Abstract
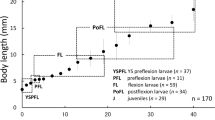
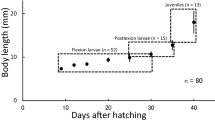
The developmental processes of larval and juvenile ayu.Plecoglossus altivelis, in the estuarine and freshwater sections of the Shimanto River were compared among cohorts hatched in November, December and January. Formation of fins and ossification of the centra, which were completed by about 35 mm BL, hardly differed among the three cohorts. In specimens over 35 mm BL, body depth and head length were smaller in the November cohort than in the other cohorts, with pigmentation in the earlierhatched cohort being completed at a grater BL. The November cohort also remained at the “whitebait” stage until reaching a larger size (about 45 mm BL), before transforming to juveniles and commencing upstream migration. In contrast, the January cohort transformed to juveniles and started upstream migration at a smaller size (under 40 mm BL). The difference in transformation size among the cohorts is probably caused by ambient water temperatures existing at the beginning of upstream migration of each.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Azuma, M. 1964. The life history of the landlocked ayufish (Plecoglossus altivelis) in Lake Biwa, with special references to their developmental stages. Physiol. Ecol., 12: 55–71. (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Fukuhara, O. and T. Fushimi. 1986. Development and early life history of the ayu reared in the laboratory. Bull. Japan. Soc. Sci. Fish., 52: 75–80.
Kawamura, K. and K. Hosoya. 1991. A modified double staining technique for making a transparent fish-skeletal specimen. Bull. Natl. Res. Inst. Aquaculture, 20: 11–18. (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Kinoshita, I. 1993. Ecological study on larvae and juveniles of sparine fishes occurring in surf zone of sandy beaches. Bull. Mar. Sci. Fish., Kochi Univ., 13: 21–99. (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Komaki, H. 1996. Temperature effects on larval growth and development of red seabream,Pagrus major under laboratory conditions. Suisanzoshoku, 44: 105–112, (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Kusuda, R. 1963. An ecological study of the anadromous “ayu”,Plecoglossus altivelis T. et S.—II. Seasonal variations in the composition of the anadromous ayu schools in the River Okumo, Kyoto, Bull. Japan. Soc. Sci. Fish., 29: 822–827. (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Moser, H. G. 1996. Principles and terminology. Pages 27–44in H. G. Moser, ed. The early stages of fishes in the California Current region. CalCOFI Atlas, 33. Allen Press, Kansas.
Noichi, T., T. Noichi and T. Senta. 1997. Comparison of ages, morphology and osteology by birth months of larval Japanese flounder settling at Yanagihama beach, Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan. Fisheries Sci., 63: 169–174.
Otake, T. and K. Uchida. 1998. Application of otolith microchemistry for distinguishing between amphidromous and non-amphidromous stocked ayu,Plecoglossus altivelis. Fisheries Sci., 64: 517–521.
Saruwatari, T. 1995. Temporal utilization of a brackish water lake, Lake Hinuma, as a nursery ground by amphidromous ayu,Plecoglossus altivelis (Plecoglossidae) larvae. Environ. Biol. Fishes, 43: 371–380.
Seikai, T., J. B. Tanangonan and M. Tanaka. 1986. Temperature influence on larval growth and metamorphosis of the Japanese flounderParalichthys olivaceus in the laboratory. Bull. Japan. Soc. Sci. Fish. 52: 977–982.
Senta, T. and I. Kinoshita. 1985. Larval and juvenile fishes occurring in surf zones of western Japan. Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc., 114: 609–618.
Shiraishi, Y. and N., Suzuki. 1962. The spawning activity of ayu-fish,Plecoglossus altivelis. Bull. Fres-water. Fish. Res. Lab., 12: 83–107. (In Japanese with English synopsis.)
Tachihara, K. and S. Kimura. 1991. Embryonic development and morphological changes with growth of the larval and juvenile ayuPlecoglossus altivelis altivelis of Lake Ikeda in Southern Kyushu. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 57: 789–795. (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Takahashi, I. 1997. Early life history of ayu, and maintenance of natural stock. Rep. Yahagi River Inst., 1: 221–235. (In Japanese with English summary.)
Takahashi, I. 1999. Larval and juvenile ayu inhabiting the Shimanto Estuary, Ryuikiken Gakkaishi, preview ver.: 66–72. (In Japanese.)
Takahashi, I., K. Azuma, H. Hiraga and S. Fujita. 1999. Different mortality in larval stage of ayuPlecoglossus altivelis by birth dates in the Shimanto Estuary and adjacent coastal waters. Fisheries Sci., 65: 206–210.
Takahashi, I., I. Kinoshita, K. Azuma, S. Fijta and M. Tanaka. 1990. Larval ayuPlecoglossus altivelis occurring in the Shimanto Estuary. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 56: 871–878. (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Takashima, F. 1976. Anomalies in hatchery reared ayu,Plecoglossus altivelis. II. Malformation of the skeleton in the larva. J. Tokyo Univ. Fish., 62: 99–112. (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Tanangonan, J. B., M. Tagawa, M. Tanaka and T. Hirono. 1989. Changes in tissue thyroxine level of metamorphosing Japanese flounderParalichthys olivaceus reared at different temperatures. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 55: 485–490.
Tsukamoto, K. 1988. Migratory mechanisms and behavioral characteristics in ayu. Pages 100–133in T. Uyeno and M. Okiyama eds. Ichthyology currents 1988. Asakura Shoten, Tokyo. (In Japanese.)
Tsukamoto, K. and T. Kajihara. 1987. Age determination of ayu with otolith. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 53: 1985–1997.
Tsukamoto, K., K. Mochizuki, T. Otake and Y. Yamasaki, 1989. Distribution, migration and growth of ayu larvae at the mouth of River Kumano. Fish. Engineer., 50: 47–57. (In Japanese.)
Uchida, K. 1958. AyuPlecoglossus altivelis Temminck et Schlegel. Pages 18–20in Studies on the eggs, larvae and juvenile (sic) of Japanese fishes, Series 1, 2nd Lab. Fish. Biol., Fish Dept., Kyusyu Univ. (In Japanese.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, I., Azuma, K., Fujita, S. et al. Differences in larval and juvenile devleopment among monthly cohorts of ayu,plecoglossus altivelis, in the shimanto river. Ichthyological Research 47, 385–391 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02674267
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02674267