Abstract
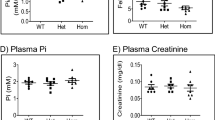
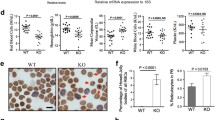
We investigated patterns of growth, haematopoiesis and alterations in serum chemistry profiles that were associated with anN-ethyl-N-nitrosourea-induced mutation in thefitness 1 locus in chromosome 7 in mice. Mice hemizygous for thefit 1 mutation [c fit 1 4226SB /Df(c Mod2 sh1) VT] had growth retardation characterised by decreased body weights, shorter body lengths and tail lengths at 40 and 60 days of age compared to normal homozygous control mice [c ch +/ c ch+]. Haemograms revealed that mice hemizygous for thefit 1 226SB mutation that were killed at 40 days had microcytic, hypochromic anaemia that was mildly regenerative in nature. No significant differences were detected in total leucocyte counts, differential leucocyte counts and platelet counts between hemizygous mutant mice and control mice. Haemograms from the surviving mice hemizygous for thefit 1 4226SB mutation that were killed at 60 days indicated that the haemoglobin concentrations, mean corpuscular volumes and mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentrations were significantly decreased compared to normal controls. The reticulocyte counts and the platelet counts from the mice hemizygous for thefit 1 4226SB mutation were mildly increased compared to normal controls killed at 60 days. Serum chemistry analyses at 40 days of age indicated that the hemizygousfit 1 mutant mice had hypoproteinaemia characterised by hypoalbuminaemia and hypoglobulinaemia. They also developed hypoglycaemia, mild hyperphosphataemia and moderate elevation in the activity of alkaline phosphatase in serum. Quantitative isozyme analysis indicated that the increase in total serum alkaline phosphatase activity in the hemizygous mutant mice was due to an increase in the bone isozyme. In addition to those alterations in the serum chemistry profile noted above, hemizygous mutant mice killed at 60 days had an extremely mild increase in urea nitrogen concentration and mildly increased activities of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase in serum. From these data, it was concluded that thefit 1 4226sb mutation m mice causes growth retardation, microcytic, hypochromic anaemia, and alterations in serum chemistry profiles that suggest lesions in one or more organ system(s). The exact mechanism(s) by which thefit 1 4226SB mutation mediates these lesions remains to be elucidated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bannerman RM, Garrick LM, Rusnak-Smalley P et al. (1986) Hemoglobin deficit: an inherited hypochromic anemia in the mouse (42307). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 182: 52–57
Brown RG (1991) Determining the cause of anemia: general approach, with emphasis on microcytic hypochromic anemias. Postgrad Med 89:161–170
Chui DHK, Sweeney GD, Patterson M et al. (1977) Hemoglobin synthesis in siderocytes of fiexed-tailed mutant (f/f) fetal mice. Blood 50:165–177
Cornelius CE (1989) Liver function. In: Clinical biochemistry of domestic animals, 4th edn. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp 364–397
Cotter PD, May A, Fitzsimons EJ et al. (1995) Late-onset X-linked sideroblastic anemia. J Clin Invest 96:2090–2096
Duncan RJ, Prasse KW, Mahaffey EA (1994) Veterinary laboratory medicine clinical pathology, 3rd edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames, IA, pp 112–129, 130–151, 193–195
Edwards JA, Bannerman RM (1970) Hereditary defect of intestinal iron transport in mice with sex-linked anemia. J Clin Invest 49:1869–1871
Edwards JA, Hoke JE (1975) Red cell iron uptake in hereditary microcytic anemia. Blood 46:381–388
Edwards JA, Sullivan AL, Hoke JE (1980) Defective delivery or iron to the developing red cell of the Belgrade laboratory rat. Blood 55:645–648
Erslev AJ (1990) Erythrocyte disorders-classification and manifestations, In: Williams WJ, Beutler E, Erslev AJ, Lichtman MA (eds) Hematology, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 423–429
Garrick LM, Gniecko K, Hoke JE et al. (1991) Ferric-salicylaldehyde isonicotinoyl hydrazone, a synthetic iron chelate, alleviates defective iron utilization by reticulocytes of the Belgrade rate. J Cell Physiol 146:460–465
Hall RL (1992) Clinical pathology of laboratory animals, In: Gad SC, Chengelis CP (eds) Animal models in toxicology. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp. 765–811
Han P, Fung KP (1991) Discriminant analysis of iron deficiency anaemia and heterozygous thalassaemia traits: a 3-dimensional selection of red cell indices. Clin Lab Haematol 13:351–362
Hoffmann WE, Kramer J, Main AR et al. (1989) Clinical enzymology, In: Loeb WF, Quimby FW (eds) The clinical chemistry of laboratory animals. Pergamon Press, New York, pp 237–278
Hoffmann WE, Everds N, Pignatello M et al. (1994) Automated and semiautomated analysis of rat alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes. Toxicol Pathol 22:633–638
Ivanovic Z, Milenković P, Vasiljevska M et al. (1995) Hematopoietic stem cells in the hereditary anemic Belgrade laboratory (b/b) rat. Exp Hematol 23:1218–1223
Jain NC (1993) Evaluation of anemias and polycythemias. In: Essentials of veterinary hematology. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 159–168
Kaneko JJ (1989) Serum proteins and the dysproteinemias. In: Clinical biochemistry of domestic animals, 4th edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 142–165
Kingston PJ, Bannerman CEM, Bannerman RM (1978) Iron deficiency anaemia in newbornsla mice: A genetic defect of placental iron transport. Br J Haematol 40:265–276
Lam SK, Quah TC (1991) Iron deficiency - a diagnostic problem. J Singapore Paediatr Soc 33:133–139
Martinell J, Whitney JB, Popp RA et al. (1981) Three mouse models of human thalassemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:5056–5060
Meyer DJ, Coles EH, Rich LJ (1992) Veterinary laborarory medicine: interpretation and diagnosis, WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 187, 258
Nelson DA, Davey FR (1991) Erythrocytic disorders, In: Henry JB (ed) Clinical diagnosis and management of laboratory methods, 18th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, PA, pp 627–676
Ney PA, Farina SF, Bodine DM et al. (1995) Microcytic anemia inmk/mk mice is not corrected by retroviral-mediated gene transfer of wild-type p45 NF-E2. Exp Hematol 23:74–80.
Potter MD (1994) Molecular and phenotypic analysis of a mutant locus, designatedfitness 1 (fit 1), specifying growth retardation, reduced viability, and abnormal hematopoiesis in the mouse [dissertation]. Knoxville, TN: The University of Tennessee. 283 p. Available from University Microfilms, Ann Arbor, MI; AADAA-I9518130.
Potter MD, Klebig ML, Carpenter DA et al. (1995) Genetic and physical mapping of the fitness 1 (fit 1) locus within the Fes-Hbb region of mouse chromosome 7. Mamm Genome 6:70–75
Prades E, Chambon C, Dailey TA et al. (1995) A new mutation of the ALAS2 gene in a large family with X-linked sideroblastic anemia. Hum Genet 95:424–428
Quimby FW (1989) The mouse. In: Loeb WF, Quimby FW (eds) The clinical chemistry of laboratory animals. Pergamon Press, New York, pp 3–18.
Riley JH, Cornelius LM (1989) Electrolytes, blood gases, and acid base balance, In: Loeb WF, Quimby FW (eds) The clinical chemistry of laboratory animals. Pergamon Press, New York, pp 345–413
Rinchik EM, Carpenter DA (1993)N-Ethyl-N-nitrosourea-induced prenatally lethal mutations define at least two complementation groups within the embryonic ectoderm development (eed) locus in mouse Chromosome 7.Mamm Genome 4: 349–353
Rinchik EM, Carpenter DA, Selby PB (1990) A strategy for fine-structure functional analysis of a 6-to 11 -cM region of mouse chromosome 7 by high-efficiency mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87;896–900
Skow LC, Burkhart BA, Johnson FM et al. (1983) A mouse model of β-thalassemia. Cell 34:1043–1052
Steel RGD, Torrie JH, Dickey DA (1997) Principles and procedures of statistics: a biometrical approach, 3rd ed, McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 77, 98, 139–177, 191–192.
Thein SL, Wood WG, Wickramasinghe SN et al. (1993)β-thalassemia unlinked to theβ-globin gene in an English family. Blood 82:961–967
Willard MD, Tvedten H, Turnwald GJ (1994) Small animal clinical diagnosis by laboratory methods, 2nd ed, WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 191–192
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schultze, A.E., Schaeffer, D.O., Potter, M.D. et al. Alterations in growth, haematopoiesis and serum chemistry profiles infitness 1 4226SB mutant mice. Comparative Haematology International 7, 143–151 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02652592
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02652592