Abstract
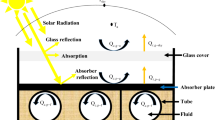
A simplified technique is described for calculating the heat loss coefficient from the absorber of the solar flat-plate collector with a combined honeycomb. The problem is treated in two ways: the coupled mode and the decoupled mode. In the analysis, the cell wall and glass cover are assumed to be specularly reflecting and diffusely emitting surfaces, while the absorber is a diffusely reflecting and emitting surface. The influences of emissivities of the absorber and the cell wall as well as the aspect ratio on the heat loss coefficient are predicted. The theoretical results are compared with experimental data reported in the literature, and the agreement is good.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.G.T. Hollands, “Honeycomb Devices in Flat Plate Solar Collectors,”Solar Energy,9, p.159, (1965).
K.G.T. Hollands and K. Iynkaren, “Proposal for a Compound Honeycomb Collector,”Solar Energy,34, pp.309–316, (1985).
H. Buchberg and D.K. Edwards, “Design Considerations for Solar Collectors with Cylindrical Glass Honeycomb,”Solar Energy,18, 193–203, (1976).
W.W.S. Charters and L.F. Peterson, “Free Convection Suppression Using Honeycomb Cellular Materials,”Solar Energy,13, pp.353–361, (1972).
W.J. Plazter, “Calculation Procedure for Collectors with a Honeycomb Cover of Rectangular Cross Section,”Solar Energy,46, pp.381–393, (1992).
D.K. Edwards and R.D. Tobin, “Effect of Polarization of Radiant Heat Transfer Through Long Passage,”J. Heat Transfer,89c, pp.132–138, (1967).
H.C. Hottel and J.D. Keller, “Effect of Reradiation on Heat Transfer In Furnaces and Through Openings,”Trans. Am Soc. Mech. Engrs,55, 39–49, (1933).
K.G.T. Hollands, G.D. Raithy, F.B. Russell and R.G. Wilkinson, “Coupled Radiative and Conductive Heat Transfer Across Honeycomb Panels and Through Single Cells,”Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer,27, pp.2119–2131, (1984).
C.L. Tien and W.W. Yuen, “Radiation Characteristics of Honeycomb Solar Collectors,”Int. J. Heat Transfer 18, pp.1409–1413, (1975).
J.R. Felland and D.K. Edwards, “Solar Infrared Radiation Properties of Parallel-Plate Honeycombs,J. Energy 2, No.5, pp.309–317, (1978).
S. H. Lin and E. M. Sparrow, “Radiant Interchange Among Curved Specularly Refecting Surface-Application to Cylindrical and Conical Cavities,”J. of Heat Transfer,87, No.2, pp.299–307, (1965).
R. Siegel, J.R. Howell, «Thermal Radiation Heat Transfer», Chapter,9, 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill, (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, X.S., Zhang, Y.Z., Huang, H.L. et al. Heat loss calculation of compound honeycomb solar collector. J. of Thermal Science 2, 254–259 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02650813
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02650813