Abstract
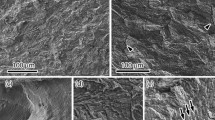
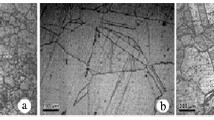
A systematic matrix of fatigue crack growth rate data in a hydrogen environment has been generated in a nickel-copper alloy and compared with the base line data in the milder oxygen and vacuum environments described in the preceding paper. It is found that crack growth in the hydrogen environment is characterized by high values of the Paris equation exponent and faster crack propagation rates as compared to those in the milder environments. Fractographic examination shows that brittle inter granular separation occurs superimposed on an otherwise ductile crack mode in the hydrogen tests. Quantitative fractographic analysis of the hydrogen affected fracture surfaces indicates that the percentage of intergranular failure (area fraction) is a uniquely related function of the mean stress intensity rather than the maximum stress intensity level of fatigue loading. This dependence is discussed in terms of dislocation sweep-in transport of hydrogen deep into the plastic zone during fatigue cycling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Purushothaman, R. J. Richards, J. K. Tien, and J. D. Frandsen:Met. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, p. 1101.
A. W. Thompson and J. A. Brooks:Met. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, p. 1431.
W. Elber: ASTM STP 486, p. 230, Am. Soc. Testing Materials, 1971.
O. Buck, J. D. Frandsen, C. L. Ho, and H. L. Marcus:The Microstructure and Design of Alloys, vol. 1, p. 462, The Inst, of Metals and The Iron and Steel Inst., 1973.
C. J. Beevers, R. J. Cooke, J. F. Knott, and R. O. Ritchie:Metal Sci, 1975, vol. 9, p. 119.
R. O. Ritchie and J. F. Knott:Acta Met., 1973, vol. 21, p. 639.
J. K. Tien:Effect of Hydrogen on Behavior of Materials, A. W. Thompson and I. M. Bernstein, eds., p. 309, TMS-AIME, New York.
J. K. Tien, R. J. Richards, O. Buck, and H. L. Marcus:Scr. Met., 1975, vol. 9, p. 1097.
J. K. Tien, A. W. Thompson, I. M. Bernstein, and R. J. Richards:Met. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, p.821.
J. K. Tien, N.Panayotou, and R.J. Richards:Proc. of the 2nd Int. Congress on Hydrogen in Metals, vol. 5, Pergamon Press, June, 1977.
J. D. Frandsen, W. L. Morris, and H. L. Marcus:Hydrogen in Metals, I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson, eds., p. 633, Am. Soc. Metals, Metals Park, Ohio, 1974.
J. D. Frandsen, N. E. Paton, and H. L. Marcus:Met. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, p. 1655.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly a Graduate Student at Columbia University
Formerly Senior Staff Associate, Science Center, Rockwell International
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richards, R.J., Purushothaman, S., Tien, J.K. et al. Kinetics of environmental fatigue crack growth in a nickel-copper alloy: Part II. In hydrogen. Metall Trans A 9, 1107–1111 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02652215
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02652215