Abstract
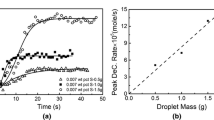
The nature of the cement copper deposit was shown to control the kinetic response of the cementation reaction under certain circumstances. In essence, the nature of the surface deposit determines the effective cathodic area and is controlled by a number of variables. What appeared to be a temperature region (0 to 35°C) where a surface reaction mechanism was rate controlling, ΔE a ≊10 kcal per mole, was, in fact, a consequence of the variation of the area of the surface deposit with temperature. Further evidence of this phenomenon was demonstrated by the results of cementation experiments in an ultrasonic field, and by the results obtained from initial “strike” experiments. Also considered in this study was the effect of the initial cupric ion concentration and the back reaction kinetics. The basic conclusion reached from this investigation was that the cementation reaction rate is controlled by boundary layer diffusion processes at all temperatures and concentrations with an activation energy of approximately 5 kcal per mole. When surface deposit effects are neglected, interpretation of cementation rate data, as well as rate data of any heterogeneous reaction involving a solid phase, can often be misleading.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. E. Wadsworth:Met. Trans., 1969, vol. 245, pp. 1381–94.
R. M. Nadkami and M. E. Wadsworth. “A Kinetic Study of the Cementation of Copper with Iron”,Advances in Extractive Metallurgy, Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, London, 1968, pp. 918–41.
R. S. Richard and M. C. Fuerstenau:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1968, vol. 242, pp. 1487–93.
J. V. Calara: “Kinetics of Copper Cementation on a Rotating Iron Disc”, Master's Thesis, University of the Philippines, Department of Metallurgy, Manila, Philippines, 1970.
A. K. Biswas and J. G. Reid:Proc. Aust. Min. Met., 1972, vol. 242, pp. 37–45.
R. L. Miller: “A Kinetic Study of the Cementation of Copper and Nickel”, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Utah, Department of Mining, Metallurgical and Fuels Engineering, Salt Lake City, Utah, 1968.
D. J. MacKinnon, T. R. Ingrahm, and R. Kirby:Can. Met. Quart., 1971, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 165–69.
E. A. von Hahn and R. R. Ingrahm:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1966, vol. 236, pp. 1098–1103.
J. D. Miller: “An Analysis of Concentration and Temperature Effects in Cementation Reaction”, to be published inMineral Science and Engineering, in press.
P. H. Strickland and F. Lawson:Proc. Aust. Inst. Min. Met., 1971, vol. 236, pp. 25–33.
L. W. Beckstead: “Surface Deposit Effects in the Kinetics of Copper Cementation by Iron”, Master's Thesis, University of Utah, Department of Mining, Metallurgy, and Fuels Engineering, Salt Lake City, Utah, 1973.
A. Roll:J. Metal Finish, 1957, vol. 55, pp. 55–58.
G. Jangg and H. Arlt:Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem, 1962, vol. 318, pp. 63–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, J.D., Beckstead, L.W. Surface deposit effects in the kinetics of copper cementation by iron. Metall Trans 4, 1967–1973 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02665425
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02665425