Abstract
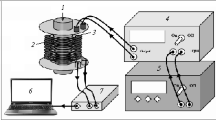
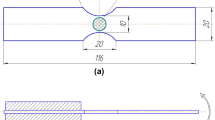
Samples of Armco iron were cathodically charged in a 1 N H2SO4 solution while their resonant frequency and internal friction were continuously monitored. The cathodic charging resulted in the initiation and growth of intergranular hydrogen-induced cracks which were later characterized by metallographic analysis. In all cases, the resonant frequency (from which the elastic modulus was calculated), decreased with the onset of cracking. A theoretical treatment by Bristow1 relating the decrease in elastic modulus to the presence of cracks in a material was modified to account for localized surface cracks. Good agreement was obtained between the measured resonant frequency (elastic modulus) loss and measured crack data from metallographic studies. The loss of resonant frequency as a function of time was found to be a two-part parallel exponential process, regardless of experimental conditions. The two processes, one far more rapid than the other, were consistent with different nucleation rates of hydrogen bubbles which produced the cracking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. R. Bristow:British J. Appl. Phys., 1960, vol. 11, pp. 81–85.
J.H. Armstrong: Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Denver, June 1985.
J. Marx:Rev. Sci. Instrum., 1951, vol. 22, pp. 503–06.
W. H. Robinson and A. Edgar: PEL Technical Note No. 204, NZ, DSIR, 1970.
W. H. Robinson, S.H. Carpenter, and J. L. Talion:J. Appl. Phys., 1974, vol. 45, pp. 1975–81.
S.H. Carpenter and J.E. Fawks:Scripta Metall., 1981, vol. 15, pp. 699–704.
I. M. Bernstein:Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 3143–50.
K. Kiuchi and R.B. McLellan:Acta Metall., 1983, vol. 31, pp. 961–84.
L.C. Weiner:Corr., 1961, vol. 17, pp. 109–15.
D.A. Westphal:Hydrogen in Metals, I. M. Bernstein and A.W. Thompson, eds., 1973, pp. 79–89.
J.K. Tien, A.W. Thompson, I.M. Bernstein, and R.J. Richards:Metall. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 821–29.
H.H. Johnson and J. P. Hirth:Metall. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 1543–48.
J.H. Armstrong and S.H. Carpenter:Mat. Sci. and Eng., 1986, vol. 82, pp. 225–30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Armstrong, J.H., Carpenter, H.S. Detection of the initiation and growth of hydrogen-induced cracks in armco iron using continuous modulus measurements. Metall Trans A 19, 473–478 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649261
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649261