Abstract
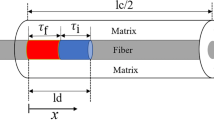
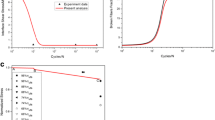
The factors contributing to the residual strength of a thermomechanically-fatigued SiC fiber-reinforced metal matrix composite were assessed based on fracture surface features. The estimated residual strength was found to be in reasonable agreement with the measured value.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.W. Neu and T. Nicholas, Effect of Laminate Orientation on the Thermomechanical Fatigue Behavior of a Titanium Matrix Composite,J Compos. Technol. Res., Vol 16 (No. 3), 1994, p 214–224
G.T. Ward, D.J. Herrmann, and B.M. Hillberry, “Fatigue-Life Behavior and Matrix Fatigue Crack Spacing in Unnotched SCS-6/TIMETAL 21S Metal Matrix Composites,” NASA Report 191467,July 1993
R.W. Neu, Nonisothermal Material Parameters for the Bodner-Partom Model,Symposium on Parameter Estimation for Modern Constitutive Equations, Winter Annual Meeting (New Orleans), American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1993
P.D. Warren, T.J. Mackin, and A.G. Evans, Design, Analysis and Application of an Improved Push-Through Test for the Measurement of Interface Properties in Composites,Acta Metall., Vol 40, 1992, p 1243–1249
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, C.G., Kanazawa, C.H. & Shockey, D.A. Residual strength of a thermomechanically fatigued TIMETAL 21S/SCS-6 composite. JMEP 4, 624–626 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649596
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649596