Abstract
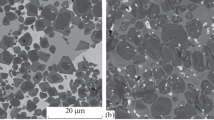
The effects of electroplated and hot-dip zinc coatings on the fracture of low-alloy steel AISI 4140 bars tempered to hardnesses in the range Rc 33 to 49 were studied. Either electroplated or hot-dip zinc coatings decrease resistance to stress corrosion cracking,i.e., they reduceK sc, the threshold stress intensity for stress corrosion cracking in 3.5 wt pct NaCl solution. AboveK scelectroplated-zinc coatings do not appear to affect the crack-growth rate, although the incubation period prior to the onset of crack growth is reduced. Hot-dip zinc coatings increase stress corrosion crack growth rates slightly because of the additive effect of internal dissolved hydrogen. Hot-dip zinc coatings reduce the critical stress intensity for fracture in the absence of a corrosive environment because of embrittlement by internal hydrogen which is released from traps during hot-dip coating and confined by the inter metallic coatings which form on the steel surface in the hot dip bath. A simple fracture mechanics analysis indicates that either increasing diameter or the presence of a zinc coating lowers the critical hardness at which the stress corrosion cracking of structural bolts can occur.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. K. Boyd and W. S. Hyler:J. Struct. Dit:, ASCE, 1973, vol. 99, pp. 1571–88.
G. J. Biefer and B. C. Syrett:Proceedings Third Inter-Naval Corrosion Con- ference, pp. 19.1–19.24, British Royal Navy, Foxhill, 1969.
G. Sandoz:Met. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 1169–76.
G. Sandoz:Met. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 1169–76.
B. F. Brown:The Theory of SCC in Alloys, pp. 186–204, NATO, Brussels, 1971.
G. A. Wacker:Materials Performance and The Deep Sea, STP 445, pp. 68–87, ASTM, Philadelphia, 1969.
R. D. McDonald:Proceedings Ninth International Conference on Hot-Dip Galvanizing, pp. 172–88, Industrial Newspapers Ltd., London, 1970.
A.J. Stavros and H. W. Paxton:Met. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 3049–55.
H. E. Townsend:Stress Corrosion Cracking, A State of the Art, STP518, pp. 155–66, ASTM, Philadelphia, 1972.
T. Toh and W. M. Baldwin:Stress Corrosion Cracking and Etnbrittlement, pp. 176–86, Wiley, New York, 1956.
C. S. Carter:Corrosion, 1971, vol. 27, pp. 471–77.
M. H. Peterson. B. F. Brown, R. L. Newbegin, and R. E. Groover:Corrosion, 1967, vol. 23, pp. 142–48.
S. Mostovoy, H. R. Smith, R. G. Lingwall, and E. J. Ripling:Eng. Fracture Mech, 1971, vol. 3, pp. 291–99.
A. M. Sullivan:Eng. Fracture Mech., 1972, vol. 4, pp. 65–76.
M. T. Wang and R. W. Staehle: Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, Unpublished Research, 1972.
R. A. Oriani:Proceedings: Fundamental Aspects of Stress Corrosion Cracking, pp. 32–50, NACE, Houston, 1969.
H. H. Johnson, J. G. Morlet, and A. R. Troiano:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1958, vol. 212, p. 528.
R. A. Oriani and P. H. Josephic:Scr. Met., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 584–86.
C.S. Carter:Met. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 584–86.
H. F. Bueckner:Fracture Toughness Testing, STP 381, p. 82, ASTM, Philadelphia, 1965.
Metals Handbook, p. 98, Metal Park, Ohio, 1948.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Townsend, H.E. Effects of zinc coatings on the stress corrosion cracking and hydrogen embrittlement of low-alloy steel. Metall Trans A 6, 877–883 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02672311
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02672311