Abstract
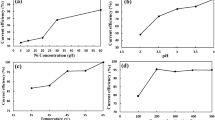
The effect of thiourea and flotation reagents on the electrowinning of zinc from industrial electrolytes was studied, and all the compounds were found to reduce the zinc deposition current efficiency and to change the properties of the zinc deposits. The effectiveness of activated carbon, two-stage cementation, and hot acid leaching on the destruction/removal of the organic compounds also was addressed. Activated carbon pretreatment of thiourea-containing electrolytes restored the current efficiency for 1-hour zinc deposits to values comparable to those obtained for thiourea-free electrolytes. The activated carbon pretreatment, however, altered the deposit morphology and orientation, but produced a cyclic voltammogram similar to that of the thiourea-free solution. Two-stage cementation did not counteract the harmful effects of thiourea. Hot acid leaching destroyed the thiourea but generated large concentrations of ferrous ion that reduced the current efficiency. The ferrous concentrations, however, were readily controlled by KMnO4 or MnO2 oxidation. None of the treatment options (activated carbon, two-stage cementation, or hot acid leaching) was effective in controlling the flotation reagents, and their moderately harmful effect on zinc electrowinning persisted. Even low concentrations of these reagents polarized zinc deposition, and this resulted in a “glue-type” zinc deposit.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. E. Dutrizac:Zinc ’85, K. Tozawa, ed., Min. Metal. Inst. Japan, Tokyo, 1985, pp. 707–27.
J. D. Scott, D. K. A. Donyina, and J. E. Mouland:Iron Control in Hydrometallurgy, J. E. Dutrizac and A. J. Monhemius, eds., Ellis Horwood, Chichester, 1986, pp. 657–75.
L. A. Painter:Lead-Zinc-Tin ’80, J. M. Cigan, T. S. Mackey, and T. J. O’Keefe, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1979, pp. 124–43.
J. M. Boxall and S. E. James:Iron Control in Hydrometallurgy, J. E. Dutrizac and A. J. Monhemius, eds., Ellis Horwood, Chichester, 1986, pp. 676–86.
M. Monta and M. Sakata:Zinc ’85, K. Tozawa, ed., Min. Metal. Inst. Japan, Tokyo, 1985, pp. 435–53.
R. Fish:Can. Min. J., 1981, vol. 102, pp. 47–69.
M. E. Chalkley, I. M. Masters, and D. R. Weir:Zinc ’83, Proc. 13th Ann. Hydrometal. Meeting, Edmonton, Can. Inst. Min. Metal., Montreal, 1983, paper 12, 27 pp.
Y. de Bellefroid:Zinc ’85, K. Tozawa, ed., Min. Metal. Inst. Japan, Tokyo, 1985, pp. 383–98.
K. Kaneko and S. Takayanaki: Silver Recovery at Mitsubishi Akita Zinc Refinery, AIME Ann. Meeting 1981, TMS paper A 81–13.
Anon.:Youse Jinshu, 1983, vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 73–79.
J. A. Mendoza, P. Gonjalez, and J. C. Muniz: Upgrading lead-silver residues at the Torreon zinc plant of MET-MEX Penoles, AIME Ann. Meeting, 1984.
Noranda Minerals Inc.: Development of a flotation process for the recovery of silver from zinc plant residues. Supply and Services Canada File No. 26SQ.23440-3-9078, 1984.
R. G. Sandberg and J. L. Huiatt:J. Metals, 1986, vol. 38, no. 6, pp. 18–22.
D. J. MacKinnon, J. M. Brannen, and V. I. Lakshmanan:J. Appl. Electrochem., 1980, vol. 10, pp. 321–34.
D. J. MacKinnon, J. M. Brannen, and R. M. Morrison:J. Appl. Electrochem., 1988, in press.
R. G. Schulze:J. Metals, 1984, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 62–65.
E. D. Nogueira, J. M. Regife, and M. P. Viegas:Chloride Hydrometallurgy, P. D. Parker, ed., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1982, pp. 59–76.
R. Brugger:Nickel Plating, Robert Draper Ltd., Teddington, England, 1970, ch. 13, pp. 258–61.
D. D. Rodier:Lead-Zinc-Tin ’80, J. M. Cigan, T. S. Mackey, and T. J. O’Keefe, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1979, pp. 144–56.
D. J. MacKinnon and J. M. Brannen:J. Appl. Electrochem., 1977, vol. 7, pp. 451–59.
D. J. MacKinnon, J. M. Brannen, and R. C. Kerby:J. Appl. Electrochem., 1979, vol. 9, pp. 55–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mackinnon, D.J., Dutrizac, J.E., Brannen, J.M. et al. The behavior of thiourea and flotation reagents in zinc electrowinning circuits. Metall Trans B 19, 187–199 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02654203
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02654203