Abstract
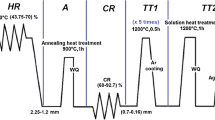
The room-temperature hydrogen embrittlement (HE) problem in iron aluminides has restricted their use as high-temperature structural materials. The role of thermomechanical treatments (TMT),i.e., rolling at 500 °C, 800 °C, and 1000 °C, and post-TMT heat treatments,i.e., recrystallization at 750 °C and ordering at 500 °C, in affecting the room-temperature mechanical properties of Fe-25A1 intermetallic alloy has been studied from a processing-structure-properties correlation viewpoint. It was found that when this alloy is rolled at higher temperature, it exhibits a higher fracture strength. This has been attributed to fine subgrain size (28/μ) due to dynamic recrystallization occurring at the higher rolling temperature of 1000 °C. However, when this alloy is rolled at 1000 °C and then recrystallized, it shows the highest ductility but poor fracture strength. This behavior has been ascribed to the partially recrystallized microstructure, which prevents hydrogen ingress through grain boundaries and minimizes hydrogen embrittlement. When the alloy is rolled at 1000 °C and then ordered at 500 °C for 100 hours, it shows the highest fracture strength, due to its finer grain size. The alloy rolled at 500 °C and then ordered undergoes grain growth. Hence, it exhibits a lower fracture strength of 360 MPa. Fracture morphologies of the alloy were found to be typical of brittle fracture,i.e., cleavage-type fracture in all the cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.S. Stoloff:Int. Met. Rev., 1984, vol. 29, pp. 123–35.
C.T. Liu, J.O. Stiegler, and F.H. Froes:Metals Handbook, 10th ed., vol. 2,Ordered Intermetallics, ASM, Materials Park, OH, 1990, pp. 913–42.
C.T. Liu and K.S. Kumar:J. Met., 1993, vol. 45, pp. 38–44.
C.T. Liu, E.H. Lee, and CG. McKamey:Scripta Metall, 1989, vol. 23, pp. 875–80.
A. Shan and D. Lin:Scripta Metall. Mater., 1992, vol. 27, pp. 95–100.
D.B. Kasul and L.A. Heldt:Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1994, vol. 25A, pp. 1285–90.
C.T. Liu, C.G. McKamey, and E.H. Lee:Scripta Metall. Mater., 1990, vol. 24, pp. 385–90.
C.G. McKamey, J.A. Horton, and C.T. Liu:Scripta Metall, 1988, vol. 22, pp. 1679–81.
CG. McKamey and C.T. Liu:Scripta Metall. Mater., 1990, vol. 24, pp. 2119–22.
R. Balasubramaniam:Scripta Mater., 1996, vol. 34, pp. 127–33.
S. Suwas:Master’s Thesis, IIT, Kanpur, 1993.
D. Lin, A. Shan, and D. Li:Scripta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 31, pp. 1455–60.
K. Oki, M. Hasaka, and T. Eguchi:Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 1973, vol. 12, pp. 1522–30.
K. Oki, M. Hasaka, and T. Eguchi:Trans. Jpn. lnst. Met., 1973, vol. 14, pp. 8–13.
H.J. McQueen and G.C. Kuczynski:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1959, vol. 215, pp. 619–22.
R.G. Davies:J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1963, vol. 24, pp. 985–92.
Ya.P. Sallisskiy:Phys. Met. Metallgr., 1961, vol. 11, pp. 124–27.
I. Baker and Y. Nagpal: inStructural Intermetallics, R. Darolia, J.J. Kewandoski, C.T. Liu, P.L. Martin, and M.B. Nathal, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 463–73.
C.G. McKamey, J.H. Devan, P.F. Tortorelli, and V.K. Sikka:J. Mater. Res., 1991, vol. 6, pp. 1779–86.
C.G. McKamey and D.H. Pierce:Scripta Metall Mater., 1993, vol. 28, pp. 1173–76.
V.K. Sikka, S. Vishwanathan, and C.G. McKamey: inStructural Intermetallics, R. Darolia, J.J. Kewandoski, C.T. Liu, P.L. Martin, and M.B. Nathal, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 483–91.
J. Friedel:Dislocations, Pergamon Press, New York, NY, 1964, pp. 320–47.
D.G. Morris and M. Leboeuf:Acta. Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 42, pp. 1817–23.
J. Friedel:Dislocations, Pergamon Press, New York, NY, 1964, pp. 12–21.
J. Friedel:Dislocations, Pergamon Press, New York, NY, 1964, pp. 158–65.
J.C.M. Li and C.T. Liu:Scripta Metall. Mater., 1992, vol. 27, pp. 1701–06.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agarwal, A., Balasubramaniam, R. & Bhargava, S. Effect of thermomechanical treatments on the room-temperature mechanical behavior of iron aluminide Fe3AI. Metall Mater Trans A 27, 2985–2993 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02663848
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02663848