Abstract
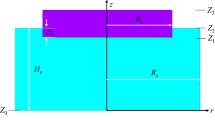
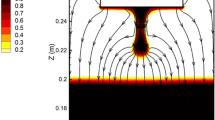
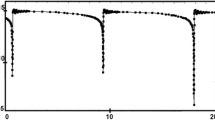
A comparison is presented between the experimentally measured velocity field in a room temperature model of an ESR system and theoretical predictions, obtained from the numerical solution of Maxwell’s equations and the turbulent Navier-Stokes equations. The experimental measurements were obtained in a horizontal trough, containing mercury, through which a current was being passedvia two electrodes. The velocity fields, which were measured, using a photographic technique were thought to model the electromagnetically driven component of the velocity field in the central plane of the slag phase in ESR systems. The agreement between the experimental measurements and the theoretical predictions is excellent, both regarding the absolute values of the velocities and the dependence of the velocity on the imposed current and on the electrode diameter. The calculations have shown that by the proper choice of the linear scale, and the current,. mercury may be used to model the electromagnetically driven flow in the slag phase of ESR systems. Furthermore, some general relationships have been developed showing the effect of the current on the velocity, the turbulence energy, and on the rate of turbulence energy dissipation. This work is thought to provide definite confirmation that the electromagnetically driven component of the velocity fields in ESR systems may be properly represented through the simultaneous solution of Maxwell’s equations and the turbulent NavierStokes equations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. H. Dilawari and J. Szekely:Metall. Trans. B, 1977, vol. 8B, pp. 227–36.
A. H. Dilawari and J. Szekely:Metall. Trans. B, 1978, vol. 9B, pp. 77–87.
J. Kreyenberg and K. Schwerdtfeger:Arch. Eisenhuttenews, 1979, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 1–6.
M. Choudhary and J. Szekely: Proc. Sixth Int. Vac. Met. Conf. on Special Melting, American Vacuum Society, New York, NY, 1979, p. 484.
M. Choudhary and J. Szekely:Metall. Trans. B, 1980, vol. 11B, pp. 439–53.
M. Choudhary and J. Szekely:lronmakinglSteelmaking, 1981, in press.
M. Choudhary: Sc.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, 1980.
B. E. Launder and D. B. Spalding:Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engr., 1974, vol. 3, pp. 269–89.
A.D. Gosman, W. M. Pun, A.K. Runchal, D. B. Spalding, and M. Wolfshtein:Heat and Mass Transfer in Recirculating Flows, Academic Press, London and New York, NY, 1969, p. 18.
W. F. Hughes and F. J. Young:The Electromagnetodynamics of Fluids, John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, 1966, p. 618.
R. H. Perry and C. H. Chilton:Chemical Engrs. Handbook, McGraw Hill, New York, NY, 1973, pp. 23–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhary, M., Szekely, J., Medovar, B.I. et al. The velocity field in the molten slag region of esr systems: a comparison of measurements in a model system with theoretical predictions. Metall Trans B 13, 35–43 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02666953
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02666953