Abstract
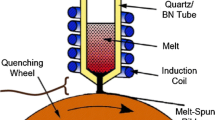
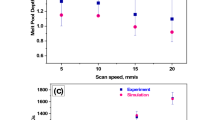
The Planar Flow Melt Spinning Process for the Rapid Solidification of metallic materials is analyzed using a mathematical model based on the principles of capillary fluid dynamics and solidification heat transfer. The results suggest the existence of a region of slowly recirculating flow inside the melt puddle which acts as a lubricant between the nozzle and the wheel. Markedly different thermal conditions across the ribbon thickness are also predicted by the model, as are the resultant microstructural variations across such thickness. The results of the model compare well with the available experimental evidence. The model is sufficiently general as to be immediately applicable to the study of other meniscus controlled continuous casting processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Jones:Rapid Solidification of Metals and Alloys, The Institution of Metallurgists, London, 1982.
Rapid Solidification Technology Source Book, R.L. Ashbrook, ed., American Society for Metals, Metals Park, OH, 1983.
Rapidly Quenched Metals 5, S. Steeb and H. Warlimont, eds., North Holland, Amsterdam, 1985, vols. 1 and 2.
S. Kavesh: inMetallic Glasses,J. Gilman and H. Leamy, eds., American Society for Metals, Metals Park, OH, 1978, pp. 36–73.
S. J. B. Charter, D. R. Mooney, R. Cheese, and B. Cantor:Journal of Materials Science, Letters, 1980, vol. 15, pp. 2658–61.
T. Anthony and H. Cline:Journal of Applied Physics, 1978, vol. 49, pp. 829–37.
L. Katgerman and W. Zalm: inNumerical Methods in Laminar and Turbulent Flow, C. Taylor, J.A. Johnson, and W. R. Smith, eds., Pineridge, Swansea, 1983, pp. 157–65.
J. Vincent, J. G. Herbertson, and H. A. Davies: inRapidly Quenched Metals 4, T. Masumoto and K. Suzuki, eds., The Japan Institute of Metals, Sendai, 1982, vol. 1, pp. 77–80.
P. den Decker and A. Drevers: inMetallic Glasses: Science and Technology, C. Hargitai, I. Bakonyi, and T. Kemény, eds., Kultura, Budapest, 1980, pp. 181–88.
K. Takeshita and P. Shingu:Transactions of the Japan Institute of Metals, 1983, vol. 24, pp. 529–36.
K. Miyazawa and J. Szekely:Metall. Trans. B, 1979, vol. 10B, pp. 349–58.
K. Miyazawa and J. Szekely:Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 1047–57.
V. Levich:Physicochemical Hydrodynamics, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1962, pp. 669–700.
P. Zielinski and D. Ast:Scripta Metallurgica, 1983, vol. 17, pp. 291–94.
M. Savage:Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1977, vol. 80, no. 4, pp. 743–68.
S. Kistler and L. Scriven:International Journal of Numerical Methods in Fluids, 1984, vol. 4, pp. 207–29.
H. Segal: Materials Engineer Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, 1983.
M. Scott:Journal of Materials Science, 1974, vol. 9, pp. 1372–74.
R. W. Jech, T. J. Moore, T. K. Glasgow, and N. W. Orth:Journal of Metals, 1984, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 41–45.
E. Gutierrez Miravete: Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, 1985.
K. Takeshita and P. H. Shingu:Transactions of the Japan Institute of Metals, 1986, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 141–48.
G.M. Oreper and J. Szekely:Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1984, vol. 147, pp. 53–79.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutierrez, E.M., Szekely, J. A mathematical model of the planar flow melt spinning process. Metall Trans B 17, 695–703 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02657132
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02657132