Abstract
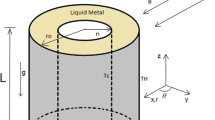
The dissolution of a copper cylinder in molten tin-lead alloys was studied at 673 K under static and dynamic conditions in the peripheral velocity range 1.9 to 75.4 cm per second using an immersion method. The dissolution rate of copper increased with increasing tin concentration and peripheral velocity. The solution rate constant increased with peripheral velocity and with diffusion coefficient of copper in the melt. The constant decreased with kinematic viscosity of the melt and diameter of the specimen. The dissolution of copper in molten tin-lead alloys was mixed control. Flow of the melt under forced convection was turbulent flow with Taylor vortices. Natural convection occurred in dissolution of stationary copper in tin rich alloys due to hydrodynamic instability from density differences in the melt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.G. Bader:Weld. J., 1969, vol. 48, pp. 551-S-557-S.
T. Ishida:Trans. Jpn. Weld. Soc., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 1–6.
H. Fidos and H. Schreiner:Z. Metallk., 1970, vol. 61, pp. 273–78.
H. Yamaguchi and Y. Hisamatsu:Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1979, vol. 19, pp. 649–58.
Y. Kim and R. D. Pehlke:Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 2527–32.
J. R. Weeks and D.H. Gurinsky:Liquid Metals and Solidification, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1958, pp. 106–61.
T. Ishida:Trans. Jpn. lnst. Met., 1973, vol. 14, pp. 37–44.
Y. Shoji, S. Uchida, and T. Ariga:Trans. Jpn. lnst. Met., 1980, vol. 21, pp. 383–89.
M. Hansen:Constitution of Binary Alloys, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, NY, 1958, pp. 633–38.
M. Hansen:Constitution of Binary Alloys, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, NY, 1958, pp. 609–12.
E. A. Moelwyn-Hughes:The Kinetics of Reaction in Solution, 2nd ed., Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1947, pp. 374–77.
Y. Shoji, S. Uchida, and T. Ariga:Weld. J., 1981, vol. 60, pp. 19-S-24-S.
W. Sutherland:Phil. Mag., 1905, vol. 9, pp. 781–85.
C.J. Smithells:Metals Reference Book, 3rd ed., Butterworths, London, 1962, vol. I, p. 136.
H.R. Thresh and A.F. Crawley:Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 1531–35.
C.H. Ma and R.A. Swalin:Acta Met., 1960, vol. 8, pp. 383–95.
J.W. Gorman and G. W. Preckshot:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1958, vol. 212, pp. 367–73.
H. Schlichting:Boundary-Layer Theory, 6th ed., McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, NY, 1968, pp. 24–43.
H.R. Thresh, A.F. Crawley, and D.W.G. White:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1968, vol. 242, pp. 819–22.
M. Eisenberg, C. W. Tobias, and C. R. Wilke:Chem. Eng. Prog. Symp. Ser., 1955, vol. 51, no. 16, pp. 1–16.
M. Kosaka and S. Minowa:Tetsu-to-Hagane, 1966, vol. 52, pp. 1748–62.
H. Schilichting:Boundary-Layer Theory, 6th ed., McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, NY, 1968, pp. 500–03.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
YOSHIFUSA SHOJI, formerly Graduate Student, Tokai University, Tokyo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shoji, Y., Uchida, S. & Ariga, T. Dissolution of solid copper cylinder in molten tin-lead alloys under dynamic conditions. Metall Trans B 13, 439–445 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02667760
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02667760