Abstract
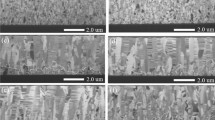
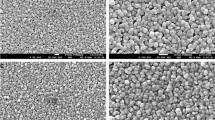
The crystallographic texture and grain size of sputtered Cu films were characterized as a function of deposition temperature, barrier layer material, and vacuum conditions. For Cu deposited in a HV chamber, (111) Cu texture was found to weaken with increasing deposition temperatures on W, amorphous C and Ta barrier layers, each deposited at 30°C. Conversely, under identical Cu deposition conditions, texture was found to strengthen with increasing deposition temperature on Ta deposited at 100°C. Median Cu grain size varied parabolically with deposition temperature on all barrier layers and was slightly higher on the 100°C Ta at a given Cu deposition temperature, relative to the other underlayers. For depositions in an UHV chamber, Cu texture was found to strengthen with increasing Cu deposition temperature, independent of Ta deposition temperature. Median Cu grain size, however, was still higher on 100°C Ta than on 30°C Ta. The observed differences between the two different chambers suggest that the trend of weak texture at elevated deposition temperatures may be related to contamination. Characterization of the Ta underlayers revealed that the strengthened texture of Cu films deposited on 100°C Ta is likely related to textural inheritance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.-L. Pai and C.H. Ting,VMIC Conf. Proc. 6, 258 (1989).
J. Tao, N.W. Cheung and C. Hu,IEEE Electron. Dev. Lett. 14, 249 (1993).
K.P. Rodbell, E.G. Colgan and C.-K. Hu,Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 337 (1994).
L. Stolt, A. Charai, F.M. D’Heurle, P.M. Fryer and J.M.E. Harper,J. Vac. Sci. Tech. A 9, 1501 (1991).
K. Holloway and P.M. Fryer,Appl. Phys. Lett. 57, 1736 (1990).
E. Kolawa, J.S. Chen, J.S. Reid, P.J. Pokela and M.A. Nicolet,J. Appl. Phys. 70, 1369 (1991).
J. Li, J.W. Strane, S.W. Russell, S.Q. Hong, J.W. Mayer, T.K. Marais, C.C. Theron and R. Pretorius,J. Appl. Phys. 72, 2810 (1992).
R.G. Purser, J.W. Strane and J.W. Mayer,Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 309 (1993), p. 481.
D.P. Tracy, D.B. Knorr and K.P. Rodbell,J. Appl. Phys. 76, 2671 (1994).
C.V. Thompson,Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 20, 245 (1990).
S. Vaidya and A.K. Sinha,Thin Sol. Films 75, 253 (1981).
J. Cho and C.V. Thompson,J. Electron. Mater. 19, 1207 (1990).
D.B. Knorr and K.P. Rodbell,Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 309 (1993), p. 345.
R.P. Vinci and J.C. Bravman,Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 308 (1993), p. 337.
D.P. Tracy and D.B. Knorr,J. Electron. Mater. 22,611(1993).
T. Ohmi, T. Saito, M. Otsuki, T. Shibata and T. Nitta,J. Electrochem. Soc. 138, 1089 (1991).
J.M.E. Harper, J. Gupta, D.A. Smith, J.W. Chang, K.L. Holloway, C. Cabrai, D.P. Tracy and D.B. Knorr,Appl. Phys. Lett. 65, 177 (1994).
E.M. Zielinski, R.P. Vinci and J.C. Bravman,J. Appl. Phys. 76, 4516 (1994).
M.J. Verkerk, G.J. van der Kolk and W.A.M.C. Brankaert,Semicon. Int. 11, 106 (1988).
G.J. van der Kolk, M.J. Verkerk and W.A.M.C. Brankaert,Semicon. Int. 11, 224 (1988).
D.R. Frear, A.N. Campbell, B.L. Draper and R.E. Mikawa,J. Electron. Mater. 18, 517 (1989).
L.G. Schulz,J. Appl. Phys. 20, 1030 (1949).
D.B. Knorr,Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 309 (1993), p. 75.
Standard Test Method for Preparing Quantitative Pole Figures, ASTM Standard E81-90 (Philadelphia, PA: American Society for Testing and Materials, 1990).
E.F. Kaelble,Handbook of X-rays (New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1967).
S. Roberts and P.J. Dobson,Thin Sol. Films 135, 137 (1986).
P.T. Moseley and C.J. Seabrook,Acta Crystallogr. B 29, 1170 (1973).
L.A. Clevenger, N.A. Bojarczuk, K. Holloway, J.M.E. Harper, C. Cabrai Jr., R.G. Schad, F. Cardone and L. Stolt,J. Appl. Phys. 73, 300 (1993).
P. Catania, J.P. Doyle and J.J. Cuomo,J. Vac. Sci. Tech. A 10, 3318 (1992).
D.B. Knorr and T.-M. Lu,Appl. Phys. Lett. 54, 2210 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zielinski, E.M., Vinci, R.P. & Bravman, J.C. Effects of barrier layer and processing conditions on thin film Cu microstructure. J. Electron. Mater. 24, 1485–1492 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02655467
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02655467