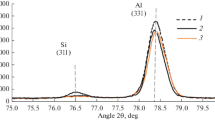
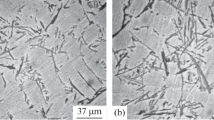
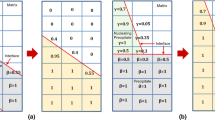
Abstract
Aluminum-iron alloys with Fe contents of up to 8 wt pct were rapidly quenched from the melt using the planar-flow melt-spinning technique. Microstructural changes that occur across the thickness of melt-spun ribbons were investigated as a function of initial melt composition and ribbon thickness. A transition exhibiting a dramatic change in the cell spacing from a microcellular to a coarse cellular region was observed for all the alloys examined. For a given alloy, the volume fraction of the microcellular region decreases significantly with increasing ribbon thickness. A theoretical explanation for the observed behavior is presented in which the heat flow and solidification characteristics are related to the undercooling achieved before the onset of nucleation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.J. Masur, J.T. Burke, T.Z. Kattamis, and M.C. Flemings:Rapidly Solidified Amorphous and Crystalline Alloys, B.H. Kear, B.C. Giessen, and M. Cohen, eds., Elsevier Science Publishing Company, New York, NY, 1982, pp. 185–89.
R.K. Grrett, Jr. and T.H. Sanders:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1983, vol. 60, pp. 269–74.
S.J. Savage and F.H. Froes:Rapidly Solidified Metastable Materials, B.H. Kear and B.C. Giessen, eds., Elsevier Science Publishing Company, New York, NY, 1984, pp. 329–33.
M.G. Chu, A. Giron, and D.A. Granger:Proc. ASM’s Int. Conf. on Rapidly Solidified Materials, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1986, pp. 311–16.
H. Jones:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1969/1970, vol. 5, pp. 1–18.
M.H. Jacobs, A.G. Doggett, and M.J. Stowell:J. Mater. Sci., 1974, vol. 10, pp. 1631–43.
T.W. Clyne:Metall. Trans. B, 1984, vol. 15B, pp. 369–81.
K. Takeshita and P.H. Shingu:Trans. JIM, 1983, vol. 24, pp. 293–300.
M.G. Chu, R.J. Rioja, G.J. Hildeman, and D.K. Denzer:Proc. 43rd Annual Meeting of the Electron Microscopy Society of America, G.W. Bailey, ed., San Francisco Press, Inc., San Francisco, CA, 1985, pp. 32–33.
W.J. Boettinger, L.A. Bendersky, and J.G. Early:Metall. Trans. A, 1986, vol. 17A, pp. 781–90.
J. Lipton, W. Kurz, and R. Trivedi:Acta Metall., 1987, vol. 35 (4), pp. 957–64.
R. Trivedi and K. Somboonsuk:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1984, vol. 65, pp. 65–74.
M. Cohen and M.C. Flemings:Proc. TMS-AIME Northeast Regional Meeting on Rapidly Solidified Crystalline Alloys, S.K. Das, B.H. Kear, and C.M. Actam, eds., The Metallurgical Society, Warrendale, PA, 1985, pp. 3–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02656585.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, M.G., Granger, D.A. Solidification and microstructure analysis of rapidly solidified melt-spun Al-Fe alloys. Metall Trans A 21, 205–212 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02656437
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02656437