Abstract
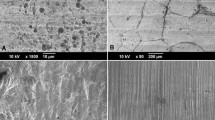
A new mechanism of fatigue-crack initiation (FCI), grain egression, was observed in the course of investigating corrosion-fatigue crack initiation in Ti-6A1-4V hip prostheses fabricated using three different processes. Extensive scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to document this new mechanism as well as the other FCI mechanisms operating. Grain egression entails the fracture and egression of primary α grains from the surface of the sample, resulting in a sharp pit that subsequently acts as the site of crack initiation. The different sizes and morphologies of the grain-egression sites observed are very similar to the sizes and morphologies of the pri-mary α grains resulting from the three different fabrication processes, providing further evidence for grain egression as an operative FCI mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
T. Takemoto, KL. Jing, T. Tsakalakos, S. Weissmann, and I.R. Kramer:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 127–32.
G.R. Leverant, B.S. Langer, A. Yuen, and S.W. Hopkins:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 251–57.
J.E. Hack and G.R. Leverant: Residual Stress Effects in Fatigue, ASTM STP 776, ASTM, 1982, pp. 204–23.
C. Gerdes and G. Luetjering:Shot Peening, Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. on Shot Peening, ICSP-2, SAE, Warrendale, PA, 1984, pp. 175–80.
L. Wagner and G. Luetjering:Shot Peening, Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. on Shot Peening, ICSP-2, SAE, Warrendale, PA, 1984, pp. 194–200.
L. Wagner and G. Luetjering:Shot Peening, Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. on Shot Peening, ICSP-2, SAE, Warrendale, PA, 1984, pp. 201–07.
A.W. Bowen and C.A. Stubbington:Titanium Science and Technology, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1973, vol. 3, pp. 2097–108.
M. Pcters, A. Gysler, and G. Luetjering:Titanium Science '80, Science and Technology, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1980, vol. 3, pp. 1777–86.
C.A. Stubbington:AGARD Conf. Proc. No. 185, NASA, Langley Field, VA, 1976, pp. 140–57.
C.A. Stubbington and A.W. Bowen:J. Mater. Sci., 1974, vol. 9, pp. 941–47.
M.A. Imam and C. M. Gilmore:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 233–40.
C. M. Gilmore and M.A. Imam:Titanium and Titanium Alloys, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1982, pp. 637–48.
J.J. Lucas:Titanium Science and Technology, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1973, pp. 2081–85.
M. Pcters, A. Gysler, and G. Lütjering:Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 1597–605.
D.K. Benson, J.C. Grosskreutz, and G.G. Shaw:Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3 (211), pp. 1239–48.
A.M. Freudenthal:Eng. Fract. Mech., 1974, vol. 6, pp. 775–93.
D.F. Neal and P.A. Blenkinsop:Acta Metall., 1976, vol. 24, pp. 59–63.
J. Ruppen, B. Bhowal, D. Eylon, and A.J. McEvily: Fatigue Mechanisms, ASTM STP 675, ASTM, 1979, pp. 47–68.
A. Puskar and S.A. Golovin:Fatigue in Materials: Cumula- tive Damage Process, Elsevier, New York, NY, 1985, pp. 233–39.
R.K. Steele and A.J. McEvily:Titanium and Titanium Alloys, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1982, pp. 589–600.
I. Weiss, F.H. Froes, D. Eylon, and G.E. Welsch:Metall. Trans. A, 1986, vol. 17A, pp. 1935–47.
J.C. Williams:Deformation, Processing, and Structure, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1982, pp. 279–354.
A.W. Bowen:Titanium Science and Technology, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1973, vol. 2, pp. 1271–81.
J.L. Gilbert: Ph.D. Thesis, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, 1987.
ASTM Designation: F-136-79.
M. Semlitsch and B. Panic:Eng. Med., 1983, vol. 12(4), pp. 185–98.
L.E. Sloter and H.R. Piehler:Corrosion and DegrActation of Implant Materials, ASTM STP 684, ASTM, 1979, pp. 328–41.
D.L. Davidson:Fatigue Mechanisms, ASTM STP 675, 1979, pp. 254–75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilbert, J.L., Piehler, H.R. Grain egression: A new mechanism of fatigue-crack initiation in Ti-6Al-4V. Metall Trans A 20, 1715–1725 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02663203
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02663203