Abstract
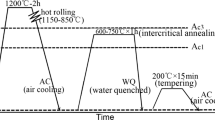
Fatigue crack propagation was studied for two intercritically tempered cryogenic steels, Fe-9Ni-0.1C and Fe-4Mn-0.15C, at both intermediate (stage II) and low (stage I, near threshold) stress intensity ranges. Propagation rates were determined for varying intercritical tempering times corresponding to varying amounts of retained austenite and untempered martensite. The results show that the heat treatments that optimize impact fracture properties in the nickel steel are also beneficial with respect to the fatigue crack propagation rate in stage I, while no beneficial effect beyond that attributable to carbon redistribution was observed for stage II. For the manganese steel, heat treatments leading to increased concentrations of retained austenite also increased the threshold stress even though no improvement in fracture toughness was observed. To clarify the origin of this improved behavior, the fracture surface was analyzed by Mössbauer Spectroscopy and Auger Electron Microprobe. The Mössbauer results indicated that the retained austenite in the crack path is transformed to martensite as was earlier shown in this laboratory for Charpy specimens. Auger composition analysis suggested a tendency for a stage I crack tip to avoid the mechanically induced brittle untempered martensite in the Fe-Mn steel, while no such preference was observed for stage II.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.W. Marschall, R. F. Heheman, and A. R. Troiano:Trans. ASM, 1977, vol. 55, p. 135.
S. Jin, S.K. Hwang, and J.W. Morris, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, p. 1721.
K.J. Kim and L.H. Schwartz:Mat. Sci. and Eng., 1978, vol. 33, p. 5.
H. Suzuki and A. J. McEvily:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, p. 475.
R. L. Miller:Materiaux et Technique, December 1977, vol. 55, p. 79.
R. O. Ritchie:J. Eng. Mat. and Tech., 1977, vol. 99, p. 195.
P. K. Liaw and J. Baker:Rev. Sci. Instrum., 1979, vol. 50, p. 1590.
H. Tada (with P. C. Paris and G. R. Irwin):The Stress Analysis of Cracks Handbook, Del Research Company, St. Louis, MO, 1977.
G. R. Irwin:Proc. of Seventh Sagamore Ordnance Materials Research Conference, Syracuse Univ. Press, Syracuse, NY, 1960, pp. IV-63.
A. J. Heckler: M. S. Thesis, Purdue University, Lafayette, IN, 1962.
R.L. Miller: U.S. Steel Res. Labs, Monroeville, PA, unpublished research, 1979.
E. Bain and H. Paxton:Alloying Elements in Steel, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1966, p. 37.
L. Kaufman and M. Cohen:Trans. AIME, 1956, vol. 206, p. 1393.
J. Danon:Chemical Applications of Mössbauer Spectroscopy, V.I. Goldanskii and R. H. Herber, eds., Academic Press, 1968, p. 160.
R.O. Ritchie:Met. Sci. J., 1977, vol. 11, p. 3.
R. O. Ritchie, C. M. Moss, and S. Suresh:J. Eng. Mat. and Tech., 1980, vol. 102, p. 293.
R. J. Bucci, B. N. Greene, and P. C. Paris: Fatigue Crack Propagation and Fracture Toughness of 5Ni and 9Ni Steels at Cryogenic Temperatures, ASTM STP 536, Am. Soc. for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, 1973, pp. 206-28.
J. Weertman:Int. J. Fract., 1973, vol. 9, p. 125.
T. Mura and C.T. Lin:Int. J. Fract. Mech., 1974, vol. 10, p. 284.
J. Weertman:Fracture Mechanics, N. Perrone, H. Liebowitz, D. Mulville, and W. Pilkey, eds., Univ. Press of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, 1978, p. 193: “Fatigue Crack Propagation Theories”, Fatigue and Microstructures, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1979, pp. 279-306.
P.K. Liaw, S.I. Kwun, and ME. Fine:Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, p. 49.
G. Simmons and H. Wang:Single Crystal Elastic Constants, The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1971, pp. 194–95.
M. E. Fine:Trans. Japan Inst. of Metals, 1981, vol. 20, p. 668.
F. A. McClintock: Mass. Inst. of Tech., Cambridge, MA, private communication with E. Tschegg and S. Stanzl, cited in Ref. 25.
E. Tschegg and S. Stanzl:Acta Met., 1981, vol. 29, p. 33.
T. Kunio and K. Yamada:Fatigue Mechanisms, ASTM STP 675, 1979, p. 342.
C. Aita and J. Weertman:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, p. 535.
E. Hornbogen and K. H. Zum Gahr:Acta Met., 1976,vol. 24,p. 581.
J. Lindigkeit, G. Terline, A. Gysler, and G. Lütjering:Acta Met., 1979, vol. 27, p. 1717.
G. T. Hahn, R.G. Hoagland, and A.R. Rosenfield:Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, p. 1189.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is based on a presentation made at the “Peter G. Winchell Symposium on Tempering of Steel” held at the Louisville Meeting of The Metallurgical Society of AIME, October 12-13, 1981, under the sponsorship of the TMS-AIME Ferrous Metallurgy and Heat Treatment Committees.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, H.J., Schwartz, L.H. Fatigue Crack Propagation in Intercritically Tempered Fe-9Ni-0.1C and Fe-4Mn-0.15C. Metall Trans A 14, 1089–1099 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02659857
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02659857