Abstract
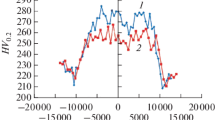
Austenitic alloy weldments in nuclear systems may be subject to stress- corrosion cracking (SCC) failure if the sum of residual and applied stresses exceeds a critical threshold. Residual stresses developed by prior machining and welding may either accelerate or retard SCC, depending on their magnitude and sign. A combined x- ray diffraction and mechanical procedure was used to determine the axial and hoop residual stress and yield strength distributions into the inside- diameter surface of a simulated Alloy 600 penetration J- welded into a reactor pressure vessel. The degree of cold working and the resulting yield strength increase caused by prior machining and weld shrinkage were calculated from the line- broadening distributions. Tensile residual stresses on the order of +700 MPa were observed in both the axial and the hoop directions at the inside- diameter surface in a narrow region adjacent to the weld heat- affected zone. Stresses exceeding the bulk yield strength were found to develop due to the combined effects of cold working of the surface layers during initial machining and subsequent weld shrinkage. The residual stress and cold work distributions produced by prior machining were found to influence strongly the final residual stress state developed after welding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.F. Hall and D.B. Scott, “Destructive Examination of Pressurizer Heater Sleeves from Calvert Cliffs Unit 2,” Report CE-NPSD- 577, Oct 1989
J.A. Gorman, “Status and Suggested Course of Action for Non- denting-Related Primary-Side IGSCD of Westinghouse-Type Steam Generators,” Report MP-4594-LD, EPRI, May 1986
J.F. Hall, J.P. Molkenthin, and P.S. Prevey, XRD Residual Stress Measurements on Alloy 600 Pressurizer Heater Sleeve Mockups,Proc. 6th Int. Symp. Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems-Water Reactors (San Diego), TMS, ANS, NACE, 1993, p 855–861
J.F. Hall, J.P. Molkenthin, P.S. Prevey, and R.S. Pathania, Meas- urement of Residual Stresses in Alloy 600 Pressurizer Penetrations,Conf. Contribution of Materials Investigation to the Resolution of Problems Encountered in Pressurized Water Reactors (Paris), Société Française d’Energie Nucleare, 12-16 Sept 1994
Inconel Alloy 600 Spec. Sheet Ni-176,Alloy Dig., July 1972
R.C. Gibbons, Ed.,Woldman’s Engineering Alloys, 6th ed., American Society for Metals, 1979, p 747
M.E. Hilley, Ed.,Residual Stress Measurement by X-Ray Diffraction, SAEJ784a, Society of Automotive Engineers, 1971
I.C. Noyan and J.B. Cohen,Residual Stress Measurement by Diffraction and Interpretation, Springer-Verlag, 1987
B.D. Cullity,Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 2nd ed., Addison- Wesley, 1978, p 447–476
P.S. Prevey, X-Ray Diffraction Residual Stress Techniques,Metals Handbook, Vol 10, 9th ed., American Society for Metals, 1986, p 380–392
P.S. Prevey, A Method of Determining Elastic Properties of Alloys in Selected Crystallographic Directions for X-Ray Diffraction Residual Stress Measurement,Adv. X-Ray Anal., Vol 20, 1977, p 345–354
P.S. Prevey, The Use of Pearson VII Functions in X-Ray Diffraction Residual Stress Measurement,Adv. X-Ray Anal., Vol 29, 1986, p 103–112
P.S. Prevey, The Measurement of Residual Stress and Cold Work Distributions in Nickel Base Alloys,Residual Stress in Design,Process and Material Selection, ASM International, 1987
P.S. Prevey, Surface Residual Stress Distributions in As-Bent In- conel 600 U-Bend and Incoloy 800 90-Degree Bend Tubing Samples,Workshop Proc: U-Bend Tube Cracking in Steam Generators, EPRI, 1981, p 12–3 to 12–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prevey, P., Mason, P., Hornbach, D. et al. Effect of prior machining deformation on the development of tensile residual stresses in weld-fabricated nuclear components. JMEP 5, 51–56 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02647269
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02647269