Abstract
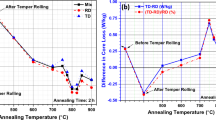
The effect of Mn and S contents on the magnetic properties of cold rolled lamination steel was investigated in eleven low C steels. The results indicated that Mn content was a major factor influencing the magnetic quality of the lamination steels. An optimum range of Mn was a prerequisite for optimum permeability and exciting power. For Mn contents up to 1.25 Pct, the core loss improved nonlinearly with increasing Mn content. At higher Mn contents, the magnetic properties deteriorated for the experimental conditions used as a consequence of poor grain size development after the final decarburizing anneal. Decreasing the S content from 0.018 Pct to 0.010 Pct improved the core loss at all induction levels. The permeability and exciting power were improved at 1 T, but a very slight deterioration in permeability and exciting power was seen at 1.5 and 1.7 T. Estimations of core loss improvement based on regression equations indicated that lowering the S content from 0.018 Pct to 0.010 Pct improved the core loss in w/lb-mil as follows: 0.0041 at 1 T, 0.0079 at 1.5 T, and 0.0093 at 1.7 T (1 w/lb-mil = 86.8 w/kg-mm). The response surface analyses indicated that Mn content in the range of 0.7 Pct to 1 Pct, depending on the S content, should develop optimum magnetic properties. However, Mn content at the low end of this range is preferred for practical applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. C. Leslie, J. T. Michalak, A. S. Keh, and R. J. Sober:Trans. ASM, 1965, vol. 58, pp. 672–86.
W. C. Leslie, J. T. Michalak, and F. W. Aul:Iron and Its Dilute Solid Solutions, Interscience Publishers, New York, NY, 1963, pp. 119–212.
W.C. Leslie:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1967, vol. 205, pp. 208–09.
J. D. Baird and J. M. Arrowsmith:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1966, vol. 204, pp. 240–47.
J. D. Baird and J. M. Arrowsmith:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1967, vol. 205, p. 209.
D. A. Witmer and G. Krauss:Trans. ASM, 1969, vol. 62, pp. 447–56.
H. Hu:Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 1567–75.
P. Messien, A. deLeval, and T. Greday: C.R.M. No. 39, 1974, pp. 51–72.
P.K. Rastogi:IEEE Trans. Magn., 1977, vol. MAG-13, No. 5, pp. 1448–50.
E. T. Stephenson and M. R. Amann:Energy Efficient Electrical Steels, Proc. TMS-AIME, 1980, Warrendale, PA, pp. 43–60.
G.E.P. Box, W. G. Hunter, and J. S. Hunter:Statistics for Experimenters, John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, 1978, pp. 631, 636-40.
S.R. Goodman:Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 2051–61.
P. L. Charpentier and J.H. Bucher:Mechanical Working and Steel Processing X, Proc. AIME, 1972, Chicago, IL, pp. 61–68.
P.K. Rastogi:Energy Efficient Electrical Steels, Proc, TMS-AIME, 1980, Warrendale, PA, pp. 183–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is based on a presentation made at the symposium “Physical Metallurgy of Electrical Steels” held at the {dy1985} annual AIME meeting in New York on February 24–28, {dy1985}, under the auspices of the TMS Ferrous Metallurgy Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, K.C. The effect of manganese and sulfur contents on the magnetic properties of cold rolled lamination steels. Metall Trans A 17, 1259–1266 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02650106
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02650106