Abstract
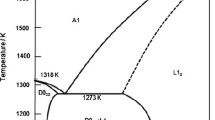
Microstructure of the bonding zones (BZs) between laser-clad Ni-alloy-based composite coatings and steel substrates was studied by means of scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) techniques. Observations indicate that for pure Ni-alloy coating the laser parameters selected for good interface fusion have no effect on the microstructure of the BZ except for its thickness. However, the addition of ceramic particles (TiN, SiC, or ZrO2) to the Ni alloy varies the compositional or constitutional undercooling of the melt near the solid/liquid interface and consequently leads to the observed changes of microstructure of the BZs. For TiN/Ni-alloy coating the morphology of y-Ni solid solution in the BZ changes from dendritic to planar form with increas-ing scanning speed. A colony structure of eutectic is found in the BZ of SiC/Ni-alloy coating in which complete dissolution of SiC particles takes place during laser cladding. The immiscible melting of ZrO2 and Ni-alloy powders induces the stratification of ZrO2/Ni-alloy coating which consists of a pure ZrO2 layer in the upper region and a BZ composed mainly of y-Ni dendrites adjacent to the substrate. All the BZs studied in this investigation have good metallurgical characteristics between the coatings and the substrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Frenk and W. Kurz:Lasers Eng., 1992, vol. 1, pp. 193–212.
S. Atamert and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia:Metall. Trans. A, 1989, vol. 20A, pp. 1037–54.
J.J. de Damborenea and A.T. Vazquez:J. Mater. Sci., 1993, vol. 28, pp. 4775–80.
H.D. Steffens and R. Kaczmarek:Weld. World, 1990, vol. 28, pp. 224–30.
C. Narayan and J.I. Goldstein:Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 1883–90.
W.J. Rutter and B. Chalmers:Can. J. Phys., 1953, vol. 31, p. 15.
W.A. Tiller, K.A. Jackson, W.J. Rutter, and B. Chalmers:Acta Metall, 1953, vol. 1, p. 428.
J. Singh and J. Mazumder:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 1981- 90.
X.B. Zhou, P.M. Bronsveld, and J. Hosson:Lasers Eng., 1991, vol. 1, pp. 145–53.
K.M. Jasim, R.D. Rawlings, and D.R.F. West:J. Mater. Sci., 1992, vol. 27, pp. 1937–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, Y.T., Ouyang, J.H. & Lei, T.C. Microstructure of bonding zones in laser-clad Ni-alloy-based composite coatings reinforced with various ceramic powders. Metall Mater Trans A 27, 391–400 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02648416
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02648416