Abstract
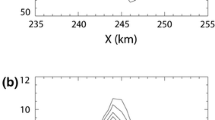
By utilizing the denser upper-air observations from the Okinawa region and Japanese islands during August 17–23, 1975, the vertical transports of heat and moisture by cumulus convection in the typhoon No. 7507 have been calculated. It is found that there exist a large apparent heat source (Q 1) and a moisture sink (Q 2) in the southern part of the typhoon at the disturbance, growing and mature stages. The magnitudes of the apparent heat source and moisture sink are rather small, or turn into the apparent heat sink in the northern sector of the typhoon. In the southern part of the typhoon, the total cloud mass flux (M c) is positive, whereas in the northern part of the typhoonM c is negative. The above-mentioned distributions ofQ 1,Q 2 andM c agree well with the major cloud patterns.
In the southern part of the typhoon,Q 2 is positive because the drying effect is always larger than the evaporative cooling, whereas in the northern part of the typhoon, the opposite case is true because both the drying and evaporating effects of liquid water make a negative contribution toQ 2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arakawa, A. and Schubert W. H., (1974), Interaction of a cumulus cloud ensemble with the large-scale environment, Part I,Jour. Atmos. Sci.,31: 674–701.
Ding Yihui, Liu Yuezhen and Zhang Jian (1986). The characteristics of condensation heating field of the typhoon No. 7507 and its relationship to development of the typhoon, Selected Papers of Typhoons in the West-Pacific Ocean, Communication press (to be puolished in Chinese).
Dopplick, T. G. (1972), Radiative heating of the global atmosphere,Jour. Atmos. Sci.,29: 1278–1294.
Nitta, T. (1976), Large-scale heat and moisture budgets during the air mass transformation experiment,Jour. Meteor. Soc. Japan,54: 1–4.
Nitta, T. (1975), Observational determination of cloud mass flux distribution,Jour. Atmos. Sci.,32: 73–91.
Nitta, T. (1977), Response of cumulus updraft and downdraft to GATE A/B-scale motion systems,Jour. Atmos. Sci.,34: 1163–1186.
Ogura, Y. and Cho, H. R. (1974), On the interaction between the subcloud and cloud layer in tropical regimes,Jour. Atmos. Sci.,31: 1850–1859.
Ogura, Y. and Cho, H. R. (1973), Diagnostic determination of cumulus cloud populations from observed large-scale variables,Jour, Atmos. Sci.,30: 1276–1286.
Yanai, M. S. Esbenson and Chu, J. H. (1973), Determination of bulk properties of tropical cloud clusters from large-scale heat and moisture budget,Jour. Atmos. Sci.,30: 611–627.
Yang Dashen and Krishnamurti, T. N. (1981), Potential vorticity of monsoonal low level flows,Jour. Atmos. Sci.,38: 2676–2695.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Liu, Y. The effect of vertical transports of heat and moisture by cumulus convection in typhoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 4, 278–286 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02663598
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02663598