Abstract
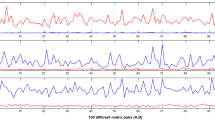
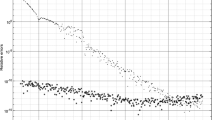
This paper considers the dependence of the convergence history of the CG method on the largest eigenvalues of a symmetric positive-definite matrix. It is demonstrated that, in solving ill-conditioned linear systems, the reproduction of largest eigenvalues can be so intensive that they cannot be treated as isolated. On the other hand, from the moment the smallest isolated eigenvalues start to govern the numerical convergence of the CG method, the convergence is mainly influenced by the smallest Ritz values. Bibliography: 2 titles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Axelsson and G. Lindskog, “On the rate of convergence of the preconditioned conjugate gradient methods,”Numer. Math.,48, 499–523 (1986).
Y. Notay, “On the convergence rate of the conjugate gradients in presence of rounding errors,”Numer. Math.,65, 301–317 (1993).
Additional information
Translated fromZapiski Nauchnykh Seminarov POMI, Vol. 248, 1998, pp. 5–16.
Translated by A. Yu. Yeremin.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeremin, A.Y., Kaporin, I.E. The influence of isolated largest eigenvalues on the numerical convergence of the CG method. J Math Sci 101, 3231–3236 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02672768
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02672768