonad somatic index (GSI) in females was no longer apparent after administration of anti-sCT antibody. There was no relationship between plasma calcium concentrations and GSI in control and anti-sCT antibody-treated males. These results suggested that CT regulates plasma calcium concentrations in different ways depending on the dosage with CT having a role in calcium physiology during vitellogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Björnsson, B. Th. 1985. Plasma calcium and calcitonin in the marine teleost,Gadus morhua. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 81A: 593–596.
Ojörnsson, B. Th., C. Haux, H. A. Bern and L. J. Deftos. 1989. 17β-estradiol increases plasma calcitonin levels in salmonid fish. Endocrinology, 125: 1754–1760.
Chakrabarti, P. and D. Mukherjee. 1993. Studies on the hypocalcemic actions of salmon calcitonin and ultimobranchial gland extracts in the freshwater teleostCyprinus carpio. Gen Comp. Endocrinol., 90: 267–273.
Dacke, C. G. 1979. Calcium regulation in sub-mammalian vertebrates. Acad. Press, London. XV+222 pp.
Fenwick, J. C., G. Flik and P. M. Verbost. 1995. A passive immunization technique against the teleost hypocalcemic hormone stanniocalcin provides evidence for the cholinergic control of stanniocalcin release and the conserved nature of the molecule. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 98: 202–210.
Flik, G., S. E. Wendelaar Bonga and J. C. Fenwick. 1984. Ca2+-dependent phosphatase and Ca2+-dependent AT-Pase activities in plasma membranes of eel gill epithelium-III. Stimulation of branchial high-affinity Ca2+-ATPase activity during prolactin-induced hypercalcemia in American eels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 79B: 521–524.
Flik, G., J. C. Fenwick and S. E. Wendelaar Bonga. 1989. Calcitropic actions of prolactin in freshwater North American eel (Anguilla rostrata LeSueur). Am. J. Physiol., 257: R74-R79.
Fouchereau-Peron, M., Y. Arlot-Bonnemains, M. S. Moukhtar and G. Milhaud. 1987. Calcitonin induces hypercalcemia in Grey mullet and immature freshwater and sea-water adapted rainbow trout. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 87A: 1051–1053.
Fouchereau-Peron, M., Y. Arlot-Bonnemains, L. Maubras, G. Milhaud and M. S. Moukhtar. 1990. Calcitonin variations in male and female trout,Salmo gairdneri, during the annual cycle. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 78: 159–163.
Hasan, N., A. K. Pandey and K. Swarup. 1993. Response of serum calcium and inorganic phosphate levels ofBufo andersoni to salmon calcitonin administration. J. Adv. Zool., 14: 70–75.
Houssami, S., D. M. Findlay, C. L. Brady, D. E. Myers, T. J. Martin and P. M. Sexton. 1994. Isoforms of the rat calcitonin receptor: Consequences for ligand binding and signal transduction. Endocrinology, 135: 183–190.
Kline, L. W. 1981. A hypocalcemic response to synthetic salmon calcitonin in the green iguana,Iguana iguana. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 44: 476–479.
Laemmli, U. K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227: 680–685.
Lafeber, F. P. J. G., G. Flik, S. E. Wendelaar Bonga and S. F. Perry. 1988. Hypocalcin from Stannius corpuscles inhibits gill calcium uptake in trout. Am. J. Physiol., 254: R891-R896.
Lopez, E., J. Peignoux-Deville, F. Lallier, E. Martelly and C. Milet. 1976. Effects of calcitonin and ultimobranchialectomy (UBX) on calcium and bone metabolism in the eel,Anguilla anguilla L. Calcif. Tiss. Res., 20: 173–186.
Norberg, B., B. Th. Björnsson, C. L. Brown, U.-P. Wichardt, L. J. Deftos and C. Haux. 1989. Changes in plasma vitellogenin, sex steroids, calcitonin, and thyroid hormones related to sexual maturation in female brown trout (Salmo trutta). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 75: 316–326.
Oguri, M. 1973. Seasonal histologic changes in the ultimo-branchial gland of goldfish. Bull. Japan. Soc. Sci. Fish., 39: 851–858.
Oughterson, S. M., R. Munoz-Chapuli, V. De Andres, R. Lawson, S. Heath and D. H. Davies. 1995. The effects of calcitonin on serum calcium levels in immature brown trout,Salmo trutta. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 97: 42–48.
Pang, P. K. T. 1971. Calcitonin and ultimobranchial glands in fishes. J. Exp. Zool., 178: 89–99.
Perry, S. F., D. Seguin, F. P. J. G. Lafeber, S. E. Wendelaar Bonga and J. C. Fenwick. 1989. Depression of whole-body calcium uptake during acute hypercalcemia in American eel,Anguilla rostrata, is mediated exclusively by corpuscles of Stannius. J. Exp. Biol., 147: 249–261.
Roos, B. A., M. Yoon, S. V. Cutshaw and D. N. Kalu. 1980. Calcium regulatory action of endogenous rat calcitonin demonstrated by passive immunization with calcitonin antibodies. Endocrinology, 107: 1320–1326.
Saito, K. 1954. Biochemical studies on the fish-blood—III. On the specific gravity and chemical components of blood and plasma. Bull. Japan. Soc. Sci. Fish., 20: 196–201.
Sasayama, Y., I. Abe, N. Suzuki and T. Hayakawa. 1996. Plasma calcium and calcitonin levels at food intake in eels and goldfish. Zool. Sci., 13: 731–735.
Wagner, G. F., R. C. Fargher, C. Milliken, B. A. McKeown and D. H. Copp. 1993. The gill calcium transport cycle in rainbow trout is correlated with plasma levels of bioactive, not immunoreactive, stanniocalcin. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 93: 185–191.
Wales, N. A. M. and A. L. Barrett: 1983. Depression of sodium, chloride and calcium ions in the plasma of goldfish (Carassius auratus) and immature freshwater-and seawater-adapted eels (Anguilla anguilla L.) after acute administration of salmon calcitonin. J. Endocrinol., 98: 257–261.
Wendelaar Bonga, S. E. 1980. Effect of synthetic salmon calcitonin and low ambient calcium on plasma calcium, ultimobranchial cells, Stannius bodies, and prolactin cells in the teleostGasterosteus aculeatus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 40: 99–108.
Wendelaar Bonga, S. E. and P. I. Lammers. 1982. Effects of calcitonin on ultrastructure and mineral content of bone and scales of the cichlid teleostSarotherodon mossambicus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 48: 60–70.
Yamane, S. and J. Yamada. 1977. Histological changes of the ultimobranchial gland through the life history of the masu salmon. Bull. Japan. Soc. Sci. Fish., 43: 375–386.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Shinozaki, F., Mugiya, Y. Effects of salmon calcitonin and anti-salmon calcitonin antibody on plasma calcium concentrations in the goldfish,Carassius auratus . Ichthyological Research 46, 1–6 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02674942
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02674942