Abstract
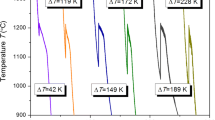
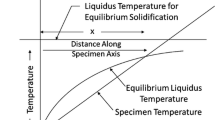
A model was developed to predict micro structural development in lead—61.9 wt pct Sn (eutectic) alloys which were undercooled 5 to 25 K below their equilibrium freezing temperature prior to being preferentially nucleated. While the initial solidification velocity rapidly increases with increasing undercooling, the model predicts it to quickly decrease, prior to 10 pct solid formation, after which growth continues near the equilibrium temperature. Experimentally, and in accordance with the prediction, the eutectic emanated from the nucleation site with an initially fine spacing that increased with distance. However, in contrast to the model, the eutectic grew outward in a spokelike manner with each arm surrounded by a globular structure, this being attributed to the difficulty of lateral nucleation. Microstructural uniformity was further compromised by equiaxed eutectic grains which grew ahead of the advancing interface in the now only slightly undercooled liquid. Consequently, while containerless techniques may ensure sample purity and permit processing of high-temperature materials, development of a continuously fine and uniformly aligned microstructure cannot be assumed.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Undercooled Alloy Phases, E.W. Collings and C.C. Koch, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1986.
C.G. Levi and R. Mehrabian:Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 221–34.
J.D. Hunt and J.P. Chilton:J. Inst. Met, 1963-64, vol. 92, pp. 21–25.
R.M. Jordan and J.D. Hunt:Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 1385- 90.
C.W. Haworth and B.F. Oliver:Trans. AIME, 1967, vol. 239, pp. 1129–36.
A. Moore and R. Elliott:J. Inst. Met., 1967, vol. 95, pp. 369–72.
G.L.F. Powell and G.A. Colligan:J. Inst. Met., 1969, vol. 97, pp. 319–20.
M.G. Chu, Y. Shiohara, and M.C. Flemings:Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 1303–10.
H.C. de Groh III and V. Laxmanan:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 2651–58.
H.C. de Groh III and V. Laxmanan:Solidification Processing of Eutectic Alloys, D.M. Stefanescu, G.J. Abbaschian, and R.J. Bayuzick, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1988, pp. 229–42.
H.C. deGroh III: NASA Technical Memorandum 102023, May 1989.
H.J. Fecht:Acta Metall. Mater, 1991, vol. 39 (5), pp. 1003–09.
G.A. Chadwick:J. Inst. Met., 1962-63, vol. 91, p. 169.
H.E. Cline:Trans. AIME, 1967, vol. 239, pp. 1489–93.
H.E. Cline and J.D. Livingston:Trans. AIME, 1969, vol. 245, pp. 1987–92.
R. Trivedi, J.T. Mason, J.D. Verhoeven, and W. Kurz:Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 2523–33.
H.J. Fecht and J.H. Perepezko:Metall. Trans. A, 1989, vol. 20A, pp. 785–94.
H.J. Fecht, M.-X. Zhang, Y.A. Chang, and J.H. Perepezko:Metall. Trans. A, 1989, vol. 20A, pp. 795–803.
ASM Metals Handbook, H. Baker, ed., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 1992, vol. 3, p. 2.335.
K.A. Jackson, J.D. Hunt, D.R. Uhlmann, and T.P. Seward III:Trans. AIME, 1966, vol. 236, pp. 149–58.
J.D. Hunt:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1984, vol. 65, pp. 75–83.
H. Fredriksson and A. Olsson:Mater. Sci. Technol, 1986, vol. 2, pp. 508–16.
R. Grugel and W. Kurz:Metall. Trans. A, 1987, vol. 18A, pp. 1137- 42.
S. Kim and R.N. Grugel:Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 1807- 15.
P.J. Prescott and F.P. Incropera:Metall. Trans. B, 1991, vol. 22B, pp. 529–40.
P. Ramachandrarao and K.S. Dubey:Int. J. Rapid Solid., 1992, vol. 7, pp. 191–99.
T. Carlberg and H. Fredriksson:J. Cryst. Growth, 1977, vol. 42, pp. 526–35.
V. Seetharaman and R. Trivedi:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 2955–64.
R.A. Pratt and R.N. Grugel:Mater. Character., 1993, vol. 31 (4), pp. 225–31.
V. De L. Davies:J. Inst. Met., 1963-64, vol. 92 (4), pp. 127–28. $
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This article is based on a presentation made in the symposium entitled “Microgravity Solidification, Theory and Experimental Results” as a part of the 1993 TMS Fall meeting, October 17-21, 1993, Pittsburgh, PA, under the auspices of the TMS Solidification Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, F., Grugel, R.N. Microstructural development in undercooled lead- tin eutectic alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 26, 2699–2706 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02669426
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02669426