Abstract
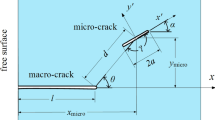
Calculations based on both linear elasticity and small scale yielding in an elastic-plastic body indicate that large normal stresses exist behind the tip of the main crack and are related to the presence of microcracks which intersect a fracture surface. This concept is applied to the specific case of microcracks which intersect a mixed mode I/II fatigue crack in Ti-40 at. pct V alloy single crystals. The microcracks, which occur on {110} and {111} planes, are associated with the radial distribution of stresses normal to the observed microcrack plane. In the Ti-40V alloy examined, microcracking may occur by cleavage on rarely observed {110} and {111} planes because of the combination of large normal stresses and flow at the microcrack tip which is controlled by the stress field imposed by the main crack.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.D. Beachem:Trans. ASM, 1967, vol. 60, pp. 324–43.
H. Nordberg and B. Aronsson:Trans. ASM, 1968, vol. 61, pp. 627–29.
P. Gauthier, H. DeRaudy, and J. Auvinet:Eng. Fract. Mech., 1973, vol. 5, pp. 977–81.
J.A. Carlson and D. A. Koss:Acta Met., 1978, vol. 26, pp. 123–32.
D. G. Chakrapani and E. N. Pugh:Met. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 1155–63.
J. W. Hutchinson:J Mech. Phys. Solids, 1968, vol. 16, pp. 337–47.
C. F. Shih:Fracture Analysis, ASTM STP 560, p. 187, ASTM, Philadelphia, 1974.
G. C. Sih, P. C.Paris, and G. R. Irwin:Int. J. Fract. Mech., 1965, vol. l,pp. 189–203.
L. Graham and G. Alers:The Physics of Solid Solution Strengthening, p. 204, Plenum Press, New York, 1975.
W. R. Tyson, R. A. Ayres, and D. F. Stein:Acta Met., 1973, vol. 21, pp. 621- 27.
R. E. Peterson:Stress Concentration Factors, p. 22, John Wiley, New York, 1974.
W. F. Brown and J. E. Srawley:Plane Strain Crack Toughness Testing of High Strength Metallic Materials, ASTM STP 410, ASTM, Philadelphia, 1966.
H. Ta’da, P. C. Paris, and G. R. Irwin:The Stress Analysis of Cracks Handbook, pp. 2–29, Dell Research, Hellertown, Pa., 1973.
R. A. Wood and H. R. Ogden: DMIC Report 110, April 17, 1959.
H. J. Rack:J. Mater. Tech., Trans. ASME, 1975, vol. 74, pp. 330–37.
J. F. McNeil and H. R. Limb:J. Inst. Metals, 1958-59, vol. 87, pp. 79–87.
D. A. Koss and C. C. Wojcik:Met. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 1243–44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stout, M.G., Koss, D.A. On the origin of microcracking behind a crack tip. Metall Trans A 9, 835–839 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649793
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649793